Date : 27/12/2023
Relevance: GS Paper 3 – Internal Security ( Also Relevant for Indian Economy and Science and Technology)
Keywords: Cyber Security, Digital India Act, 2023 , CAG, KYC
Context-
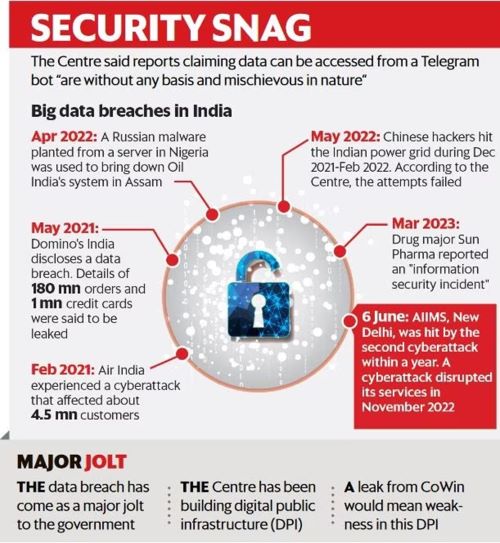
In October, the revelation by Resecurity, a US company, regarding the availability of sensitive personal data of 815 million Indians on the dark web sent shockwaves globally. The compromised data included Aadhaar numbers, passport information, and other personally identifiable details, raising serious concerns about the security of digital information in India. This incident is not an isolated one, as previous breaches have exposed vulnerabilities in the nation's digital infrastructure, posing risks to the privacy and financial well-being of its citizens.
The Persistent Threat:
- Data breaches have become alarmingly common, with incidents such as the leak from the Cowin website and the ransomware attack on AIIMS highlighting the urgent need for a robust cybersecurity strategy in India. Despite being one of the fastest-growing economies globally, the country lacks a comprehensive long-term plan to counteract cyber threats, putting its citizens at risk of identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
The Aadhaar Conundrum:
The widespread adoption of Aadhaar, despite a Supreme Court prohibition against making its registration mandatory, has exacerbated the risks associated with data breaches. The government's failure to implement a cohesive cybersecurity strategy has left every Indian citizen exposed to potential digital catastrophes. The leakage of Aadhaar numbers, names, and other sensitive information not only facilitates identity theft but also opens avenues for financial scams, underscoring the urgency of addressing these vulnerabilities.
Government's Response Gap:
Unlike some countries that promptly respond to data breaches with incident response plans, India seems to lack a structured approach. The absence of clear communication to affected citizens, coupled with a lack of education on mitigating risks, leaves individuals to navigate the aftermath of breaches on their own. The government's inertia in implementing a long-term cybersecurity strategy further compounds the problem.
The constant flow of news about data breaches, whether at government agencies or private entities, has normalized the massive losses of personal data. Despite claims of Aadhaar making India a global leader, concerns raised by institutions like Brookings, Moody's, and the CAG regarding the lack of regulation, transparency, and accountability persist.
Global vision for Digital Transformation
India's global vision for digital transformation encompasses a comprehensive impact on all facets of society through initiatives promoting digital access, service delivery, and inclusion. This transformation, facilitated by sustainable and affordable technology, is positioned to extend its influence worldwide.
On the international stage, India advocates for a governance framework and digital public infrastructure within the G20, emphasizing equal accessibility for all nations. As part of the broader theme of "One Earth, One Family, One Future" (Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam) during its G20 presidency, India underscores the significance of data for development in this overarching vision.
A Pioneering step in this regard : Digital India Act, 2023
The introduction of the Digital India Act, 2023 (DIA) marks a pivotal stride in the development of a contemporary legal infrastructure for India's rapidly expanding digital landscape. This initiative becomes particularly noteworthy as India is actively engaged in its digital transformation, and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has taken a proactive approach to synchronize with the ambitious 'Digital India' program. The DIA addresses the pressing need for a forward-looking regulatory framework amid the ongoing evolution of the country's digital ecosystem.
Objective:
- To establish adaptable regulations aligned with evolving tech trends for the country's digital infrastructure.
- To provide accessible adjudication for online offenses, ensuring timely remedies, resolving disputes, and upholding internet rule of law.
- To prioritize overarching principles for compliance.
Key Components:
- Open Internet: Envisioned with choice, competition, online diversity, fair market access, and startup-friendly compliance.
- Online Safety and Trust: Focus on cyber threat protection, digital rights, and combating fake news on social media.
- Accountable Internet: Enhance accountability through legal mechanisms, constitutional rights in cyberspaces, algorithmic transparency, and data disclosure norms.
Salient Features:
- Replaces the outdated Information Technology Act, adapting to dynamic internet growth.
- Focuses on online safety, trust, accountability, open internet, and regulation of AI and blockchain.
- Collaborates with related laws, reviews 'safe harbor,' imposes KYC for retail wearable devices.
- Aligns with Digital India Goals for a USD 1 trillion digital economy by 2026.
Digital Technology's Impact on Various Sectors in India
- Healthcare Revolution:
Digital technology has been a driving force behind the transformation of India's healthcare sector. The successful execution of the world's largest Covid-19 vaccination program is a testament to the efficiency that technology has brought. Initiatives like the National Digital Health Mission and National Digital Health Blueprint have significantly strengthened healthcare delivery. The adoption of telemedicine, AI-enabled medical devices, and electronic medical records is rapidly modernizing India's health systems. The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission is a key initiative further propelling the digitization of healthcare, making the system more citizen-centric, holistic, and proactive. - Tourism's Digital Overhaul:
India's tourism and travel sector has undergone a profound transformation due to the digital revolution. The internet has played a pivotal role in reshaping how people explore, plan, and experience travel. Online bookings, virtual tours, and travel content creation have become integral aspects of the traveler's journey. The internet has evolved into an indispensable tool for both tourists and businesses in the tourism sector, fundamentally altering the way the industry operates. - Digital Payments Reshaping Businesses:
Digital payments have ushered in a paradigm shift in the way businesses operate in India. Simplifying payment processes, reducing operational work, and increasing productivity are key benefits brought about by the rapidly expanding digital payments landscape. Small and medium-sized enterprises, in particular, have experienced transformative changes, saving both time and money. By offering digital payment options, businesses can focus on their core competencies, tap into a larger market, and attract new customers. The widespread adoption of digital payments is fundamentally reshaping the business landscape in India.
Recommendations for a Secure Digital Future:
To address the escalating cybersecurity challenges, the Government of India must take decisive actions:
- Prioritize cybersecurity as a national and economic security imperative.
- Establish a collaborative cybersecurity board with government and private sector participants to analyze and recommend improvements.
- Adopt a zero-trust architecture and mandate a standardized playbook for responding to cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
- Urgently modernize and defend state networks, updating incident response policies.
- Put people at the center of policies, ensuring immediate and transparent communication, proactive protection measures, and assistance in the aftermath of cyber incidents.
Conclusion
As India aspires to be a digital leader on the global stage, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is paramount. The recent data breaches underscore the critical need for the government to act swiftly, implementing comprehensive strategies and engaging in proactive communication to protect its citizens from the escalating threats in the digital realm. A Digital India is desirable, but achieving this goal requires a concerted effort to address the current shortcomings in cybersecurity and data protection.
Probable Questions for UPSC mains Exam-
- In the context of the growing cybersecurity challenges, discuss the importance of a comprehensive legal infrastructure to safeguard sensitive digital information. Evaluate the effectiveness of existing strategies and propose measures to enhance national cybersecurity, considering both governmental and private sector collaboration. (10 marks, 150 words)
- Examine the transformative impact of digital technology on key sectors in India, such as healthcare, tourism, and business. Illustrate specific initiatives and their contributions to sectoral growth. Assess the role of digital technology in realizing broader economic goals and propose recommendations for securing a resilient digital future for the country. (15 marks, 250 words)
Source- Indian Express