Date : 23/10/2023
Relevance – GS Paper 3 – Indian Economy – Agriculture
Keywords - FPOs, Economies of Scale, Productivity, Kalanamak Rice
Context
Over the last couple of years, there has been substantial progress in the export of vegetables and fruits from Eastern Uttar Pradesh (UP). This surge in exports can be credited to the instrumental role played by Farmer Producers’ Organizations (FPOs). These organizations have been essential in promoting farming based on clusters, encouraging the adoption of modern technologies, and assisting farmers in effectively marketing their agricultural products.
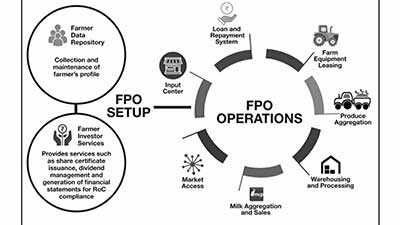
What are Farmer Producers’ Organizations (FPOs)?
Farmer Producers’ Organizations (FPOs) are voluntary associations operated by farmers themselves, giving them control over policies and decisions that can improve their socio-economic conditions and that of their communities.
Objectives of FPOs:
Leveraging Economies of Scale: FPOs enhance productivity and sustainable farming practices by efficiently using resources, reducing costs, and promoting income-oriented farming through economies of scale in production and marketing.
Role of FPOs in Modernizing Indian Agriculture:
- Cost Reduction and Increased Income: FPOs reduce farmers’ costs through bulk purchases of inputs and facilitate better marketing of farm products. They aggregate produce and offer bulk transport solutions.
- Modernization of Agriculture: FPOs promote agricultural modernization, particularly benefiting small and marginal farmers who lack access to modern equipment.
- Specialized Farming: FPOs lead initiatives such as cultivating special crops like Kalanamak rice in districts like Siddharthnagar (UP).
- Addressing Small Land Holdings: FPOs encourage collective farming, addressing productivity challenges associated with limited farm size, a common issue among Indian farmers.
- Enhancing Bargaining Power: FPOs empower farmers by boosting their bargaining power and income levels, allowing them to compete with large corporate enterprises.
- Unique Recognition: FPOs have successfully registered local products under Geographical Indications, such as Adam Chini rice and Banarasi langda, giving local produce unique recognition.
- Access to Technology: FPOs provide access to modern technologies, credit, capacity-building, training, and ensure traceability of agricultural produce.
- Easy Access to Credit: Farmers within FPOs have easier access to funds and support services from the government, donors, and service providers.
- Eliminating Intermediaries: FPOs play a crucial role in eliminating non-transparent intermediaries in agricultural marketing, leading to better incomes for farmers.
- Value Addition: FPOs minimize post-harvest losses through value addition and efficient management of value chain facilities.
- Collective Strength: FPOs facilitate the collectivization of small, marginal, and landless farmers, providing them with collective strength to address issues like crop failure and market access.
- Managing Price Fluctuations: Practices like contract farming and agreements, enabled by FPOs, help manage price fluctuations in agricultural markets.
- Effective Communication: FPOs enable efficient communication, disseminating information about prices, volumes, and other farming-related advisories.
- Nutritional Focus: FPOs enhance local diets by developing the value chain of nutrient-rich agricultural products such as millets, mushrooms, moringa, and fortified cereals.
- Local Campaigns: FPOs collaborate with local authorities for campaigns like “Aahaar Se Upchar Tak” in places like Rampur, supplying nutrition-rich products to anganwadi kendras, thus enhancing local nutrition.
Issues Faced by Farmer Producers’ Organizations (FPOs):
- Lack of Professional Management: Trained rural manpower is scarce, making it challenging for FPOs to have effective professional management.
- Weak Financials: Limited resources among small and marginal farmers within FPOs hinder their ability to provide quality products and services initially.
- Inadequate Access to Credit: Credit guarantee schemes often have high membership requirements, leaving many small FPOs without access to credit benefits.
- Lack of Risk Mitigation Mechanism: Existing insurance schemes cover production risks for farmers but neglect business risks for FPOs.
- Inadequate Access to Markets: FPOs struggle with limited connections to industry players, large retailers, and other market participants.
- Inadequate Access to Infrastructure: Essential facilities like transport, storage, value addition, processing, brand building, and marketing are lacking for FPOs.
- Lack of Technical Skills/Awareness: Farmers lack awareness of the benefits of collective farming, and there is a shortage of competent agencies to provide support.
Government Initiatives to Address Agricultural Challenges:
- Scheme for 10,000 FPOs: Establishment of 10,000 Farmer Producer Organizations to enhance agricultural profitability and benefit farmers.
- Equity Grant Fund Scheme: Supporting FPOs in improving viability, sustainability, and creditworthiness through an equity grant fund.
- Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme: Providing collateral-free credit to FPOs, facilitating their access to financial resources for agricultural activities.
- Scheme for Backward and Forward Linkages: Bridging supply chain gaps by facilitating raw material availability and market linkages for FPOs.
- Operation Greens (TOP to TOTAL): Promoting FPOs, agri-logistics, processing facilities, and professional management to boost agricultural value chains.
- 100% Tax Deduction for FPOs: Offering tax incentives to FPOs with turnovers within the specified limit, encouraging their growth and development.
Support Initiatives by the Uttar Pradesh Government for FPOs:
- Formation Plans: The central goal of establishing 10,000 FPOs nationwide includes the creation of one FPO in each of Uttar Pradesh's 826 blocks annually for five years.
- Dedicated Support: Uttar Pradesh has established a specialized FPO cell to guide these organizations, ensuring coordination among schemes and addressing compliance issues.
- FPO Shakti Portal: Launched in Uttar Pradesh, this portal provides grievance redressal mechanisms and business partnership opportunities for FPOs. Currently, 1,600 FPOs with a turnover of Rs 229 crore have registered on the portal as of July 15.
- Financial Assistance: FPOs receive a 3% interest subvention from the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund. Uttar Pradesh further adds another 3%, significantly reducing the loan interest to around 3%.
- Subsidies: Both central and state-sponsored schemes offer capital subsidies, encouraging the development of post-harvest infrastructure for FPOs.
Conclusion:
To enhance FPOs, there is a critical need to scale and strengthen these organizations. This can be achieved through amendments to the APMC Act to provide fee exemptions, the development of farm-level infrastructure, enabling MSP (Minimum Support Price)
procurement, attracting private investors, extending funding schemes, creating flexible policies, and conducting awareness programs in rural farming communities. These steps are vital for the sustainable growth and empowerment of Farmer Producers’ Organizations in Uttar Pradesh.
Probable Question for UPSC Mains Exam
- "1. Explain the pivotal role of Farmer Producers’ Organizations (FPOs) in Indian agriculture, focusing on their impact on sustainable practices, farmers' incomes, and rural development. Highlight key challenges faced by FPOs and propose strategies for their comprehensive growth.(10 marks, 150 words)
- "2. Assess the effectiveness of government initiatives like the Scheme for 10,000 FPOs and the Equity Grant Fund Scheme in supporting Farmer Producers’ Organizations. Discuss their influence on FPOs' financial viability, credit accessibility, and market outreach. Recommend ways to enhance the impact of these initiatives.(15 marks, 250 words)
Source – Indian Express