Context:
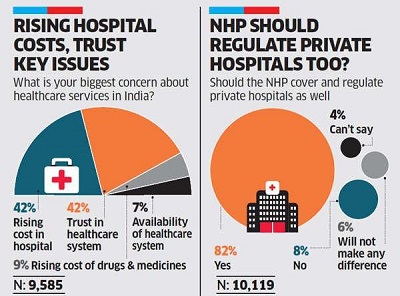
An audit of 100 consent documents from different hospitals revealed that almost all the documents lacked around one-third of the essential medical information they needed.
Informed Consent: A Crucial Component
Informed consent is considered the cornerstone of a doctor-patient relationship, yet it is often neglected in practice. Informed consent means that a patient needs to be given all the information regarding their condition, treatment options, procedure steps, and possible complications. This information allows the patient to make a well-informed decision about their treatment.
Personal Experience: A Case Study
In April, a popular private hospital in Guwahati faced scrutiny when a patient's relative, accompanying his father-in-law who needed treatment for a pleural effusion, was asked by a nurse to sign an unfilled consent form. This incident highlights a common issue in India where consent is often obtained improperly. Consent should be taken by the doctor performing the procedure and explained clearly to the patient before obtaining their signature.
Challenges in Informed Consent in India
- Inadequate Consent Process in India
- Studies reveal gross inadequacies in the process of obtaining consent from patients in India. For instance, a 2015 study published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology India found that while 75% of women who underwent caesarean sections were informed why they needed the surgery, only 25% were told about the procedure steps and potential complications.
- Similarly, a 2019 study in the Journal of Medical Society audited 100 consent documents and found that almost all lacked about one-third of the essential medical information.
- Studies reveal gross inadequacies in the process of obtaining consent from patients in India. For instance, a 2015 study published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology India found that while 75% of women who underwent caesarean sections were informed why they needed the surgery, only 25% were told about the procedure steps and potential complications.
- Issues in Biomedical Research
- Informed consent is crucial in biomedical research. A 2023 study in Perspectives in Clinical Research found that out of 44 online surveys audited, 10 lacked informed consent forms entirely, and the remaining 34 had incomplete or non-adherent forms according to ICMR guidelines.
- Informed consent is crucial in biomedical research. A 2023 study in Perspectives in Clinical Research found that out of 44 online surveys audited, 10 lacked informed consent forms entirely, and the remaining 34 had incomplete or non-adherent forms according to ICMR guidelines.
- Legal and Ethical Importance
- K. Mathiharan, a forensic medicine and medical law expert, emphasizes the legal significance of informed consent. A signed consent form proves that the patient was counseled about complications and consented to the procedure with full knowledge. However, a signature alone does not guarantee that the information was communicated.
- K. Mathiharan, a forensic medicine and medical law expert, emphasizes the legal significance of informed consent. A signed consent form proves that the patient was counseled about complications and consented to the procedure with full knowledge. However, a signature alone does not guarantee that the information was communicated.
- Barriers to Proper Consent
- Language barriers and literacy issues often hinder the informed consent process. Many consent forms are in English, making them inaccessible to non-English speakers who rely on doctors or nurses to explain the content.
- Language barriers and literacy issues often hinder the informed consent process. Many consent forms are in English, making them inaccessible to non-English speakers who rely on doctors or nurses to explain the content.
- Real-World Consequences
- Inadequate informed consent can lead to patients unknowingly signing forms that state they left the hospital against medical advice, as observed by a duty doctor in Satribari Christian Hospital, Guwahati. This practice underscores the need for better consent procedures.
- Inadequate informed consent can lead to patients unknowingly signing forms that state they left the hospital against medical advice, as observed by a duty doctor in Satribari Christian Hospital, Guwahati. This practice underscores the need for better consent procedures.
|
Types of Consent in Medicine
|
Importance of Informed Consent
- Ensuring Best Possible Outcomes
- Proper informed consent improves patient satisfaction and treatment outcomes. It also fosters shared decision-making, where patients and doctors collaborate to ensure the best possible outcome while considering patient preferences.
- Proper informed consent improves patient satisfaction and treatment outcomes. It also fosters shared decision-making, where patients and doctors collaborate to ensure the best possible outcome while considering patient preferences.
- Protecting Healthcare Providers
- Effective informed consent protects doctors by demonstrating that patients were informed about potential complications. In India, where distrust of doctors has led to violence, building rapport and trust through detailed communication is crucial.
- Effective informed consent protects doctors by demonstrating that patients were informed about potential complications. In India, where distrust of doctors has led to violence, building rapport and trust through detailed communication is crucial.
- A Moral Imperative
- Informed consent is a moral imperative, especially in cases where the loss of life or organs is involved. Patients deserve to know what is happening to their bodies and the potential consequences of treatments or procedures.
- Informed consent is a moral imperative, especially in cases where the loss of life or organs is involved. Patients deserve to know what is happening to their bodies and the potential consequences of treatments or procedures.
- Raising Patient Awareness
- Patients should be aware of their right to information and should not sign consent forms without understanding their content. Hospitals should provide forms in local languages and use image or video-based tools to enhance understanding.
- Patients should be aware of their right to information and should not sign consent forms without understanding their content. Hospitals should provide forms in local languages and use image or video-based tools to enhance understanding.
- Informed Consent for Blood Transfusion
- Infections or contamination from transfusions can lead to severe complications, including bacterial or viral infections such as hepatitis or HIV. Proper screening and handling procedures are crucial to minimize these risks in blood transfusion practices.
- Infections or contamination from transfusions can lead to severe complications, including bacterial or viral infections such as hepatitis or HIV. Proper screening and handling procedures are crucial to minimize these risks in blood transfusion practices.

Steps to Obtain Informed Consent in Healthcare
- Patient Assessment: Determine the patient's capacity to understand and make decisions about their healthcare. This includes evaluating their mental status, language comprehension, and cognitive ability.
- Information Disclosure: Provide comprehensive information about the patient's condition, treatment options, the procedure itself, potential risks and benefits, possible complications, and alternatives. This information should be presented in a clear, understandable language suitable for the patient’s level of comprehension.
- Discussion and Questions: Engage in a dialogue with the patient, allowing them to ask questions and express concerns. This interaction ensures that the patient fully understands the information provided.
- Documentation: Use a consent form that includes all relevant information about the procedure or treatment. The form should be in the patient’s preferred language, if possible, and written in a manner that is easy to understand.
- Signature and Witnessing: Obtain the patient's signature on the consent form after they have confirmed their understanding and willingness to proceed. The process should be witnessed by a healthcare professional who can verify that informed consent was properly obtained.
- Review and Update: Review the consent process periodically, especially if there are changes in the patient's condition or treatment plan. Ensure that the patient remains informed and consents to any new procedures or modifications to their care.
- Shared Decision Making in Emergency Medicine: Informed consent involves collaborative decision-making between patients and providers, crucial for assessing risks and benefits of procedures like CT scans and thrombolytics. Challenges include patient engagement, legal concerns, time constraints, and lack of validated tools.
Conclusion
India's informed consent process needs significant improvement. By prioritizing patient education, ensuring clear communication, and adopting innovative tools, healthcare providers can uphold the ethical standards of informed consent and enhance patient trust and safety. Additionally, all healthcare team members involved in patient care should understand the procedures and interventions, as they may serve as witnesses in the informed consent process. This ensures that all necessary information is communicated effectively and that any omissions by the primary provider are addressed.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam-
|
Source: The Hindu