Context-
India's Northeast region, known for its cultural diversity and abundant natural resources, holds immense potential for development. However, it lags behind the national average in key human development indices and contributes only a small fraction to India's GDP. To catalyze comprehensive progress, strategic partnerships with global entities are crucial across various domains such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and digital advancements.
|
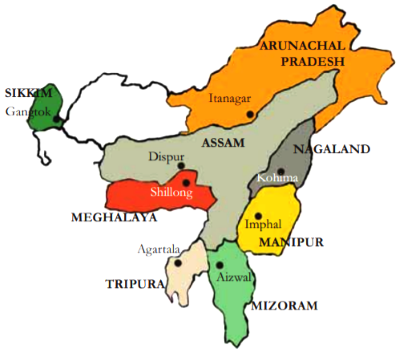
Significance of Northeast India: The Northeast region of India, often referred to as the 'seven sisters', comprises Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura. Sikkim, although part of the Northeast, is distinct due to its geographic separation by the Siliguri Corridor and is considered the 'brother' of the seven states. ● Strategic Location: The region is landlocked and dependent on the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow 21 km strip connecting it to the rest of India. Safeguarding this corridor is crucial for national security, especially during times of conflict. ● Act East Policy: Geographically adjacent to Southeast Asia, particularly Myanmar, the Northeast serves as India's gateway to this region. Strengthening ties with countries like Thailand and Singapore can boost trade and development opportunities. ● Energy Resources: Abundant hydroelectric potential from rivers like the Brahmaputra, along with crude oil reserves (e.g., Digboi oil fields) and recent discoveries of natural gas in the Arakan Basin, make the region significant for energy production. ● Carbon Sink: The dense forest cover in states like Mizoram offers substantial potential for carbon sequestration, aligning with India's commitments under the Paris Agreement. ● Agricultural Resources: The Northeast boasts valuable agricultural products such as Assam tea (a major foreign exchange earner), bamboo for industry, and Mizoram's unique Bird's Eye Chilli with a Geographical Indication (GI) tag. ● Ecotourism and Environment: The region's natural beauty, tribal culture, and diverse ecosystems make it an ideal destination for ecotourism and rural tourism. It offers opportunities for both passive and adventure tourism, including wildlife sanctuaries, waterfalls, and scenic landscapes. |
Education and Vocational Training
Challenges in Higher Education
Despite comparable literacy rates, Northeast India faces challenges in higher education due to limited economic progress and a shortage of skilled labor. The region has only 7% of India's total universities, inhibiting educational opportunities and workforce development.
Partnerships for Curriculum Enhancement
Collaborations with international universities can help align curricula with global industry demands. Enhanced teacher training and skill development programs, facilitated by organizations like USAID, are essential to equip students with relevant skills for the evolving job market.
Virtual Learning and Cross-cultural Exchange
Promoting virtual learning platforms and cross-cultural exchanges broadens educational horizons, retaining students and fostering economic development.
Strengthening Healthcare
Addressing Healthcare Migration
A significant percentage (84%) of the Northeast's population migrates due to inadequate medical facilities. Partnerships with national and international health organizations can facilitate knowledge sharing in critical areas such as public health management and telemedicine.

Capacity Building and Advanced Medical Technology
Collaboration with medical technology firms can enhance access to advanced equipment and diagnostics, improving regional healthcare delivery. Capacity building for medical personnel is essential to meet healthcare demands effectively.
Physical Infrastructure Investments
Connectivity Challenges
Inadequate physical and digital connectivity impedes economic integration. Investments in transportation networks, including roads, railways, waterways, and airports, are crucial to connect cities within the Northeast and neighboring trade centers.
Government Initiatives and Investments
Government initiatives like NESIDS allocate significant budgets to improve road networks and develop renewable energy sources to meet rising energy needs sustainably.
Digitization and Entrepreneurship
Addressing Digital Inclusion
The region's internet subscription rate (43%) is below the national average. Expanding broadband connectivity and promoting digital literacy programs are essential for economic growth.
Promoting Digital Innovation and Startups
Incentives for startups and streamlined regulatory structures encourage innovation. Skilling the workforce in digital technologies through collaborations with global educational institutions fosters entrepreneurship and diversifies the economy.
FDI and Strategic Partnerships
Challenges in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
FDI in Northeast India remains minimal compared to other regions. Enhancing stakeholder involvement and strategic partnerships with global entities like the United States and Japan are vital to attract investments.
Leveraging International Expertise
Think tanks and stakeholders facilitate needs assessments and partnership facilitation, leveraging international expertise to address investment challenges effectively.
Conclusion
Strategic collaborations across education, healthcare, infrastructure, and digital advancements are imperative to bridge developmental disparities in India's Northeast. Partnerships with global stakeholders offer avenues for rejuvenating the region's economy and amplifying its significance within the broader Indo-Pacific narrative. By building a supportive ecosystem and leveraging international expertise, Northeast India can achieve sustainable development and robust economic growth.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam- Question 1: Discuss the strategic significance of the Northeast region of India, highlighting its unique geographic position and its role as a gateway to Southeast Asia. How can strengthening ties with neighboring countries under India's Act East Policy contribute to the economic development of the region? (10 Marks, 150 Words) Question 2: Evaluate the challenges faced by Northeast India in higher education and healthcare sectors despite comparable literacy rates. Suggest strategic measures and international partnerships that can be implemented to address these challenges and foster holistic development in the region. (15 Marks, 250 Words) |
Source- ORF