Context:
Nepal’s Prime Minister, K P Sharma Oli, is scheduled to make his first official visit to China next month, marking a key diplomatic engagement just four months after assuming office. Set for December 2–5, Oli’s visit signifies a notable shift from the traditional practice of Nepali Prime Ministers prioritizing India for their initial international trips. This decision indicates Nepal's efforts to diversify its foreign relations and could reflect a recalibration of its diplomatic stance, especially as it manages relations with its two powerful neighbors, India and China.
- This visit offers an opportunity to understand the broader dynamics between Nepal, India, and China, and explore how Nepal’s growing relationship with China may influence its longstanding ties with India, particularly in critical areas such as trade, political cooperation, security, energy, and cultural exchanges.
Areas of Cooperation between India and Nepal:
Oli’s upcoming visit to China and Nepal’s expanding engagement with Beijing underline the need for India to reinforce and strengthen its relationship with Nepal across various dimensions.
1. Trade and Development
Trade and Investment: India has historically been Nepal’s largest trading partner and its primary source of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). In the fiscal year 2019-20, bilateral trade between India and Nepal reached over USD 7 billion, although there remains a trade deficit favoring India. Nepal’s economic dependency on India presents an opportunity for India to support Nepal in diversifying its exports and fostering economic resilience.
Connectivity and Development Partnership: India has actively contributed to Nepal’s infrastructure development, especially by enhancing connectivity through:
-
- A line of credit amounting to USD 680 million for developing three major transmission corridors in Nepal: the Bheri Corridor, Nijgadh-Inaruwa Corridor, and the Gandak-Nepalgunj Corridor.
- Twin Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) established in 2023 at Rupaidiha in India and Nepalgunj in Nepal to facilitate cross-border trade.
- A revised transit treaty to provide Nepal access to India’s inland waterways, offering cost-effective trade routes for Nepali goods.
- A line of credit amounting to USD 680 million for developing three major transmission corridors in Nepal: the Bheri Corridor, Nijgadh-Inaruwa Corridor, and the Gandak-Nepalgunj Corridor.
Through these initiatives, India aims to strengthen Nepal’s infrastructure and foster mutual development. However, Oli’s visit to China may bring additional Chinese investments, potentially shifting Nepal’s infrastructure priorities toward China.
2. Political and Security Cooperation
Political Cooperation: High-level visits between India and Nepal highlight Nepal’s significance under India’s ‘Neighbourhood First’ policy. Oli’s decision to prioritize China for his initial international visit, however, could indicate a realignment that India may need to address through diplomatic channels.
Defence Cooperation: Defence ties between India and Nepal include:
-
- The recruitment of Nepali soldiers into the Gorkha regiments of the Indian Army.
- Surya Kiran, an annual joint military exercise conducted alternately in each country, strengthening military cooperation and mutual trust.
- The recruitment of Nepali soldiers into the Gorkha regiments of the Indian Army.
Multilateral platforms like BBIN (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Nepal), BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation), and SAARC foster regional cooperation, where both India and Nepal are active participants. Nepal’s recent membership in the International Solar Alliance (ISA), an India-led initiative, also underscores potential areas of collaboration in renewable energy. Oli’s engagement with China, however, may influence Nepal’s alignment in these multilateral settings, especially if it pursues projects under China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) more aggressively.
3. Energy Cooperation
· Power Exchange Agreement: India and Nepal have maintained a Power Exchange Agreement since 1971, helping both nations meet energy demands in border regions. In 2023, India approved Nepal’s first trilateral power trade agreement, enabling Nepal to export 40 megawatts of electricity to Bangladesh via India. This arrangement exemplifies the potential for regional energy cooperation that benefits all three countries.
· Hydropower Cooperation: Hydropower has been a central area of collaboration between India and Nepal. Joint hydropower projects leverage Nepal’s abundant water resources, meeting Nepal’s energy demands and supporting energy exports. These projects carry significant geopolitical value, as India’s support in Nepal’s hydropower sector can be viewed as a counterbalance to China’s infrastructure investments in Nepal.
4. Cultural and People-to-People Ties
· Cultural Exchange: India and Nepal share a deep cultural bond and strong people-to-people connection, particularly in border areas. Cultural initiatives like the Swadesh Darshan scheme’s Buddhist and Ramayana circuits connect religious sites in Nepal, such as Lumbini and Janakpur, with their Indian counterparts, boosting tourism and reinforcing cultural ties.
· Disaster Management: India has also been a vital partner in times of crisis. Following Nepal’s 2015 earthquake, India launched Operation Maitri, delivering immediate relief and assistance. Additionally, during the COVID-19 pandemic, India’s Vaccine Maitri Initiative supplied Covishield vaccines to Nepal, strengthening humanitarian cooperation.
Major Issues in India-Nepal Relations:
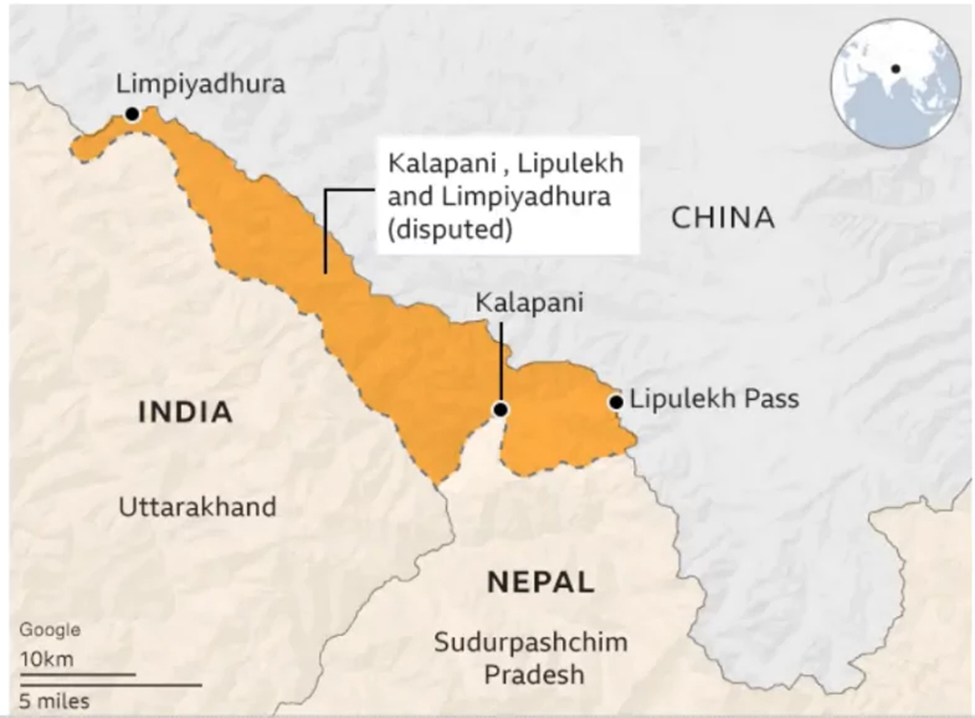
- Border Dispute: Relations between the two countries were strained in 2020 after Nepal published a new political map that included the disputed areas of Limpiyadhura, Kalapani, and Lipulekh as part of its territory. This territorial issue remains unresolved and requires diplomatic efforts to avoid further escalation.
- Chinese Influence: China’s expanding economic engagement with Nepal, including projects under the BRI, poses a strategic challenge for India. China’s increasing political influence in Nepal could lead to a shift in Nepal’s stance on issues traditionally aligned with India, necessitating proactive engagement from India to maintain its position.
- Trust Deficit: Perceptions of India’s slow pace in implementing projects and alleged political interference have contributed to a trust deficit. Addressing these concerns by expediting developmental projects and maintaining respect for Nepal’s sovereignty could help India rebuild trust.
- Security Concerns: The porous India-Nepal border presents a security challenge, allowing for arms smuggling, terrorist activities, and counterfeit currency flow. Enhanced cooperation in border management is crucial to address these security risks.
- Gurkha Recruitment: Recently, Nepal blocked recruitment of Nepalese Gorkhas into the Indian Army, citing that the Agnipath Scheme violates the 1947 Tripartite Agreement. This has added strain to defence ties, necessitating diplomatic dialogue for resolution.
- 1950 Treaty of Peace and Friendship: Nepal has criticized this treaty as outdated, advocating for a revision to reflect current realities. Revisiting the treaty as recommended by the Eminent Persons Group could help reduce tensions and demonstrate India’s respect for Nepal’s autonomy.
Conclusion:
Prime Minister K P Sharma Oli’s upcoming visit to China is indicative of Nepal’s evolving diplomatic approach. While India has traditionally been Nepal’s closest ally, Oli’s focus on China for his first foreign visit suggests a potential shift that India may need to address with a nuanced, strategic response. For India, maintaining strong relations with Nepal amid China’s rising influence requires a comprehensive approach that emphasizes development partnerships, security cooperation, and cultural connections. As neighbors with intertwined histories and shared interests, both countries stand to benefit from sustained dialogue, mutual trust, and collaborative efforts that support shared prosperity and regional stability.
|
Probable questions for UPSC Mains exam: Analyze the economic dimensions of India-Nepal relations, focusing on trade, investment, and connectivity infrastructure. How Nepal’s deepening engagement with China might impact India’s development projects and economic ties in Nepal? |







