Introduction
Lifestyle diseases, also known as Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs), are caused by unhealthy living habits such as poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, and substance abuse. These conditions are a leading cause of death worldwide, with India facing a significant burden. Diabetes, a prominent lifestyle disease, reflects the country’s growing health crisis.
What Are Lifestyle Diseases?
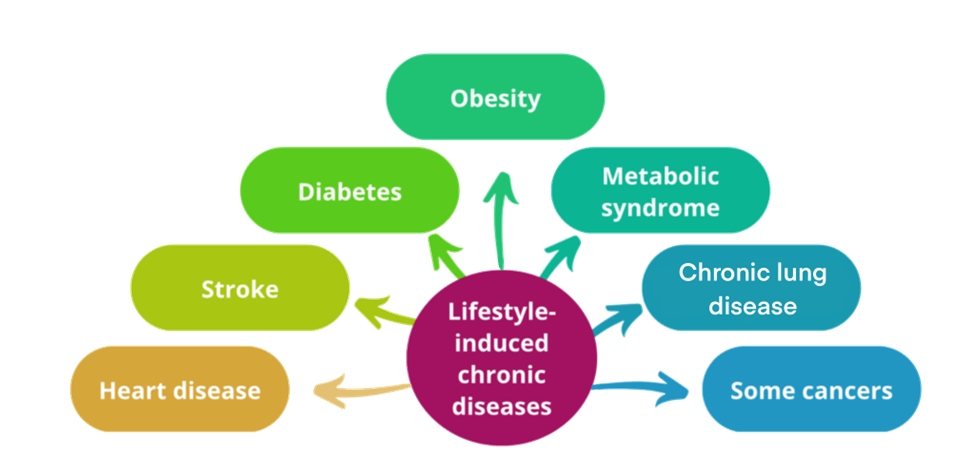
Lifestyle diseases are health conditions stemming from the way people live their lives. They often develop over time and are preventable with conscious changes in habits. Common examples include:
1. Diabetes: A condition that affects how the body processes glucose.
2. Cardiovascular Diseases: Such as heart attacks and strokes.
3. Obesity: Excessive body fat accumulation.
4. Respiratory Issues: Often caused by smoking.
5. Mental Health Disorders: Linked to chronic stress and substance abuse.
As per a World Health Organization (WHO) report, lifestyle diseases in India account for 6 million deaths annually, and it is estimated that chronic illnesses could cost the country $6 trillion by 2030.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition where the body’s ability to process blood sugar (glucose) is impaired. Glucose is the primary source of energy, and insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate its levels. Diabetes occurs when:
1. The pancreas produces insufficient insulin.
2. The body cannot effectively use the insulin produced.
If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, vision loss, and nerve damage. India is referred to as the Diabetes Capital of the World, with over 10.1 crore people affected as per the 2023 ICMR INDIAB study.
- By 2030, this number is expected to increase significantly, driven by urbanization and unhealthy lifestyles.
- WHO estimates show that 14% of Indian adults live with diabetes.
- Diabetes is the primary contributor to kidney failure, cardiovascular diseases, and amputations caused by nerve damage.
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
o An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
o Requires lifelong insulin therapy.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
o A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it.
o Linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, obesity, and inactivity.
3. Gestational Diabetes
o Temporary diabetes that occurs during pregnancy.
o Increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
4. Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) and Impaired Fasting Glycaemia (IFG)
o Pre-diabetic stages where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes symptoms vary based on type and severity but may include:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination.
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds and frequent infections.
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet.
Preventing Diabetes and Lifestyle Diseases
The key to combating diabetes and lifestyle diseases lies in prevention. Steps include:
1. Healthy Eating: Avoid processed foods and excess sugar while focusing on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
2. Physical Activity: Engage in at least 30 minutes of exercise daily to maintain healthy weight and insulin sensitivity.
3. Regular Check-ups: Monitor blood sugar levels regularly to detect and manage diabetes early.
4. Stress Management: Practice yoga, meditation, or other relaxation techniques to reduce stress-related risks.
5. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Both are significant risk factors for diabetes and other lifestyle diseases.
World Diabetes Day 2024: Breaking Barriers, Bridging Gaps
Observed annually on November 14, World Diabetes Day focuses on raising awareness about the prevention, treatment, and management of diabetes. The 2024 theme, “Breaking Barriers, Bridging Gaps,” aims to ensure high-quality and affordable diabetes care, particularly for underserved populations.
Government Initiatives to Combat Diabetes
India’s government has launched several programs to address the rising burden of diabetes and other NCDs:
1. National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD): Focuses on early detection and management through health centers and screenings.
2. Fit India Movement: Encourages active living and fitness to combat sedentary lifestyles.
3. Free Drugs Service Initiative and PMBJP (Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana): Provide affordable insulin and medications for diabetes.
4. Ayushman Bharat Scheme: Strengthens healthcare delivery for all, especially low-income households.
WHO Response
WHO aims to encourage and support the adoption of effective methods for the surveillance, prevention and control of diabetes and its complications, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. To this end, WHO:
· provides scientific guidelines for the prevention of major noncommunicable diseases including diabetes;
· develops norms and standards for diabetes diagnosis and care;
· builds awareness on the global epidemic of diabetes, marking World Diabetes Day (14 November); and
· Conducts surveillance of diabetes and its risk factors.
In April 2021 WHO launched the Global Diabetes Compact, a global initiative aiming for sustained improvements in diabetes prevention and care, with a particular focus on supporting low- and middle-income countries.
In May 2021, the World Health Assembly agreed a Resolution on strengthening prevention and control of diabetes. In May 2022 the World Health Assembly endorsed five global diabetes coverage targets to be achieved by 2030.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of diabetes and other lifestyle diseases in India highlights the urgent need for preventive measures, healthcare reforms, and public awareness campaigns. By adopting a proactive approach involving individuals, healthcare providers, and policymakers, India can effectively combat lifestyle diseases, ensuring a healthier and more productive future.
Key Takeaways for UPSC Aspirants
· Lifestyle Diseases: Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity are preventable and linked to unhealthy habits like poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress.
· Diabetes in India: India has over 10.1 crore diabetes cases, expected to rise, with major health complications like kidney failure and heart disease.
· Types of Diabetes: Type 1 (autoimmune), Type 2 (insulin resistance, lifestyle factors), Gestational (during pregnancy), and pre-diabetic stages (IGT, IFG).
· World Diabetes Day 2024: Theme “Breaking Barriers, Bridging Gaps” promotes affordable diabetes care for underserved populations.
· Prevention: Healthy eating, regular exercise, stress management, avoiding smoking/alcohol, and regular check-ups.
· Government & WHO Actions: India’s NP-NCD and Fit India programs, WHO’s Global Diabetes Compact focus on prevention and care.
|
Potential UPSC Mains Question Critically evaluate the role of government initiatives like the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD) in combating lifestyle diseases in India. |








