Date : 15/07/2023
Relevance: GS 3: Awareness in the field of space, Developments in Science and Technology
Key Phrases: Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstration (RLV-TD),
Context-
- Potentially saving millions of taxpayers’ money, space agencies around the world aim to use reusable launch vehicles for rockets.
- A SpaceX Falcon 9 Reusable rocket carrying a Qatari communications satellite launches from the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, on November 15, 2018.
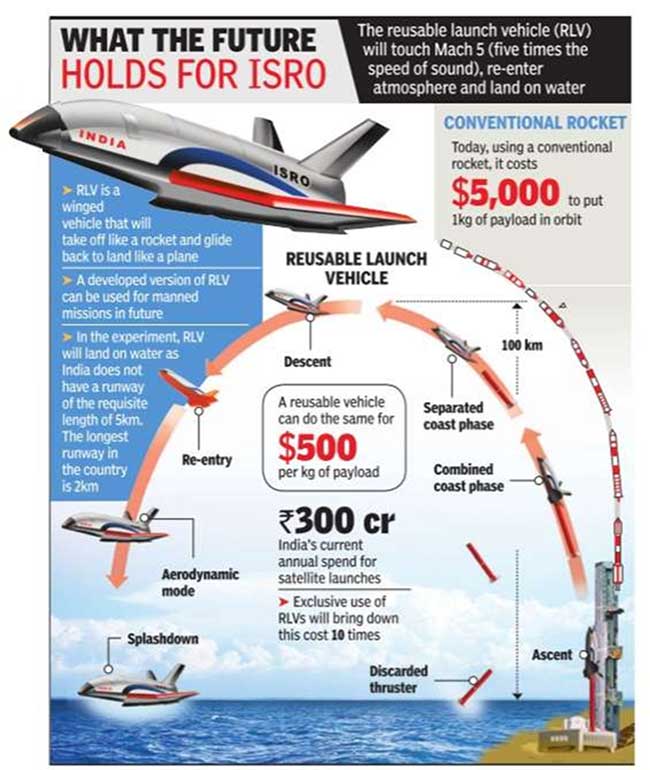
- Inching closer to a fully reusable launch vehicle, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully carried out the landing experiment of the Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstration (RLV-TD) program on April 2, 2023.
- ISRO executed the landing experiment at the Aeronautical Test Range in Challakere, Chitradurga. The RLV was dropped by an Indian Air Force (IAF) Chinook helicopter from an altitude of 4.5 km. The vehicle performed approach and landing maneuvers on the runway autonomously, under the conditions in which a re-entry vehicle from space might return at high speed and without human inputs, to achieve a stable landing. The success of this test marks yet another milestone in ISRO’s mission to develop a fully reusable launch vehicle as part of its vision to enable low-cost access to space.
What is a reusable launch vehicle?
Reusable launch vehicles (RLVs) are rockets designed with components that can be recovered and reused for multiple missions, significantly reducing the cost of space launches. The primary focus of reusability is on the rocket stages, but smaller parts like engines and boosters can also be reused. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the space industry by making access to space more affordable and sustainable.
Have RLVs been used in the past?
- Various space agencies and companies are actively pursuing the development and utilization of reusable launch vehicles. SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, has been at the forefront of this technology. Their Falcon 9 rockets have successfully landed and been reused numerous times. As of May 19, 2023, Falcon 9 first stages have completed 220 launches, with 178 landings and 155 re-flights.
- Blue Origin, another prominent company in the space industry, has also made significant progress in reusable technology. Their New Shepard spacecraft, which is designed for suborbital flights, has performed successful landings after reaching high altitudes.
- Other organizations involved in the research and development of reusable launch systems include the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the United Launch Alliance (ULA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
ISRO’s Vision
- ISRO's vision of a fully reusable launch vehicle aligns with its goal of enabling low-cost access to space. By reducing the need to manufacture new components for each launch, reusable technology has the potential to make space missions more affordable and sustainable. It can open up new opportunities for scientific research, commercial ventures, and exploration beyond Earth's atmosphere.
Conclusion:
The advent of reusable launch vehicles holds immense promise for transforming the space industry. With reusable technology, the cost of accessing space can be substantially reduced, opening up new opportunities for scientific research, commercial ventures, and exploration beyond Earth's atmosphere. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have already demonstrated the feasibility of reusable rocket stages, and ISRO's progress with the RLV-TD program indicates the growing global interest in this technology. As advancements continue, reusable launch vehicles have the potential to make space more accessible, sustainable, and economically viable, ultimately driving innovation and progress in the field of space exploration.
Currently, ISRO has four active launch vehicles:
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV): PSLV has been a versatile launch vehicle deployed for launching all three types of payloads viz. Earth Observation, Geo-stationary, and Navigation.
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV): GSLV with indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage has enabled the launching of up to the 2-tonne class of communication satellite
- Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM3): The LVM3 is the next generation launch vehicle capable of launching 4-tonne class of communication satellites and a 10-tonne class of payloads to LEOs.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is being developed with complete indigenous technologies to meet the small satellite launch market on demand driven basis
Probable questions for UPSC main exam-
- What is a reusable launch vehicle? How far ISRO has been successful in achieving this technology? How can RLV technology transform the space industry? (10 Marks,150 Words)
- How do reusable launch vehicles work, and how is ISRO progressing towards achieving full reusability in their launch vehicles? (15 Marks ,250 Words)
Source : The Hindu