Context:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Nigeria is of immense importance for both India and Nigeria, marking his first visit to the country after 17 years. Nigeria, Africa’s most populous nation and its second-largest economy, shares strong historical ties with India, making this visit an important step toward strengthening bilateral relations.
Historical and Geopolitical Context
- Mutual Historical Links: India and Nigeria, both large, multi-ethnic democracies, share a history as members of the Commonwealth. They face similar challenges, such as governance, corruption, and terrorism.
- Strategic Location: Nigeria's geopolitical position in Africa, with its growing economy and large population, offers significant potential for bilateral cooperation.
Importance of India-Nigeria Relations
- Trade and Investment: India is Nigeria’s second-largest trading partner, with a bilateral trade volume of $7.9 billion. Despite a decrease from its peak, this figure still indicates the strong economic link between the two countries.
- Indian Diaspora: India has a sizable diaspora in Nigeria, with nearly 50,000 Indians living there, contributing to the economic and cultural ties between the two nations.
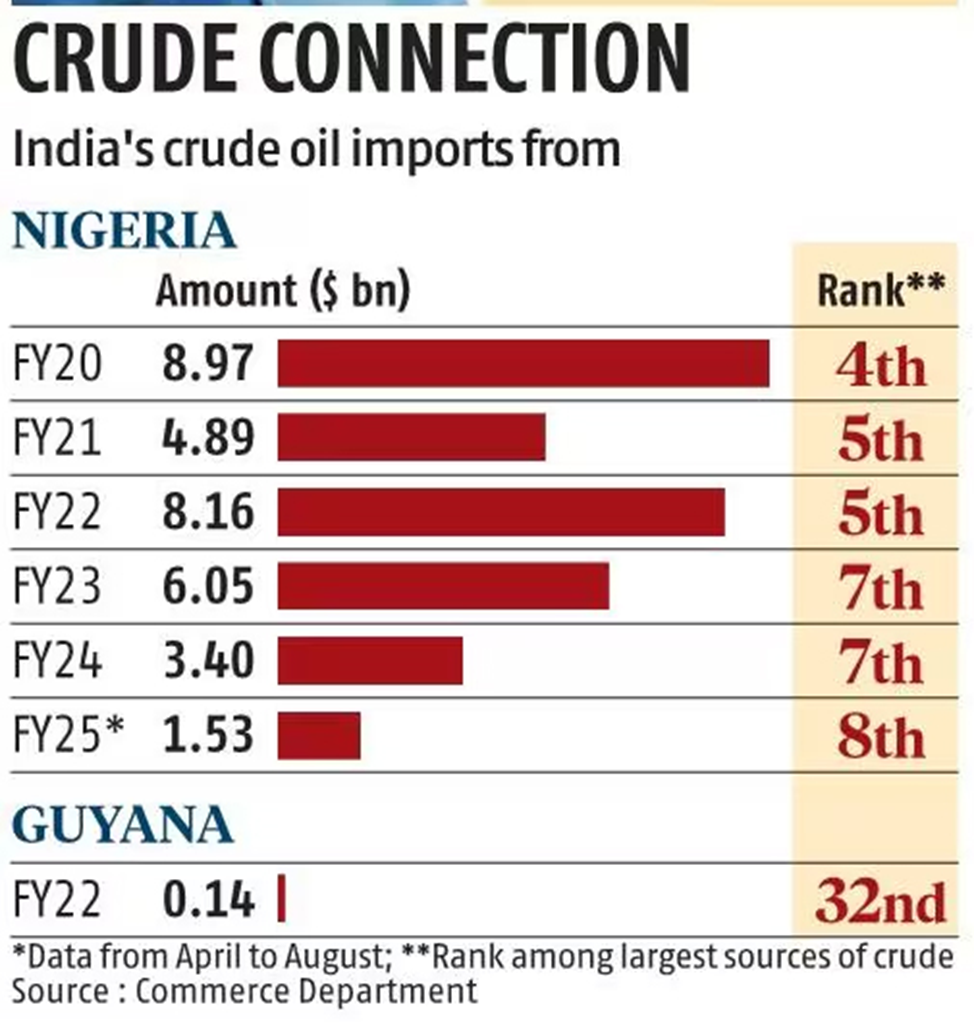
- Energy Cooperation: While India is a major buyer of Nigerian crude oil, it has no upstream hydrocarbon assets in Nigeria. This presents an opportunity for India to strengthen its energy partnership with Nigeria.
Current State of India-Nigeria Relations
Economic Cooperation
- Bilateral Trade: India’s exports to Nigeria declined by 29.7% in 2023-24, dropping to $7.9 billion. Nevertheless, Nigeria remains an important trade partner for India.
- Indian Investment in Nigeria: Over 150 Indian companies operate in Nigeria, investing approximately $27 billion. This reflects the strong presence of Indian businesses in Nigeria’s diverse sectors.
Strategic Areas for Cooperation
- Defense and Security: Nigeria faces security challenges such as Boko Haram, piracy, and oil theft. India can offer defense supplies, training, and remote sensing technology to help tackle these issues.
- Economic Stabilization: Nigeria is grappling with high inflation and foreign exchange shortages. India can support Nigeria’s economy by forming strategic partnerships in energy, infrastructure, and trade.
- Capacity Building: India can assist Nigeria in areas like education, healthcare, and technology to strengthen its human resources.
What India Can Offer Nigeria
Defense Support
- Countering Terrorism and Piracy: Nigeria’s security challenges, such as terrorism and piracy, can be mitigated through Indian support in defense training and technology.
- Training Nigerian Officers: India has a long history of training Nigerian military officers. Seven Nigerian presidents have trained in India’s defense institutions.
Economic and Financial Support
- Hydrocarbon Partnerships: Despite being a major buyer of Nigerian crude oil, India can explore partnerships in the energy sector, including upstream oil exploration.
- Barter Trade: To help Nigeria address its foreign exchange issues, India can offer to increase exports in essential goods like pharmaceuticals and foodstuffs and explore rupee-based trade.
Developmental Assistance
- Infrastructure Development: India can help Nigeria in developing key sectors such as infrastructure, technology, and healthcare.
- Human Resource Development: Providing training and expertise in IT, healthcare, and education will contribute to Nigeria’s socio-economic development.
Historical Context of India-Africa Relations
India and Africa share deep-rooted historical ties that date back to the early 20th century. India’s freedom movement played a significant role in inspiring African countries to fight for their independence from colonial rule.
Post-Independence Support
- Support for African Decolonization: After India’s independence in 1947, it became a vocal supporter of African decolonization at international platforms like the United Nations.
- South-South Cooperation: Despite its economic challenges, India continued to extend its support to African nations, sharing resources under the South-South cooperation model.
Launch of ITEC Program
- Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC): Launched in 1964, the ITEC program has been instrumental in providing technical and human resource development to African nations. It remains one of India’s most impactful foreign aid initiatives.
Current Status of India-Africa Relations
Economic Ties
- Bilateral Trade: India’s trade with Africa in 2020-21 amounted to $55.9 billion, with $27.7 billion in exports and $28.2 billion in imports. The trade includes minerals, crude oil, pharmaceutical products, and vehicles.
- Indian Investments: India has invested around $70 billion in Africa, with numerous lines of credit (LoCs) helping in various developmental projects, including irrigation and energy.
Social and Educational Cooperation
- Scholarships and Capacity Building: The Indian government has granted about 50,000 scholarships to African students over five years. India’s ITEC program remains a vital platform for skill development across Africa.
- Digital Education: The Pan African e-Network, launched in 2009, provides remote learning opportunities for African students and healthcare workers, offering free tele-education and telemedicine services.
Security and International Cooperation
- Maritime Security: Many African nations are part of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), aimed at enhancing maritime safety. India and African nations cooperate closely in ensuring the security of the Indian Ocean region.
- Joint Global Platforms: India and Africa have frequently collaborated in global institutions like the WTO and WIPO, advocating for the rights of developing nations.
Significance of the India-Africa Relationship
Huge Economic Potential
- African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA): The AfCFTA creates opportunities for enhancing India-Africa trade by establishing the largest free trade area globally. India can leverage this opportunity to increase its economic presence on the continent.
- Sectoral Opportunities: India’s strengths in Information Technology (IT), mobile payments, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine provide new opportunities for collaboration in Africa.
Infrastructure Development
- Digital Infrastructure: India’s strong start-up ecosystem and digital infrastructure capabilities can play a crucial role in strengthening Africa’s infrastructure.
- Cross-Border Supply Chains: By helping to build efficient cross-border supply chains in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals, India can contribute significantly to Africa’s development.
Soft Power and Common Agendas
- Cultural Diplomacy: India’s soft power in Africa is bolstered by the presence of a large diaspora and its cultural diplomacy efforts.
- Shared Global Interests: India and Africa have common positions on global issues such as climate change, UNSC reform, and trade policies, strengthening their political ties.
Challenges in the India-Africa Relationship
Developmental Strategy
- Lack of Focused Goals: India’s development strategy in Africa lacks clear long-term goals. Efforts like Lines of Credit (LoCs) and technical cooperation are not sufficiently aligned with broader developmental objectives such as food security and climate resilience.
- Implementation Challenges: The poor disbursal rate and delays in project completion hinder the effectiveness of Indian development cooperation in Africa.
Geopolitical Competition
- Chinese Presence: China has been highly active in Africa, particularly in terms of infrastructure investment and vaccine diplomacy, creating significant competition for India.
- Racial Tensions: Racial attacks on African nationals in India have posed challenges to India’s image, potentially straining its relations with African countries.
Steps to Strengthen India-Africa Relations
Clear Strategy for Africa
- Focused Development Goals: India needs to develop a focused Africa strategy, prioritizing key areas like food security, healthcare, and climate adaptation, which align with both India’s and Africa’s needs.
Enhanced Capacity Building
- Human Capital Development: A continued focus on education and skills training will help build a skilled workforce across Africa, benefiting both India and African nations.
Strengthening People-to-People Connections
- Diaspora Engagement: India should engage its diaspora and collaborate with Indian NGOs to implement affordable development projects in Africa.
- Improving African Students’ Experience: India must invest in its higher education sector to attract more African students, fostering stronger ties.
Conclusion
The India-Africa relationship is poised for further growth, driven by shared goals and mutual benefits. India’s engagement with Africa should be more strategically focused, addressing specific developmental needs, enhancing human resource capacities, and fostering economic partnerships. By doing so, India can contribute to Africa’s sustainable development while benefiting from the continent’s growth potential.







