Context:
Madhav National Park, located in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, has officially been declared as India’s 58th tiger reserve, marking a major milestone in the country’s ongoing efforts to protect its tiger population.
About Madhav National Park:
- Spanning an area of 375.233 square kilometers, Madhav National Park is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and water bodies.
- This varied terrain supports an array of wildlife species such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and numerous bird species, making it a critical area for conservation.
The park’s ecological diversity plays a vital role in maintaining the region's overall environmental health.
Significance of the Tiger Reserve:
· One of the main objectives of declaring Madhav National Park as a tiger reserve is to strengthen wildlife corridors in the region.
· These corridors are vital for connecting fragmented tiger populations and allowing for genetic exchange, which is essential for the survival of the species.
· This move also aims to improve the overall ecological balance of the area, benefiting a wide range of flora and fauna.
About Tiger Reserves in India:
- Tiger Reserves in India are protected areas specifically designated for the conservation of tigers and their habitats. These reserves are created under Project Tiger, which was launched in 1973 by the Indian government to safeguard the endangered Bengal tiger population.
- Tiger reserves can also function as national parks or wildlife sanctuaries, offering legal protection and ecological safety to tigers.
- As of 2025, India has 58 tiger reserves spread across various states. These reserves collectively cover around 82,000 square kilometers, representing more than 2.3% of India’s total land area. The most recent addition is the Madhav National Park Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh, which was designated as the 58th Tiger Reserve in 2025.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change. It is responsible for overseeing the implementation of Project Tiger and ensuring the effective management of tiger reserves.
- The NTCA provides financial aid to state governments, enforces legal protection, and monitors tiger populations to ensure their sustainable growth.
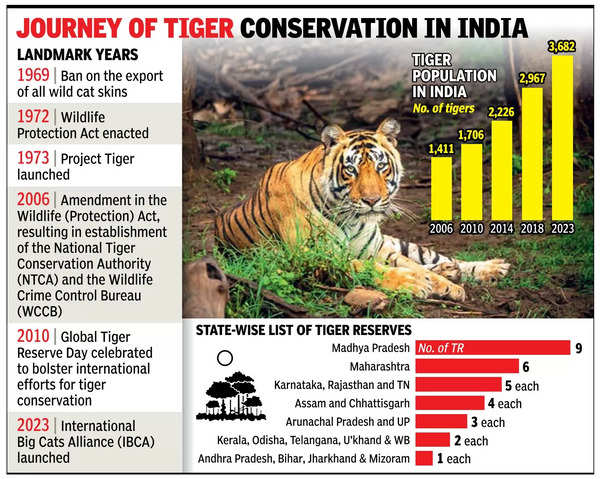
Initiatives to protect tiger in India:
India’s tiger conservation efforts are bolstered by several initiatives:
- Project Tiger: Launched in 1973, it provides financial and technical assistance to state governments for tiger conservation.
- Tiger Census: A periodic survey conducted to estimate the tiger population in India.
- M-STrIPES: A monitoring system to track and improve patrolling activities in Tiger Reserves.
- St. Petersburg Declaration on Tiger Conservation: A commitment by India and other tiger-range countries to double the global tiger population by 2022 (TX2 initiative).
Conclusion:
India is home to over 70% of the world's wild tiger population, with 3,682 tigers. The country's tiger conservation efforts have evolved significantly over the years, from initial bans on hunting and trade to multifaceted conservation strategies involving legal frameworks, international cooperation, and community engagement. The declaration of Madhav National Park as a tiger reserve is a testament to India's commitment to environmental protection and wildlife conservation.







