Relevance: GS-2: India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
Key phrases: Palk bay, Bottom trawlers, Deep sea fishing project
Why in news?
- Arrest of 68 Indian fishermen by Sri Lankan navy
Analysis:
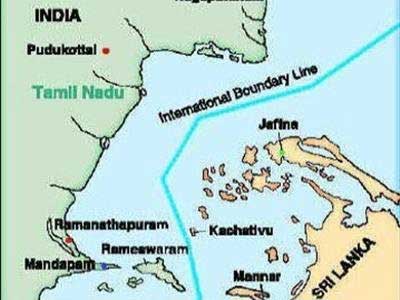
What is the Palk Bay?
- The Palk Bay, a narrow strip of water separating the state of Tamil Nadu in India from the Northern Province of Sri Lanka.
- The bay, which is 137 km in length and varies from 64 to 137 kilometers in width, is divided by the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL).
- Bordering it are five Indian districts and three Sri Lankan districts.
What is the conflict about?
- In 1974 and 1976 treaties were signed between the two countries to demarcate the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL).
- The small islet of Katchatheevu, hitherto used by the fishermen for sorting their catch and drying their nets, fell on the other side of the IMBL
- The main problem with Indian fishermen is that a large number of them are dependent on fishing in Sri Lankan waters, which is prohibited by the 1976 Maritime Boundary Agreement.
- The main issue is the oversized fleet of Tamil Nadu trawlers that fish regularly in Sri Lankan waters. Trawlers greatly damage the ecosystem and hence are unsustainable way of fishing. The Sri Lankan government recently passed a legislation banning trawling.
What is government doing for this?
- The IMBL is imaginary, but it was geo-tagged and is visible to the fishermen, due to Global Positioning System (GPS) sets.
- Deep Sea Fishing Scheme: Promoted as an alternative to bottom trawling by Tamil Nadu’s fishermen off the Palk Bay, the scheme envisages the provision of 2,000 deep sea fishing boats in place of trawlers by 2019-20.
Strengths of India Sri Lanka relations
- First responder to Sri Lanka- 2004 tsunami, PM's visit after Easter attacks
- Shared culture steeped in similar myths, legends-advent of Buddhism to Sri Lanka during Ashoka’s reign-ancient Anuradhapura hosts ties with ancient India
- India is time tested ally-opposed UN resolution for probe into Sri Lankan excesses -Pakistan and china favored the resolution
- Civil nuclear cooperation agreement with Sri Lanka – it is the first with any country
- India has been maintaining Sri Lanka’s autonomy against international investigations as well as prompting Sri Lanka to provide justice and power to minority Tamils -India’s abstinence from voting in UNHRC resolution against Sri Lanka
Weaknesses of our relation
- Growing influence of China- building of lotus tower in Colombo, China now accounts for 18 percent of Sri Lankan import, India 19-SL member of BRI
- India's FDI was more than China for Sri Lanka in 2015 but reversed by ‘18
- India's waning influence and growing resentment for India- scrapping of Hambantota port originally offered to India and given to China-Chinese maritime silk route policy
- Serious ethnic issues - Sinhala and Tamil-war crime probes and accountability issues
- Unresolved, decades old problem of fishermen on both sides-politically significant in TN -high handedness of Sri Lankan navy
Way ahead
- The damage to the Indian fishermen could be ameliorated if the announcement is followed by two steps. The trawlers can be used in the Odisha coast where waters are very deep
- The Tamil Nadu Fisheries Departments have to seriously monitor, control and carry out surveillance (MCS) of the decommissioning process.
- Beyond the deep sea vision, other solutions such as buy-backs, alternative livelihoods and skill development need to be rolled out.
Source: The Hindu