Context
President’s Rule has been imposed in Manipur following the state’s inability to form a new government after the resignation of Chief Minister N. Biren Singh on February 9, 2025. The decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, who, upon assessment, determined that the state government could not function in accordance with the Constitution.
Implications of President’s Rule in Manipur
-
- Governance: The administration of the state will be managed by the Governor on behalf of the President, with assistance from the Chief Secretary and other appointed advisors.
- Legislative Assembly: The state legislative assembly may be either suspended or dissolved.
- Ordinances: The President has the authority to issue ordinances regarding the state’s administration when Parliament is not in session.
- Governance: The administration of the state will be managed by the Governor on behalf of the President, with assistance from the Chief Secretary and other appointed advisors.
Constitutional Aspects
About President’s Rule
-
- President’s Rule is implemented under Article 356 of the Indian Constitution when a state government is deemed unable to function as per constitutional provisions. During this period, the Union Government assumes direct control, the Chief Minister and Council of Ministers are dismissed, and the Legislative Assembly may be either prorogued or dissolved.
- President’s Rule is implemented under Article 356 of the Indian Constitution when a state government is deemed unable to function as per constitutional provisions. During this period, the Union Government assumes direct control, the Chief Minister and Council of Ministers are dismissed, and the Legislative Assembly may be either prorogued or dissolved.
Conditions for Imposition
-
- Breakdown of governance, such as a coalition collapse, a no-confidence vote, or the inability to elect a Chief Minister.
- Failure to adhere to Constitutional norms, as reported by the Governor.
- Postponement of elections due to exceptional circumstances such as war, natural disasters, or pandemics.
- Breakdown of governance, such as a coalition collapse, a no-confidence vote, or the inability to elect a Chief Minister.
Criticism and Recommendations
-
- Concerns Regarding Misuse: Some interpretations suggest that Article 356 has been utilized in ways that impact the federal structure of governance.
- Recommendations for Limited Use: The Sarkaria Commission (1983) advised that President’s Rule should be implemented only in exceptional cases, following the exhaustion of all alternative measures.
- Concerns Regarding Misuse: Some interpretations suggest that Article 356 has been utilized in ways that impact the federal structure of governance.
Notable Instances of President’s Rule
-
- The S. R. Bommai case (1994) led to stricter regulations governing its imposition.
- In Jammu and Kashmir, the state was placed under Governor’s Rule, which later transitioned to President’s Rule after the revocation of Article 370 in 2019.
- The S. R. Bommai case (1994) led to stricter regulations governing its imposition.
-
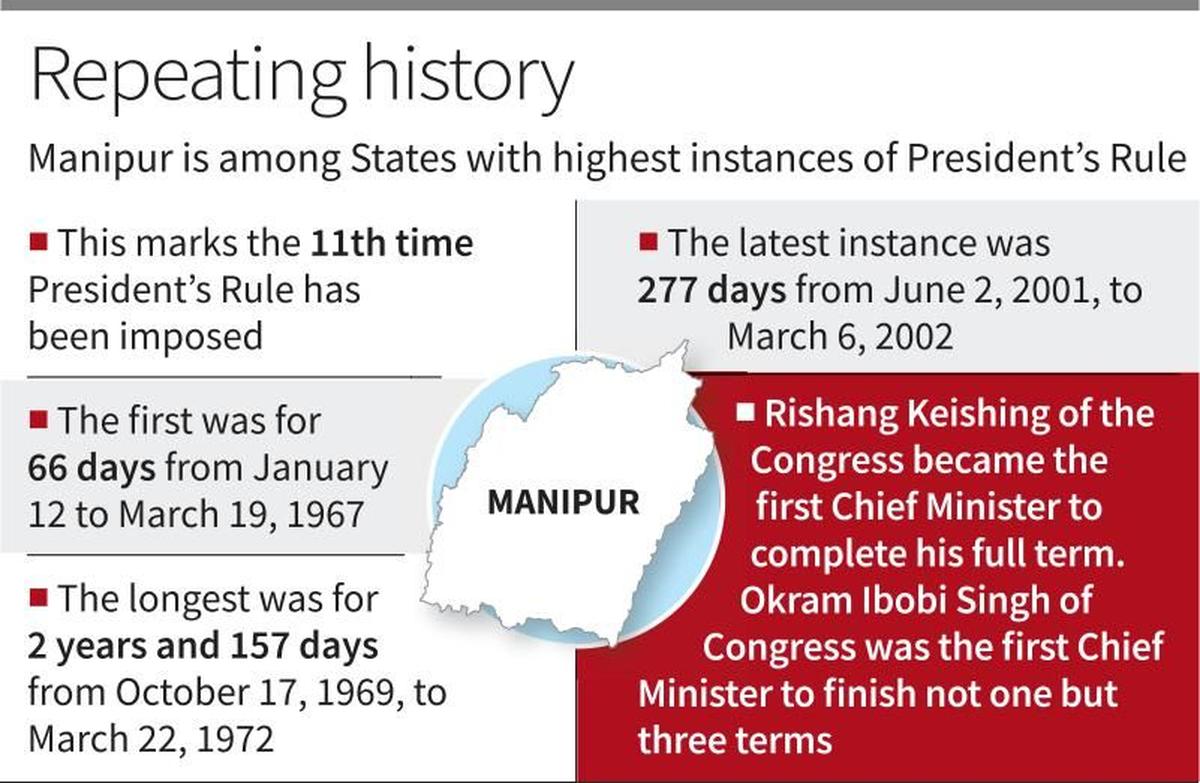
- Manipur has seen President’s Rule imposed 11 times, the highest among Indian states.
- Chhattisgarh and Telangana have not experienced President’s Rule to date.
- Manipur has seen President’s Rule imposed 11 times, the highest among Indian states.
Ethnic Violence in Manipur
The ethnic violence that began in May 2023 has contributed to the ongoing instability in Manipur. The conflict primarily involves the Meitei community, which constitutes the majority, and the Kuki-Zo community, which forms a minority.
The tensions escalated following a Manipur High Court ruling, which recommended extending certain benefits to the Meitei community. The situation intensified due to the geographical and demographic distribution of the communities, with the Meitei population concentrated in the valley regions and the Kuki-Zo population residing in the hills. The conflict has resulted in widespread violence, including arson, vandalism, and other serious offenses, affecting the overall stability of the state.
The imposition of President’s Rule in Manipur reflects the administrative challenges and ongoing tensions in the region. The situation continues to be monitored, with efforts directed toward restoring stability and governance.