GS 3- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc
Key Phrases: Inland waterways, Freight transport, National Waterways, Comparative Advantage, Regional trade, Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP), Sagarmala Project, Interlinking of Rivers Programme
Why in News?
- Recently, a group of Economists, highlighted that India has an extensive network of Inland Waterways, but they are highly underutilized for freight transport. Despite being cost-effective and environment-friendly, domestic waterways play a limited role in hinterland connectivity. They argued that an optimum utilization of Inland waterways is essential to reduce logistics cost from 14% of GDP to around 10% of GDP (GoI target).
- As per Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), 25 of the 111 National Waterways (NWs) are fit for cargo and passenger traffic.
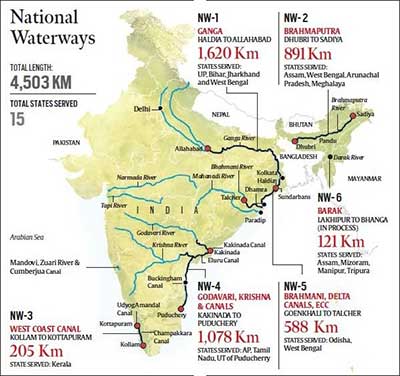
Key Inland Waterways:
- Out of the 25 National Waterways found viable for cargo/passenger movement, developmental activities are under way for 13.
- The Ganga-Bhagirathi-Hooghly River system designated as National Waterways 01 is 1,620 km long and runs across Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Gujarat, Kerala, Goa, Assam, and Andhra Pradesh are also among the states that have inland waterways under development.
Benefits of Waterways:
- Comparative Advantage: Inland Waterways are highly cost-effective and environment-friendly compared to other means of transport, specifically in long distances. For example, According to Rail India Technical and Economic Service, an arm of the Indian Railways, inland water transport is significantly cost-efficient compared to rail and road transport.

- Enhance Decongestion: Inland Waterways transport will also help with de-congestion of overcrowded rail and road networks in India.
- Boost to Regional trade: Inland Waterway mode has been agreed for inclusion in the trade treaty between India and Nepal. Recently, Stone exporters from Bhutan have identified inland waterways as an alternative mode of transportation.
- Efficient and Effective energy consumption : One horsepower can carry 4000 kg load in water whereas it can carry 150 kg & 500 kg load by road & rail respectively.
- Low maintenance cost: The cost of construction and maintenance of canals is much less, moreover, the cost of operation of inland water transport is very low.
Limitations of Inland Waterways in India:
- Phenomenon of Flood and Drought: In monsoon rivers are over flooded, while rest of year, there is water scarcity.
- Indian Dilemma: water for irrigation or water for transport
- River’s of south India flow is rocky areas. Hence they are not fit for plying boats because of waterfalls.
- Poor last mile connectivity: As compared to boats, railways has better end to end connectivity.
Steps taken to reform the sector:
- To promote inland waterways as a supplementary mode of transport, the Ministry Of Ports, Shipping, And Waterways last year waived user charges for a period of three years.
- The government also came up with digital solutions such as a portal giving information on cargo and cruise movement and a portal for river navigation and infra-structure information.
- To promote economical and safe transportation and to bring uniformity in the law, the government tabled the Inland Vessels Bill 2021 in the Lok Sabha on 22 July,2021.
- Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP) seeks to improve the navigational capacity of National Waterway-1 (NW-1). The project is being implemented by the Government of India with technical assistance and investment assistance of the World Bank.
- Sagarmala Project: Along with the development of coastal shipping routes, the project aims at inland waterways to accelerate industrial development. It seeks to minimize the logistics costs by increasing the share of domestic waterways in the modal mix from the current 6%.
- Interlinking of Rivers Programme: The project is expected to offer potential benefits to the transport sector through navigation.
Conclusion:
- The development of Inland Waterways in India offers a huge potential for the growth and development of New India. However, it should not be done at the cost of disturbing the fragile fluvial ecosystem. The need is to ensure proper safeguards and measures to make the Inland Water Transport more efficient as well as sustainable in the long run.
Mains Question
Q. Despite various steps taken to reduce the logistics cost per GDP, the results still are not very encouraging. Discuss the significance of Inland waterways in reducing the logistics cost and promoting the environmental friendly cheap means of transportation. (15 marks)
Sources- Mint, The Hindu