Context:
A concerning trend has emerged in India's employment landscape, with income levels of the salaried class stagnating in recent years. According to recent data, real wages for salaried jobs were 1.7% lower in the June quarter of 2024 compared to the June quarter of 2019. After showing a modest increase in 2020, wages fell by 6% in 2021 and by 1% in 2022, illustrating a trend of wage stagnation over the years.
What is meant by real wages?
Real wages refer to the income earned by workers adjusted for inflation. This metric reflects the actual purchasing power of an individual's earnings, showing how much they can buy with their salary over time, accounting for inflationary pressures. It helps to understand if income growth is keeping pace with the rising cost of living.
Reason behind wages for salaried jobs stagnation:
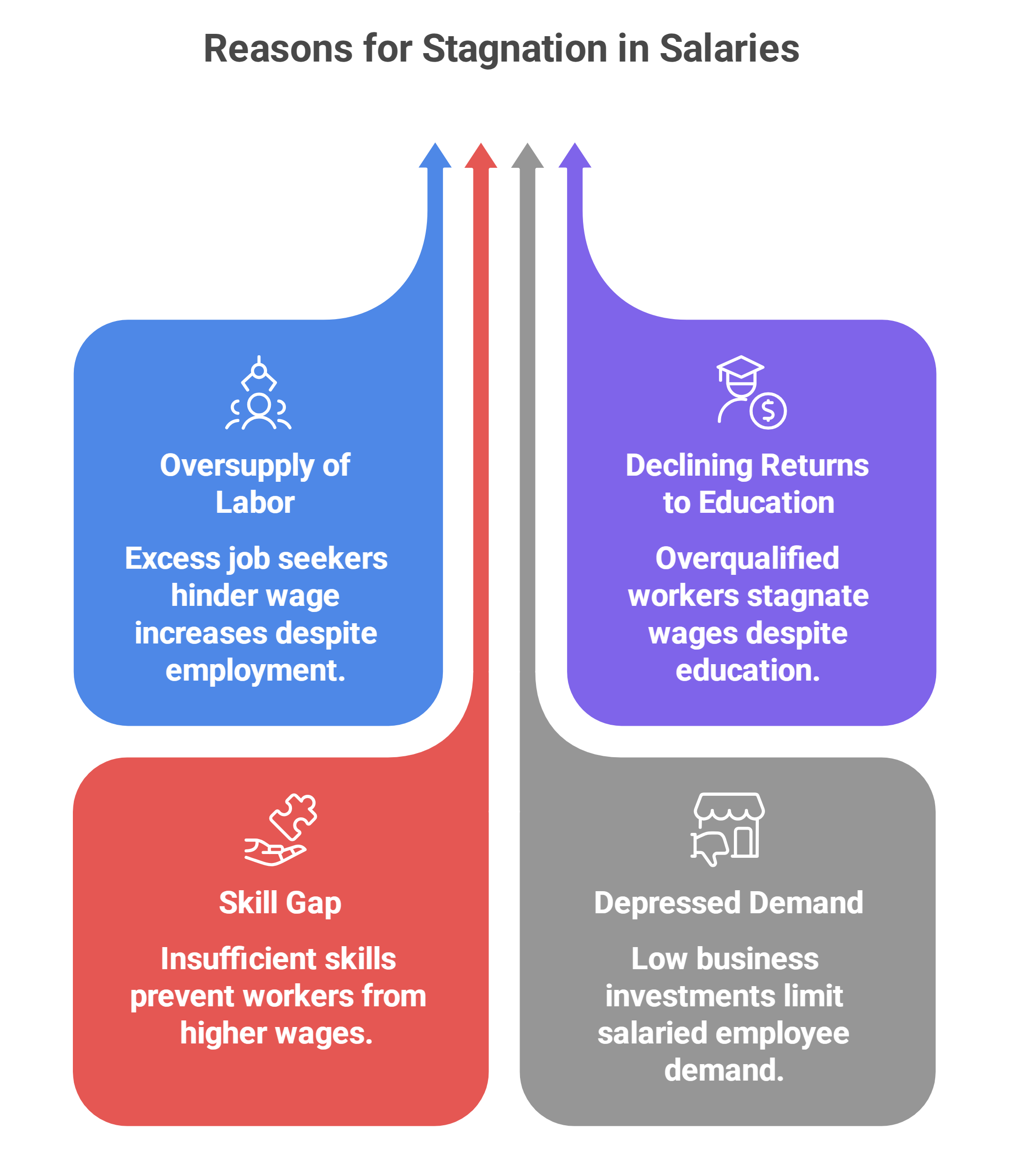
o Oversupply of labor: There are more job seekers than available high-paying jobs, making it harder for workers to see wage growth despite an increase in employment numbers.
o Declining returns to higher education: Many educated workers are overqualified for the jobs they hold, leading to wage stagnation.
o Skill gap: A lack of adequate skill development across various sectors means workers are unable to demand higher wages.
o Depressed demand: The slowdown in business investments has limited the demand for salaried employees, affecting wage growth.
Effects on casual labor and self employed workers:
o Casual Labor: In contrast to salaried workers, wages for casual laborers have increased significantly in real terms. In June 2024, real wages for casual labor were 12.3% higher than in 2019, with rural areas seeing larger increases. However, casual labor is highly irregular and insecure, and its increase is not necessarily a net positive for the economy.
o Self-Employed Workers: Wages for self-employed workers have also improved since the pandemic, but real wages were still 1.5% lower in June 2024 compared to 2019. A rise in the share of self-employed individuals, particularly in unpaid roles, reflects distress in the labor market, suggesting low earnings for a significant portion of the workforce.
Suggestions:
Experts recommend several measures:
o Skill development: There is a need for better skill training at all educational levels to ensure workers are equipped to meet the demands of the modern job market.
o Investment in the economy: Increased investment by businesses could drive demand for salaried employees and foster job creation.
o Policy support: Government interventions, such as changes in tax policies, can help boost consumption and demand, potentially spurring economic growth and improved wages.







