Context-
India is at a critical juncture where recalibrating strategies is imperative to navigate the evolving economic landscape. Embracing a holistic approach that seamlessly integrates traditional sectors like manufacturing with burgeoning segments such as new-age services is essential. This comprehensive strategy aims to bridge existing gaps, optimize resource utilization, and foster sustainable economic growth.
Structural Transformation: Balancing Capital and Labor
● Capital-Output Ratio and Capital-Labor Ratio Dynamics: India's post-economic reform trajectory showcases a noteworthy decline in the capital-output ratio, indicating enhanced capital productivity propelled by technological innovations. Simultaneously, there's been a surge in the capital-labor ratio, signaling a shift towards more capital-intensive production methods, especially in manufacturing. This trend, while reflecting technological advancements, also raises concerns about potential labor surplus, particularly in agriculture.
● Impact on Employment and Productivity: The increasing capital intensity, particularly in manufacturing and utilities, has implications for employment generation and productivity. While it denotes improved capital productivity, the efficiency of capital utilization remains a question. The surge in capital intensity has led to a decline in national employment growth rates, underscoring the need for policies that balance capital investment with job creation, especially in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
Services Sector: Engine of Employment Growth
● Dominance in National Output and Employment: The services sector emerges as a pivotal player in India's employment landscape, constituting over half of the national income and approximately 30.7% of total employment. Despite its significance, the services sector faces challenges such as skill mismatches and uneven growth, particularly in high-tech versus low-skill services.
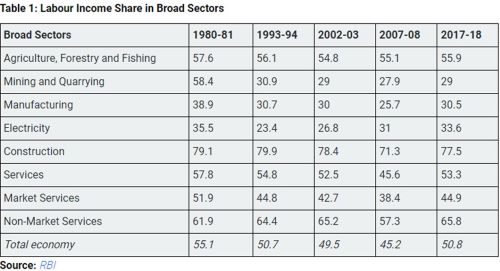
● Role of Skill Development and Diversification: Investing in skill development is paramount to unlock the full potential of the services sector. While high-tech services attract skilled workers, there's a need to facilitate skill development for low-skilled workers to ensure inclusive growth. Achieving this balance entails a concerted effort towards diversification and upskilling to cater to evolving market demands.
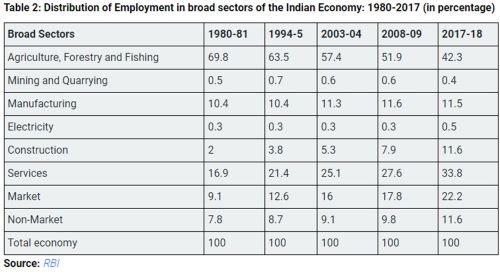
Employment Dynamics Across Sectors
● Historical Trends and Shifts: India's employment landscape has undergone significant transformations over the decades, with a notable shift from agriculture to services. India has experienced a significant shift from agriculture to services, particularly since the 1990s with the ICT revolution. While this leapfrogging to services indicates economic evolution, there's a need to address the mismatch between job aspirations and available opportunities, especially among low-skilled workers.
● Challenges and Opportunities: The demand-supply dynamics of employability pose a significant challenge, exacerbated by skill gaps and inadequate industry engagement. Despite governmental initiatives like the Skill India Mission and National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme, there's room for improvement in training standardization and placement rates. However, initiatives like Startup India and infrastructure development projects present opportunities to stimulate job creation and foster a conducive business environment.
Policy Interventions and Future Outlook
● Policy Imperatives: Addressing the employment conundrum requires a multifaceted approach encompassing policy interventions, skill development, and industry collaboration. A recent study projects a 22% rise in employment by 2030, accompanying India's goal of achieving a US$ 5 trillion economy by 2028. Efforts to streamline training programs, enhance industry participation, and alleviate bureaucratic hurdles are crucial steps towards fostering inclusive growth and reducing unemployment rates.
● Future Projections and Strategic Interventions: Projections for India's employment landscape highlight the potential for substantial job creation, especially in urban centers, driven by the services sector and industrial value chain expansion. Strategic interventions aimed at bridging the gap between traditional and emerging sectors are imperative to leverage India's demographic dividend effectively. By tapping into the vast potential of its young labor force, India can propel sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
Conclusion
India stands at a pivotal juncture where recalibrating strategies and adopting a holistic approach are imperative to navigate the complex economic terrain. Balancing capital and labor dynamics, harnessing the potential of the services sector, and addressing employment challenges across sectors are critical imperatives for sustainable and inclusive growth. Through concerted policy interventions, skill development initiatives, and strategic investments, India can unlock the full potential of its demographic dividend, ensuring a prosperous future for all its citizens.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam- 1. How can India effectively bridge the gap between traditional sectors like manufacturing and emerging sectors like new-age services to ensure sustainable economic growth and inclusive development? (10 Marks, 150 Words) 2. What specific policy interventions and initiatives can India undertake to address the challenges of skill gaps, inadequate industry engagement, and inefficient resource utilization, particularly in the context of employment generation and labor market dynamics? (15 Marks, 250 Words) |
Source- The Indian Express







