Date : 19/06/2023
Relevance: GS Paper2 : Government policies and Intervention
Main Words: Gig Economy, Code on Social Security (2020), Employee Provident Fund, Niti Aayog, Digital Economy
Context -
- The gig economy, driven by digital advancements, has revolutionized the way people work and connect in the modern era. However, gig workers face a significant challenge when it comes to social security.
- Ensuring social security benefits for gig workers has become an urgent concern in order to protect their well-being and create a fair and sustainable work environment.
Understanding the Gig Economy and Gig Workers:
- Gig Economy: A free market system where temporary positions are common, and organizations engage independent workers for short-term projects.
- Gig Worker: Individuals who engage in gig work outside the traditional employer-employee relationship and earn from such activities.
Gig Economy in India:
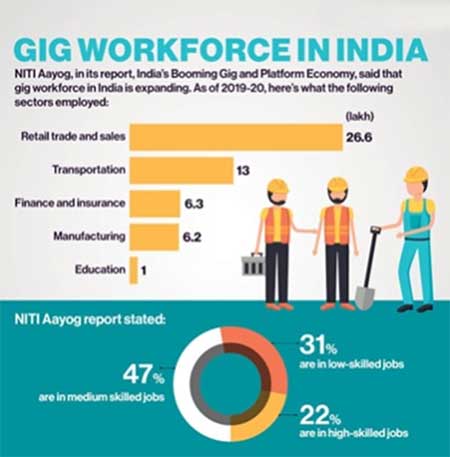
- Rapid Growth: India has become one of the largest countries for flexi staffing or gig workers, with approximately 7.7 million workers engaged in the gig economy.
- Expected Growth: The number of gig workers is projected to reach 23.5 million by 2029-30, constituting around 4% of the country's overall livelihood.
- Job Distribution: Currently, 31% of gig work is low-skilled (e.g., cab driving, food delivery), 47% is medium-skilled (e.g., plumbing, beauty services), and 22% is high-skilled (e.g., graphic design, tutoring).
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers in Accessing Social Security:
- Exclusion from Benefits: Gig workers are often excluded from social security and labor legislation due to their ambiguous employment status, depriving them of basic labor rights and protections.
- Economic Insecurity: The nature of gig work, driven by demand-based assignments, leads to job insecurity and income uncertainty, making social security benefits crucial for economic stability.
- Health and Well-being: Lack of access to employer-sponsored health insurance and other benefits leaves gig workers vulnerable to unexpected medical expenses, emphasizing the need for social security coverage.
- Equity in Opportunities: Exemption from traditional employment protections exposes gig workers to exploitative working conditions and inadequate compensation, highlighting the importance of social security in ensuring a level playing field.
- Long-term Financial Security: Without employer-sponsored retirement plans, gig workers may face difficulties in saving for their future, necessitating the provision of social security benefits.
Main Challenges in Providing Social Security for Gig Workers:
- Classification Complexity: Determining the extent of company obligations towards gig workers is challenging due to blurred boundaries between self-employment and dependent-employment.
- Flexibility Dilemma: The gig economy's flexibility, allowing workers to choose their hours and workload, poses a complex task in designing social security benefits that accommodate this flexibility.
- Funding and Cost Distribution: Traditional social security systems rely on employer and employee contributions, but in the gig economy, where workers are often self-employed, identifying appropriate funding mechanisms becomes intricate.
- Coordination and Data Sharing: Efficient coordination and data sharing among gig platforms, government agencies, and financial institutions are necessary to assess gig workers' earnings, contributions, and eligibility accurately.
- Education and Awareness: Many gig workers may lack awareness of their rights and entitlements regarding social security benefits, making it challenging to ensure proper coverage.
Steps to Ensure Social Security for Gig Workers:
- Implementing the Code on Social Security (2020): Urgent implementation of the Code on Social Security is necessary to provide legal provisions and create a Social Security Fund managed by a government-led board.
- Learning from Global Models: Emulating models like the UK, which categorizes gig workers as "workers" with associated benefits, or Indonesia, which provides insurance coverage, can help India establish appropriate social security frameworks.
- Expanding Employer Responsibilities: Gig companies should take greater responsibility for the wellbeing of gig workers by providing benefits comparable to regular employees, particularly in cases where gig workers cannot enter into direct contracts with clients.
- Wider Health Coverage: Employers should provide on-work accident insurance, and options for health insurance should be expanded to ensure adequate coverage for gig workers.
- Government Support: The government should facilitate high-skill gig work in sectors such as education, finance, and customer management, making it easier for Indian gig workers to access global markets. Collaborative efforts among governments, gig platforms, and labor organizations are necessary to establish fair and transparent mechanisms for providing social security benefits.
Conclusion:
Addressing the regulation of gig work in India is critical as it is expected to engage a significant number of people in the coming decade. Delaying the establishment of a regulatory framework for gig workers will not only impact India's thriving digital economy but also the well-being of its workers. Tripartite consultations involving the government, businesses, and gig workers are essential for formulating a legal framework that supports both economic growth and gig workers' welfare.
Probable questions for Main Exam-
- Question 1: What is the gig economy, and why is it important to address social security issues for gig workers? (10 marks)
- Question 2: How can the Code on Social Security (2020) contribute to addressing the social security needs of gig workers? (15 Marks)