Relevance: GS-3: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Key phrases: ISFR 2021, FSI, Forest cover, tree cover, mangroves, carbon stock.
Why in News?
- Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, has today released the ‘India State of Forest Report 2021’ prepared by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) which has been mandated to assess the forest and tree resources of the country.
What is India State of Forest Report?
- India State of Forest Report (ISFR) is a biennial publication of Forest Survey of India (FSI) an organization under the Ministry of Environment Forest & Climate Change Government of India.
- The report is published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) which has been mandated to assess the forest and tree resources of the country including wall-to-wall forest cover mapping in a biennial cycle.
- Starting 1987, 17 assessment have been completed so far. ISFR 2021 is the 17th report in the series.
- In the current report, FSI has introduced a new chapter related to the assessment of forest cover in the tiger reserves, corridors, and lion conservation area of India.
Forest Survey of India
- Forest Survey of India (FSI) is an organisation under the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India Its principal mandate is to conduct survey and assessment of forest resources in the country.
- It started as an organization called Pre- Investment Survey of Forest Resources (PISFR) in 1965 as FAO/UNDP/GOI Project.
- The changing information needs resulted in enlarging the scope of activities of PISFR and it was re- organized as Forest Survey of India in 1981.
Key findings of ISFR 2021:
Some key findings of this year’s assessment include the following:
Forest and tree cover:
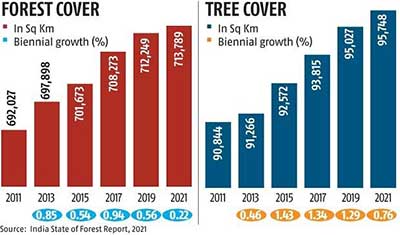
- According to the report, India's total forest and tree cover is now spread across 80.9 million hectares, which is 24.62 per cent of the geographical area of the country.
- The total tree-and-forest cover in the country includes an increase of 1,540 square kilometres of forest cover and 721 sq km of tree cover compared to the 2019 report.
- The top five states in terms of increase in forest cover are Andhra Pradesh (647 sq km), Telangana (632 sq km), Odisha (537 sq km), Karnataka (155 sq km) and Jharkhand (110 sq km).
- The gain in forest cover or improvement in forest canopy density may be attributed to better conservation measures, protection, afforestation activities, tree plantation drives and agroforestry
- Area-wise, Madhya Pradesh has the largest forest cover in the country followed by Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Maharashtra.
- The report also added that the north-east did not show positive results as the current assessment showed a decrease of forest cover to the extent of 1,020 sq km in the region.
- Arunachal Pradesh lost the maximum forest cover of 257 sq km, followed by Manipur which lost 249 sq km, Nagaland 235 sq km, Mizoram 186 sq km and Meghalaya 73 sq km.
- The report said 17 states/UTs have above 33 per cent of the geographical area under forest cover.
- Out of these states and UTs, Lakshadweep, Mizoram, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya have more than 75 per cent forest cover, while 12 states/UTs (Manipur, Nagaland, Tripura, Goa, Kerala, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Chhattisgarh, Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu, Assam, Odisha) have forest cover between 33 per cent to 75 per cent.
- The Kanha to Navegaon-Nagzira-Tadoba-Indravati corridor has the highest area under ‘Very Dense Forest’ comprising 857.65 sq km.
- It also has the highest area under ‘Moderately Dense Forest’ at 882.87 sq km. The Pench-Satpura-Melghat corridor has the highest area under ‘Open Forest’ at 392.25 sq km.
- The Ranthambore-Kuno-Shivpuri-Madhav tiger corridor in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh has the highest area under scrub at 15.68 sq km.
Mangrove:
- Total mangrove cover in the country is 4,992 sq km.
- It also recorded an increase of 17 sq km in mangrove cover in the country as compared to the previous assessment of 2019.
- Top three states showing mangrove cover increase are Odisha (8 sq km) followed by Maharashtra (4 sq km) and Karnataka (3 sq km).
Carbon Stock:
- According to the report, the total carbon stock in the country's forest is estimated to be 7,204 million tonnes and there is an increase of 79.4 million tonnes in the carbon stock of the country as compared to the last assessment of 2019.
- The annual increase in the carbon stock is 39.7 million tonnes.

Forest cover And Tree cover
The Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change defines ‘forest cover’ in India Includes all lands having trees more than one hectare in area with tree canopy density of more than 10%, irrespective of ownership, legal status of the land and species composition of trees and ‘tree cover’ are all patches of trees occurring outside RFA which are of size less than 1 ha including the scattered trees. Tree cover forms an important part of the trees outside forests (TOF).
The Forest Survey of India has listed four categories of forests. They are:
- Very Dense Forest (with tree canopy density of 70 per cent or above)
- Moderately Dense Forest (tree canopy density of 40 per cent or above but less than 70 per cent)
- Open Forest (tree canopy density of 10 per cent or above but less than 40 per cent)
- Scrub (tree canopy density less than 10 per cent)
Source: PIB
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the key findings of the recently released Forest Survey of India Report 2021? Does current rate of increase in forest fulfil the target of India under UNFCC Paris agreement? Critically Examine.







