Context:
World Mental Health Day is celebrated on October 10, 2024.
According to the World Health Organization, depression and anxiety alone result in a loss of approximately 12 billion workdays each year. Addressing the mental health issues of employees is imperative for organizations, as these issues can lead to decreased performance, increased absenteeism, and higher staff turnover. Employee satisfaction and productivity are closely linked; therefore, creating a healthier workspace and implementing measures to alleviate stress is crucial. This year, World Mental Health Day emphasizes "Mental Health at Work," highlighting the need for organizations to focus on mental well-being in the workplace. Since 60% of the world’s population works in some form, it’s important to create safe and supportive workplaces.
World Mental Health Day, observed annually on October 10, was initiated by the World Federation for Mental Health in 1992 to raise awareness about mental health and support efforts to improve care.
Mental health in India:
India, with one of the largest populations in the world, faces unique challenges in addressing mental health issues. The country has a history of underfunded mental health services and significant stigma surrounding mental illness. However, recent developments indicate a positive shift toward improving mental health care infrastructure and policies.
Economic Survey 2023-24:
- For the first time, the Economic Survey 2023-24, presented by Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman on July 22, 2024, emphasized mental health as a crucial driver of both individual and national development. Key findings from the survey include:
- Prevalence of Mental Disorders: According to the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) 2015-16, approximately 10.6% of adults in India suffer from mental disorders, with a staggering treatment gap ranging from 70% to 92% for various conditions.
- Urban vs. Rural Mental Health: The survey indicates that the prevalence of mental morbidity is higher in urban metro regions (13.5%) compared to rural areas (6.9%) and urban non-metro areas (4.3%).
- Adolescent Mental Health: Citing the NCERT’s Mental Health and Well-being of School Students Survey, the Economic Survey highlights an alarming trend of declining mental health among adolescents, particularly exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings show that 11% of students reported feelings of anxiety, 14% experienced extreme emotions, and 43% reported mood swings.
Economic Impact of Mental Health
The survey further outlines the economic implications of mental health disorders, which are associated with:
Productivity Losses: Mental health issues lead to significant productivity losses due to absenteeism, decreased work performance, disability, and increased healthcare costs.
Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty exacerbates mental health risks through stressful living conditions, financial instability, and limited opportunities for upward mobility, contributing to increased psychological distress.
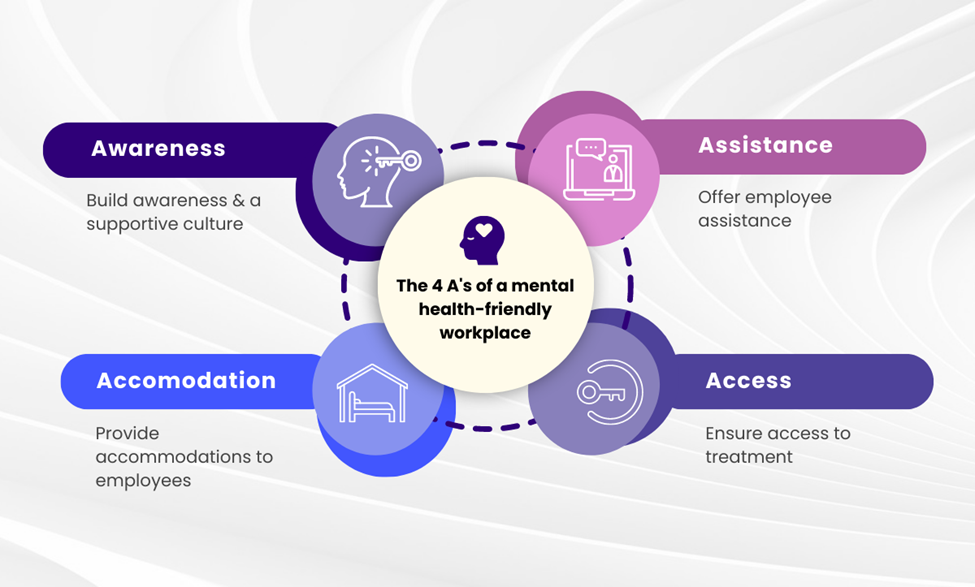
Mental Health and Work: Policy and Social Perspective:
- Role of Employers and Government: Employers and governments must collaborate to create mentally healthy work environments. This includes enforcing labor laws, implementing workplace mental health programs, and ensuring safe and inclusive conditions. Initiatives aimed at preventing burnout, reducing workplace stress, and supporting employees with mental health challenges are vital for promoting well-being at work.
- Social Justice and Vulnerable Groups: Vulnerable groups, such as those in low-paid, insecure jobs, are disproportionately affected by mental health issues. Public policies need to address these inequities by offering protections and resources to those most at risk. This emphasizes the role of mental health in achieving broader goals of social justice and equality, ensuring that all individuals have access to mental health services regardless of socioeconomic status.
- Stigma as a Social Challenge: Stigma around mental health remains a significant barrier to seeking help and maintaining employment. Reducing stigma through awareness programs, training, and inclusive policies is critical for fostering supportive work environments. This also plays a role in broader societal inclusion, as addressing mental health stigma promotes acceptance and well-being.
- Supporting Workers to Thrive: Ensuring reasonable workplace accommodations for employees with mental health conditions is essential. Employers can support workers by offering regular check-ins, breaks, and gradual reintroduction to tasks. Such measures help employees manage their conditions while remaining productive, contributing to their overall well-being and job satisfaction.
- Government Action and Collaboration: Collaborative efforts between governments, employers, and civil society organizations are essential to create policies that promote mental well-being and protect against risks. By working together, these stakeholders can ensure that workplaces prioritize mental health and foster environments that support individuals in thriving both personally and professionally.
Key Initiatives by Government:
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP): The NMHP aims to provide mental health services across the country. One of its main components is the District Mental Health Programme (DMHP), which has been rolled out in 767 districts. This program focuses on suicide prevention, workplace stress management, life skills training, and counseling for schools and colleges.
- Facility Enhancements: Services include outpatient counseling, psycho-social interventions, and a 10-bed inpatient facility at the district level. Over 1.73 lakh Sub Health Centres (SHCs) and Primary Health Centres (PHCs) have been upgraded to Ayushman Arogya Mandirs, integrating mental health services into their care packages.
- National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP): Launched on October 10, 2022, the NTMHP aims to improve access to quality mental health counseling and care. Currently, 53 Tele MANAS Cells are operational across 36 states and union territories, having handled over 14.5 lakh calls as of October 08, 2024.
- Strengthening Mental Health Resources: The government is also focused on increasing the number of mental health professionals, with plans to raise the psychiatrist ratio from 0.75 psychiatrists per lakh population in 2021 to the WHO norm of 3 per lakh population.
Conclusion:
World Mental Health Day highlights the importance of mental health care in both personal and professional life. With mental health and work closely connected, governments, employers, and stakeholders must create supportive, inclusive environments. While global initiatives like those from WHO and WFMH are advancing, more work is needed to raise awareness, reduce stigma, and improve access to services. India's efforts to address mental health challenges through policies and programs are commendable, but ongoing collaboration is crucial to ensure accessible, stigma-free care that allows everyone to thrive in both work and life.
|
Probable questions for UPSC Mains exam: Evaluate the challenges faced by India in addressing mental health issues. How do socioeconomic factors contribute to the mental health crisis in the country? |
Source: PIB







