Context:
The recurrence of the deadly Nipah virus has placed India on high alert and is indicative of the urgent need to understand health security with an ecological perspective. The One Health strategy is pivotal, emphasising an integrated approach that balances and optimises the health of people, animals, and ecosystems. Despite its theoretical advocacy by policymakers and international organisations, there remains a gap between theory and practice.
One Health Strategy
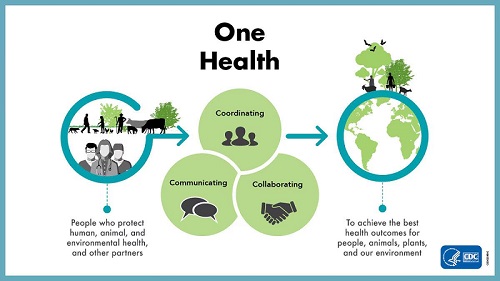
Concept : The One Health approach advocates for a unified framework that considers the interconnections between human, animal, and environmental health. This strategy aims to address the underlying factors that contribute to zoonotic diseases and other health threats by promoting multidisciplinary collaboration.
Components of the One Health Concept : The One Health concept is an interdisciplinary approach that acknowledges the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
Interconnectedness of Health Domains
- Human Health: Human well-being is closely linked to the health of animals and the environment. Diseases can be transmitted between humans and animals, and environmental factors significantly influence health outcomes.
- Animal Health: The health of both domestic and wild animals affects human health through the transmission of zoonotic diseases, which are diseases that can be spread between animals and humans.
- Environmental Health: The state of ecosystems, including air quality, water resources, and biodiversity, directly and indirectly impacts the health of both humans and animals.
COVID-19 Pandemic
- Pandemic Lessons : The global response to COVID-19 focused on virus containment measures such as social distancing, mask-wearing, and vaccine production. However, these strategies overlooked the underlying causes of the pandemic, which are rooted in the human-animal-environment interface. Early warning systems and multidisciplinary stakeholder collaboration could have shed light on the mechanisms of SARS-CoV2 emergence and mitigated speculative analyses about the virus's origin. Integrating a One Health approach into the health security agenda is essential to understand and manage the factors causing zoonotic spillover events.
- The Role of the Pandemic Fund : The Pandemic Fund is a mechanism designed to operationalize the One Health approach by enhancing India’s animal health security and pandemic preparedness. This fund aims to identify and implement actions to control cross-species transmission risks, forming a crucial step toward readiness for future epidemics or pandemics.
The Nipah Virus Outbreak
- Nipah Virus : The ongoing Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala exemplifies the need for a One Health approach to health security. Nipah virus is a highly pathogenic zoonotic virus with significant mortality rates in humans and no available vaccine. Since its first outbreak in Malaysia in 1998, the virus has predominantly affected South and Southeast Asia, with multiple outbreaks in Kerala. Human infection typically occurs through contact with infected fruit bats or contaminated fruit products, or through human-to-human transmission.
- Public Health Response : Kerala’s response to the Nipah outbreak has involved stringent public health measures such as social distancing, mask mandates, containment strategies, and curfews. While these measures help prevent human-to-human transmission, they do not address the root causes of zoonotic diseases. Given the lack of vaccines and effective treatments for Nipah, preventative strategies are critical.
|
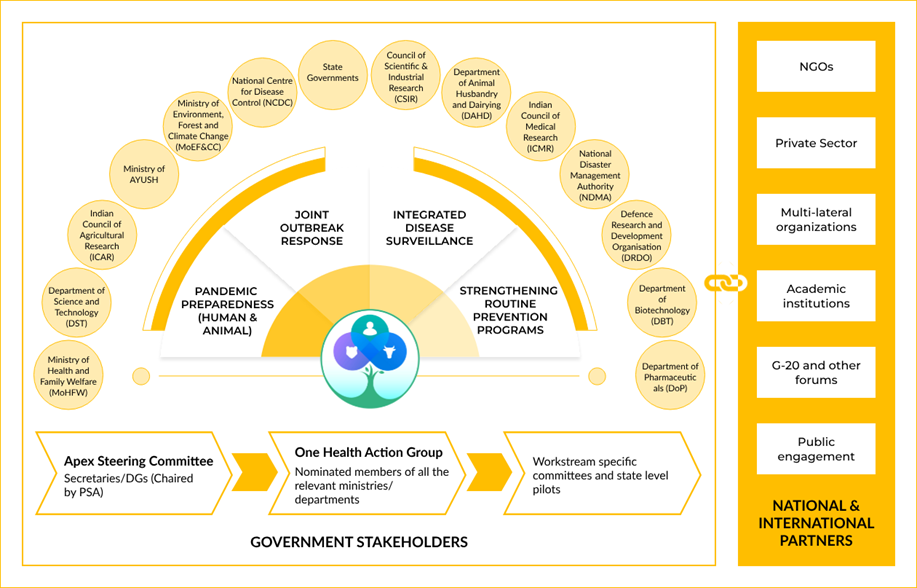
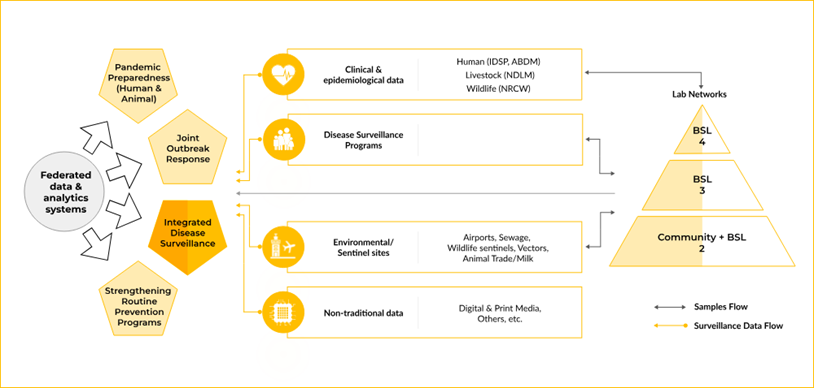
National One Health Mission Set up by the Prime Minister's Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) in July 2022, the National One Health Mission represents a significant step toward a comprehensive approach to health and pandemic preparedness. A key milestone in this mission is the establishment of the National Institute for One Health in Nagpur, which will serve as the central coordinating body for both national and international One Health activities. The Prime Minister laid the foundation stone for this institute on December 11, 2022.
Goals and Strategies of The National One Health Mission
|
One Health Strategies and Initiatives
- An Inclusive Strategy for Surveillance : An effective surveillance system should monitor the Nipah virus within its ecosystem, identify potential intermediate hosts, and understand factors triggering viral spillover events. Anthropogenic activities, such as deforestation and urbanisation, alter bat habitats and increase human-bat interactions, thus enhancing spillover risks. A One Health approach would involve using remote sensing, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and AI tools to assess these drivers and implement strategies to mitigate spillover risks.
- Existing One Health Initiatives : The Quadripartite partnership—comprising the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Health Organisation (WHO), and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)—has launched the One Health Joint Plan of Action. This plan aims to enhance capacity to respond to emerging challenges. Similarly, the CDC in the USA and the UK’s One Health initiative focus on global health security and antimicrobial resistance, respectively. Regional efforts by China and Brazil also contribute to One Health goals through health infrastructure development and vector-borne disease surveillance.
- India’s One Health Efforts : India’s National One Health Mission has held its inaugural executive committee meeting focusing on integrated disease control. The Centre for One Health under the National Centre for Disease Control collaborates with stakeholders to manage zoonotic diseases, demonstrating the country's commitment to a One Health approach.
Conclusion
To effectively address emerging zoonotic diseases, a holistic approach considering the human-animal-ecosystem interface is crucial. Preventative strategies, enabled by a One Health framework, can significantly improve health security. Collaborative efforts through international partnerships, regional initiatives, and national projects will strengthen the approach to combating infectious diseases. India has the opportunity to lead in integrating One Health into its health security agenda, enhancing its preparedness for future health challenges.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains
|
Source: ORF India