Context:
The 9th meeting of the Mission Steering Group (MSG) of the National Health Mission (NHM) was recently chaired by Union Health Minister Shri Jagat Prakash Nadda in New Delhi. This meeting marked a significant milestone in India's healthcare progress, reviewing key achievements and setting future priorities.
Mission Steering Group (MSG) and Its Role
The MSG is the highest policy-making body under NHM, responsible for providing strategic direction, governance, and oversight to various health sector programs. It comprises senior officials and experts who ensure the mission’s objectives—improving healthcare infrastructure, service delivery, and health outcomes—are effectively met.
Key Achievements Highlighted in the Meeting
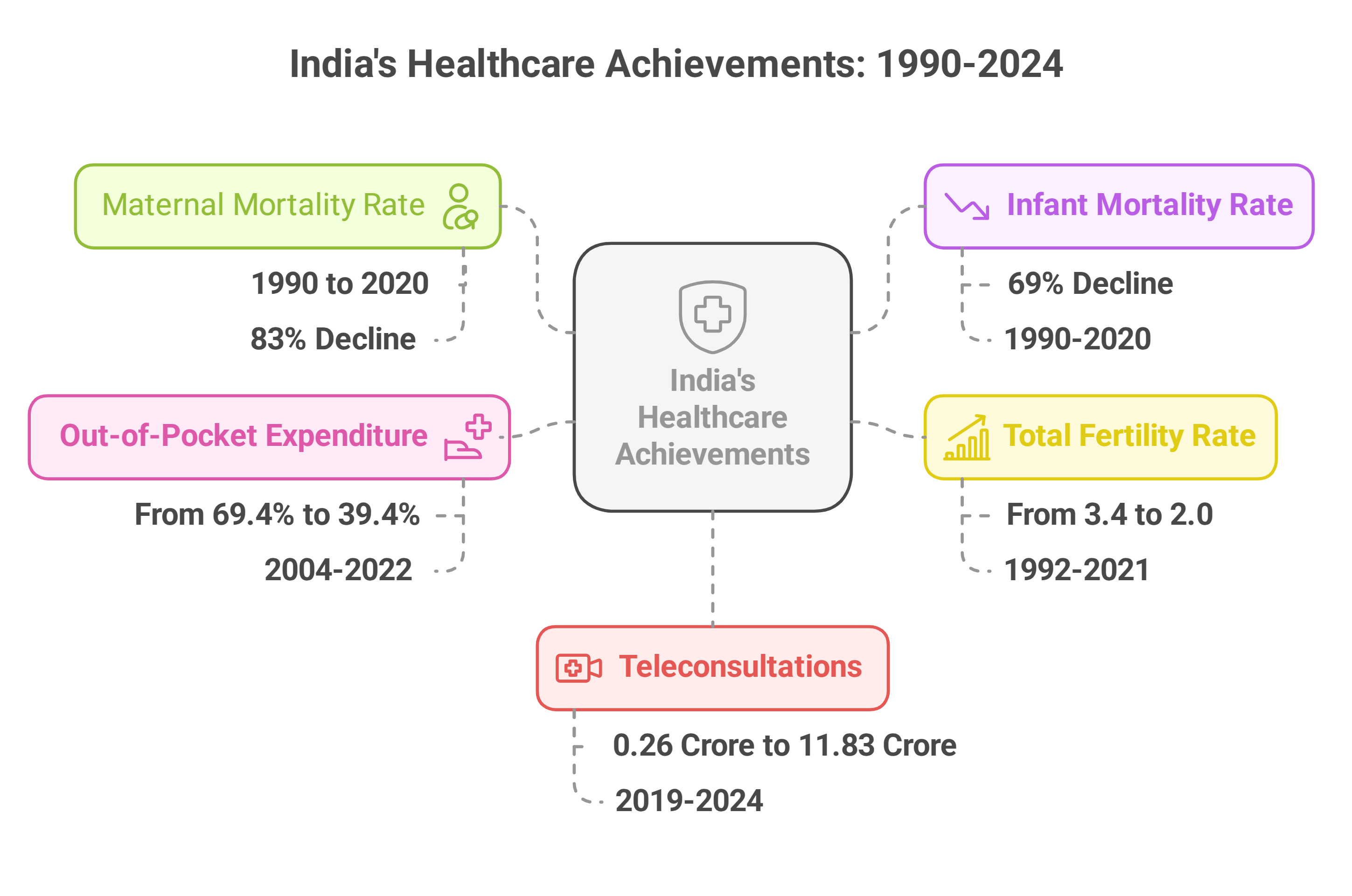
- Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR): India successfully met the National Health Policy target, reducing MMR to 100 deaths per 1 lakh live births—an 83% decline between 1990 and 2020.
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): IMR showed a significant 69% decline in the same period.
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR): TFR reduced from 3.4 in 1992-93 to 2.0 in 2019-21, indicating improvements in family planning and reproductive healthcare.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OPE): OPE dropped from 69.4% in 2004-05 to 39.4% in 2021-22, enhancing healthcare affordability.
- Teleconsultations: Usage surged from 0.26 crore in 2019-20 to 11.83 crore in 2023-24, expanding access to healthcare services.
National Health Mission (NHM): An Overview
Launched in 2013, NHM aims to strengthen healthcare delivery nationwide. It integrates two key initiatives:
- National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) (2005): Focuses on improving healthcare access in rural areas.
- National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) (2013): Addresses healthcare needs in urban settings.
Both missions collectively ensure accessible and equitable healthcare services across demographics.
Key Programmatic Components of NHM
- Reproductive-Maternal-Neonatal-Child-Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A): Enhances maternal and child health, ensures quality care during pregnancy and childbirth, and promotes adolescent well-being.
- Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Targets both infectious diseases (e.g., tuberculosis, malaria, HIV) and non-communicable conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, cancer) through prevention, early detection, and treatment.
Objectives of NHM
The mission strives for universal health coverage, ensuring quality healthcare for all, especially marginalized and underserved communities. It aims for an accountable and responsive healthcare system that effectively addresses India’s vast and diverse population needs.
Way Forward
To sustain and enhance progress, the government outlined key focus areas:
- Capacity Building: Strengthen the skills of healthcare professionals, especially Chief Medical Officers (CMOs), to improve service delivery.
- Healthcare Infrastructure Improvement: Continue infrastructure enhancement with a focus on integrating technology for efficient healthcare services.
- Empowerment of ASHA Workers: Provide additional support and welfare measures, recognizing their crucial role in community healthcare delivery.
The 9th MSG meeting reaffirmed the government’s commitment to strengthening healthcare systems and making healthcare more affordable and accessible for all.







