Context:
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), Government of India, has released the 26th edition of its publication, Women and Men in India 2024: Selected Indicators and Data. This comprehensive report provides gender-disaggregated statistics across key domains, including population, education, health, economic participation, and decision-making.
Key Findings of the Report:
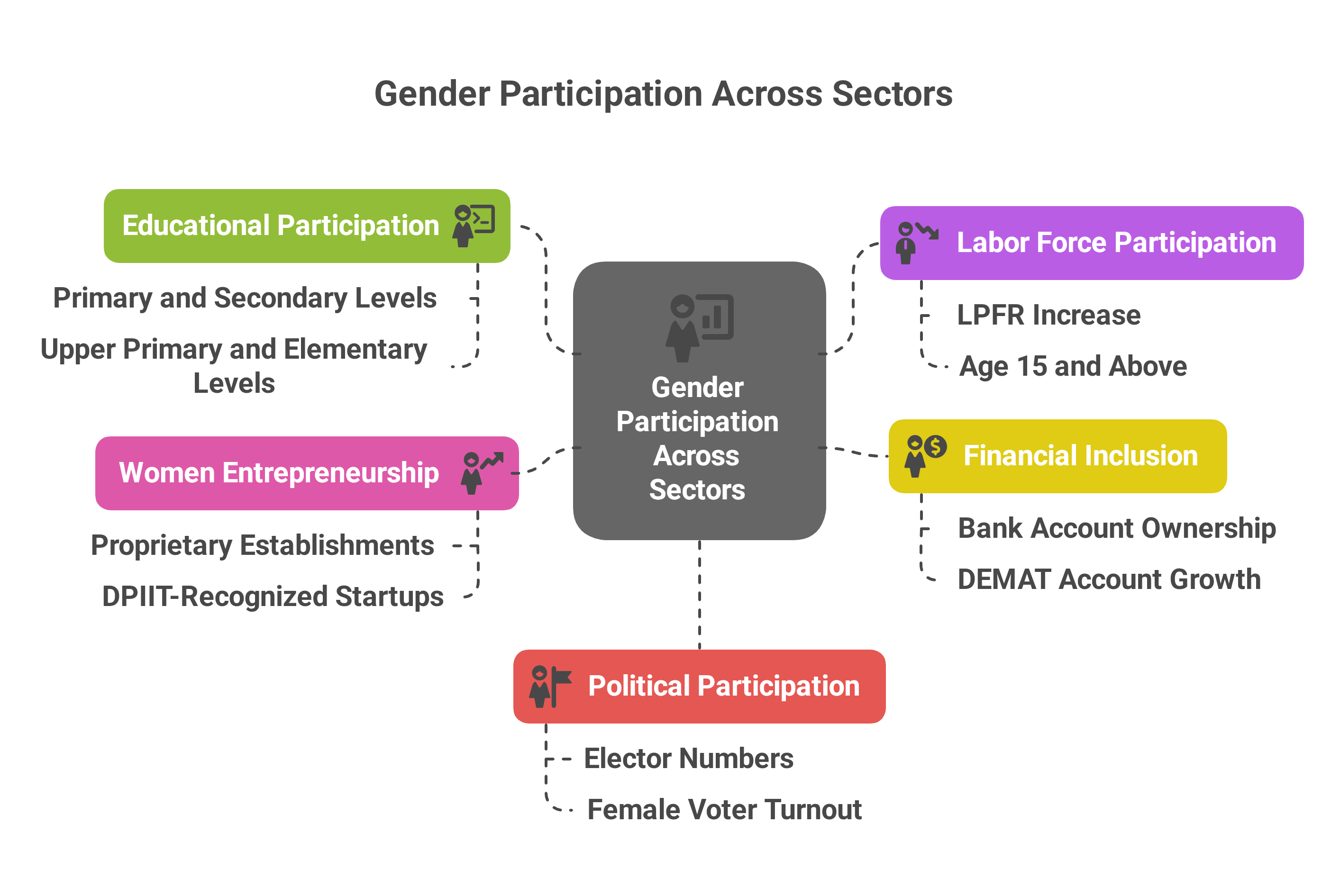
Educational Participation: The Gender Parity Index (GPI) remains high at the primary and higher secondary levels, indicating strong female enrolment. Upper primary and elementary levels have shown fluctuations but remained close to parity.
Labor Force Participation: The Labor Force Participation Rate (LPFR) for individuals aged 15 and above has increased from 49.8% in 2017-18 to 60.1% in 2023-24, reflecting a rise in workforce engagement.
Financial Inclusion: Women own 39.2% of all bank accounts and contribute to 39.7% of total deposits, with rural areas showing the highest participation (42.2%). The number of DEMAT accounts surged from 33.26 million in 2021 to 143.02 million in 2024. While male account holders remain the majority (26.59 million in 2021 to 115.31 million in 2024), female participation has grown significantly (6.67 million to 27.71 million).
Women Entrepreneurship: The percentage of female-headed proprietary establishments in manufacturing, trade, and services has increased steadily from 2021-22 to 2023-24. Additionally, DPIIT-recognized startups with at least one-woman director have grown from 1,943 in 2017 to 17,405 in 2024, signaling rising female entrepreneurship.
Political Participation: The number of electors increased from 173.2 million in 1952 to 978 million in 2024, with a notable rise in female voter registration. Female voter turnout, which was 67.2% in 2019, slightly declined to 65.8% in 2024. However, the gender gap in voting has narrowed, with female turnout surpassing male turnout in 2024.
Conclusion:
The Women and Men in India 2024 report provide a critical overview of gender-related trends in India. While significant progress has been made in education, workforce participation, financial inclusion, entrepreneurship, and political engagement, persistent disparities remain. The insights from this report underscore the need for continued efforts in policy development and socio-economic interventions to promote gender equality and inclusive development.