Daily-current-affairs
/
01 Nov 2020
Super Typhoon Goni : Daily Current Affairs
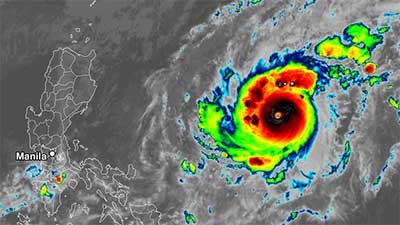
Super Typhoon Goni
Why in NEWS ?
- Super Typhoon Goni slammed into the Philippines with authorities warning of
“catastrophic” conditions in the region expected to receive the hardest hit, where nearly a
million people have been evacuated.
About
- Philippine officials ordered evacuation of thousands of residents in the southern part
of the main Luzon island as a category 5 storm – Typhoon Goni – that is the world’s
strongest in 2020 approaches the Southeast Asian nation.
- The strongest typhoon of the year so far made landfall on Catanduanes Island with
maximum sustained wind speeds of 225 kilometres (140 miles) per hour, will make
landfall as the strongest typhoon to hit the Philippines since Haiyan that killed more
than 6,300 people in November 2013.
- Goni -- which intensified into a “super” typhoon as it neared the Philippines -- comes
a week after Typhoon Molave hit the same region of the natural disaster-prone
archipelago.
- Pre-emptive evacuations have started in coastal and landslide-prone communities.
- Authorities are facing another hurdle as social distancing needs to be imposed in
evacuation centres to prevent the spread of coronavirus.
- Typhoon Goni, moving westward from the Pacific Ocean, will bring intense rains over
the capital of Philippines (Manila) and 14 provinces nearby, threatening of floods
and landslides.
- Around 20 typhoons hit the Philippines every year.
- Thus, as cyclones carries destructive force there is a need for timely dissemination of
warning and increasing preparedness of disaster management authorities.
What is the impact of such a typhoon?
- As per PAGASA (The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services
Administration), strong winds associated with the storm have damaged high-risk
structures and have partially damaged houses made with “first-class” materials.
- In addition, while some banana plantations have suffered total damage, coconut
plantations are expected to suffer extensive damage. Rice and corn plantations also
may suffer severe losses.
What are Super Typhoon?
- Since 2009 the Hong Kong Observatory has divided typhoons into three different
classifications: typhoon, severe typhoon and super typhoon.
- A typhoon has wind speed of 64–79 knots (73–91 mph; 118–149 km/h), a severe
typhoon has winds of at least 80 knots (92 mph; 150 km/h), and a super typhoon has
winds of at least 100 knots (120 mph; 190 km/h).
Cyclones
- Cyclone is an intense vortex or a whirl in the atmosphere with very strong winds
circulating around it in anti-clockwise direction in the Northern Hemisphere and
in clockwise direction in the Southern Hemisphere. For Ex- Cyclone Titli
- A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure
center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral
arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain or squalls.
- Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different
names-
- Cyclones in the Indian Ocean
- Hurricanes in the Atlantic
- Typhoons in the Western Pacific and the South China Sea
- Willy-willies in Western Australia
- Some of the special characteristics of tropical cyclones are as follows:
- Cyclones have intense low pressure areas and pressure increases outwards.
- They mainly originate mainly in zones between 5– 30 °C Norther & South of
latitude.
- These originate over oceans in tropical areas & move to coastal areas.
- They have large destructive force caused by violent winds, heavy rainfall & storm
surges.
- Tropical cyclones follow a parabolic path and its axis is parallel to the isobars.
- Some of the necessary condition for the formation of tropical cyclones are as
follows:
- Continuous supply of abundant warm and moist air.
- Sea temperature in lower latitudes should be around 27°C.
- The cyclones require presence of large Coriolis force to deflect winds
blowing toward the low pressure centre.
- There must also be pre-existence of weak tropical disturbances.
- Further, there should be presence of anticyclonic circulation at the height
of 9 to 15 km above the surface.
Difference between tropical cyclones and temperate cyclones
- Tropical cyclone is confined between 5-30° N-S of the equator, whereas temperate
cyclone originate between 30 to 60° N-S of the equator.
- Coriolis force plays vital role in the origin of tropical cyclone, whereas for temperate
cyclone frontogenesis is the driving force.
- Temperate cyclone covers large area as compared to tropical cyclone.
- Tropical cyclone generally originates over water surface but the temperate cyclone
originates over mid-latitude land mass.
- Temperate cyclone generally moves eastward, while tropical cyclone moves
from east to west.
- Cyclone’s eye is a typical feature in case of tropical cyclone, while temperate cyclone
have no such concept.







