Relevance: GS-3: Indian Economy and Government Budgeting, Government Policies & Interventions.
Key phrases: current account, capital account, BOP, deficit, surplus, export, import.
Why in News?
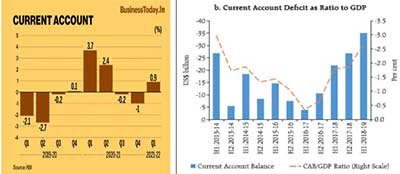
- India’s current account balance slipped into a deficit of $9.6 billion in Q2 (July-September) 2021-22 as against a surplus of $6.6 billion in Q1 (April-June), mainly due to widening of trade deficit and an increase in net outgo of investment income.
What is a Current Account Deficit?
- The current account deficit is a measurement of a country’s trade where the value of the goods and services it imports exceeds the value of the products it exports.
- The current account includes net income, such as interest and dividends, and transfers, such as foreign aid, although these components make up only a small percentage of the total current account.
- The current account represents a country’s foreign transactions and, like the capital account, is a component of a country’s balance of payments (BOP).
Balance Of Payments (BOP)
- The balance of payments (BOP), also known as the balance of international payments, is a statement of all transactions made between entities in one country and the rest of the world over a defined period, such as a quarter or a year.
- It summarizes all transactions that a country's individuals, companies, and government bodies complete with individuals, companies, and government bodies outside the country.
- For preparing a BOP account, economic transactions are grouped under two broad categories:
- Current Account: It includes export and import of gods and services i.e. visible and invisible trade. This type of transaction changes (increase or decreases) the current level of consumption of the country.
- Capital Account: The capital account keeps track of the net change in a nation's assets and liabilities during a year. Inflow and outflow of capital including foreign investment, gold and foreign exchange reserves. This is of stock nature.

Factors: Current Account Deficit:
- There are various factors which could cause a current account deficit:
- Overvalued exchange rate: If the currency is overvalued, imports will be cheaper, and therefore there will be a higher quantity of imports. Exports will become uncompetitive, and therefore there will be a fall in the quantity of exports.
- Economic growth: If there is an increase in national income, people will tend to have more disposable income to consume goods. If domestic producers cannot meet the domestic demand, consumers will have to import goods from abroad. Therefore, if there is fast economic growth there tends to be a significant increase in the quantity of imports and a deterioration in the current account.
- Trade Deficit: We see a gradual recovery and elevated commodity prices pressurizing the import bill. We expect import growth exceeding export growth, while higher losses in oil-led terms of trade imply that the current account-to-GDP will be back to a deficit in FY22. As per the RBI, the CAD was mainly due to the trade deficit widening to $44.4 billion from $30.7 billion a quarter ago.
- Higher inflation: Inflation rises faster than our main competitors then it will make exports less competitive and imports more competitive. This will lead to deterioration in the current account. However, inflation may also lead to a depreciation in the currency to offset this decline in competitiveness.
- Recession in other countries: If the country’s main trading partners experience negative economic growth, then they will buy less of our exports, worsening the country current account.
- Borrowing money: If countries are borrowing money to invest e.g., third world countries, then this will lead to deterioration in current account position.
Trend in Current Account Deficit in India:
- The rising import bill on account of elevated global fuel and commodity prices is expected to widen the current account deficit (CAD) to around 1.5 per cent of gross domestic product in 2021-22 compared with a current account surplus of 0.9 per cent in the previous fiscal, according to economists. As Omicron fears recede, oil prices have started increasing again, which is expected to widen CAD.
- While exports grew by 50.7 per cent in the first eight months of the current fiscal at US$ 262.46 bn, imports have grown at a sharper 75.39 per cent to US $384.4 billion, leaving a trade gap of US $121.98 billion.
Consequences of Current Account Deficit:
- Economic growth: In the short-run, a current account deficit is helpful to the debtor nation. Foreigners are willing to pump capital into it. That drives economic growth beyond what then country could manage on its own.
- Weakening of demand: In the long run, a current account deficit saps economic vitality. Foreign investors question whether economic growth will provide enough return on their investment. Demand weakens for the country’s assets, including the country’s government bonds.
- Rise in bond yields: As foreign investors withdraw funds, bond yields rise. The national currency loses value relative to other currencies. That lowers the value of the assets in the foreign investors’ strengthening currency. It further depresses investor demand for the country’s assets. This can lead to a tipping point where investors will dump the assets at any price.
- Rise in value of foreign assets: The only saving grace is that the country’s holdings of foreign assets are denominated in foreign currency. As the value of its currency declines, the value of the foreign assets rise. That further reduces the current account deficit.
- Setting in of Inflation: In addition, a lower currency value increases exports as they become more competitively priced. The demand for imports falls once prices rise as inflation sets in. These trends stabilize any current account deficit.
- Lower Standard of Living: Regardless of whether the current account deficit unwound via a disastrous currency crash or a slow, controlled decline, the consequences would be the same. That’s a lower standard of living for the country’s residents.
Source: The Hindu BL
Mains Question:
Q. India’s current account balance slipped into a deficit of $9.6 billion in Q2 (July-September) 2021-22 as against a surplus of $6.6 billion in Q1.In this context explain what is current account deficit? What are the main factors responsible for recent increase of current account deficit? Illustrate.







