Context:
Nearly 18 years after the Indo-US nuclear deal was inked, the US Department of Energy (DoE) has approved an American company to build and design nuclear reactors in India, in a major development in the ties between both nations.
Key facts
The US Department of Energy has granted Holtec International authorization to transfer small modular reactor (SMR) technology to India.The approval, issued on March 26, 2025, allows Holtec to collaborate with three Indian entities:
· Holtec Asia: Holtec's regional subsidiary.
· Larsen& Toubro Ltd: A major Indian multinational engaged in technology, engineering, construction, and manufacturing.
· Tata Consulting Engineers Ltd: A subsidiary of the Tata Group, providing engineering and technology solutions.
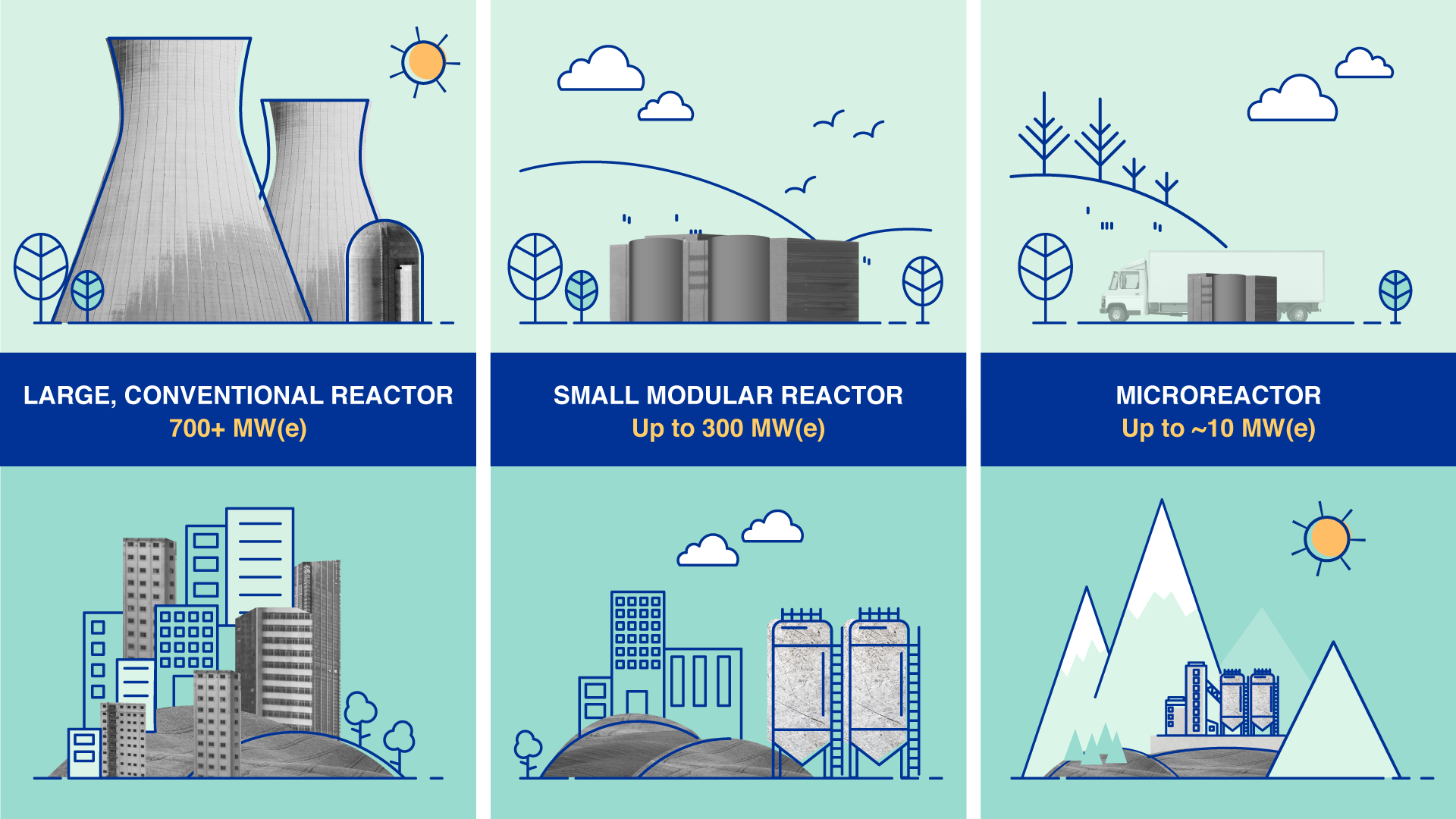
About Small Modular Reactor
- A Small Modular Reactor (SMR) is a type of nuclear reactor that is smaller in size and power output compared to traditional nuclear reactors.
- SMRs are designed to be factory-built and then transported to a site for assembly, offering a more flexible and cost-effective alternative to conventional large reactors.
- The key advantage of SMRs lies in their modularity, which means they can be scaled up by adding more units, and small size, making them ideal for locations where large reactors would not be practical.
Benefits of SMRs:
- Increased Safety: Many SMR designs focus on passive safety features, which reduce the need for human intervention and complex mechanical systems.
- Cost-Effective: They can be cheaper to build and maintain than traditional large reactors, making nuclear power more accessible to countries or regions with limited budgets for large-scale energy infrastructure.
- Scalability: SMRs can be scaled to meet changing energy needs, making them more adaptable than large reactors.
- Environmental Impact: Like all nuclear energy, SMRs produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, making them an attractive option for clean energy production.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Regulatory Approvals: While SMRs have a lot of potential, they still face regulatory challenges in terms of licensing, safety standards, and international agreements.
- Public Perception: Nuclear energy, including SMRs, often faces public concern about safety, waste disposal, and environmental impacts, which can slow down the development process.
- Economics: While SMRs promise lower costs, the economic viability depends on the number of units built and the cost of building infrastructure.
Way Forward
SMRs represent an exciting development in nuclear energy, offering the potential for safer, more flexible, and cost-effective nuclear power. Their successful implementation could help address the world's growing demand for clean energy while reducing the environmental impact of fossil fuel use.