Context-
Recent statements on redistribution contrasted with a polarizing rebuttal from political leadership, have brought the issue of inequality to the forefront.
Defining Inequality
The United Nations describes inequality as “the state of not being equal, especially in
status, rights, and opportunities”.
Economic inequality is the unequal distribution of income. Social inequality is the uneven distribution of resources based on societal norms. These types are interconnected; for instance, gender inequality affects women's income
|
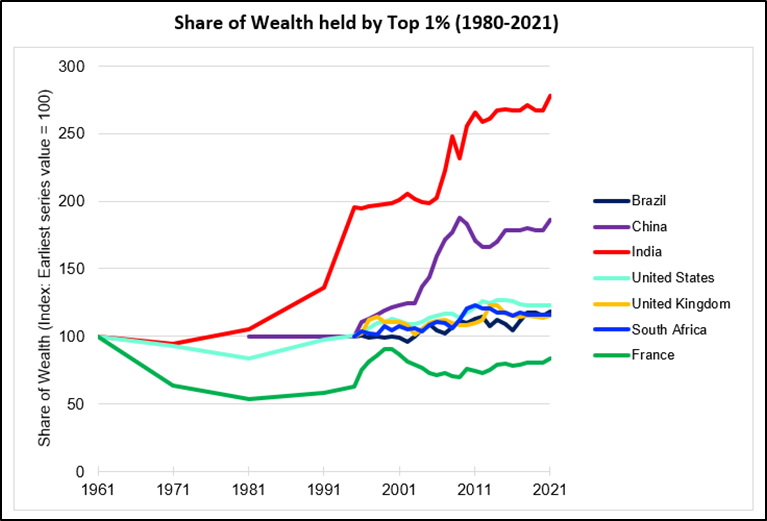
Status of Inequality in India
|
Inequality's Impact on Democracy and Growth
- Democratic Processes : There is a school of thought that argues inequality harms democratic processes. The argument here is that significant disparities in wealth can lead to disproportionate influence over political and economic systems by the wealthy, undermining democratic ideals and fairness.
- Incentives for Entrepreneurship : Conversely, some argue that a certain degree of inequality is beneficial. This perspective posits that inequality incentivizes entrepreneurs to start businesses, thus boosting employment and overall welfare. The underlying belief is that the prospect of wealth accumulation drives innovation and economic dynamism.
The Negative Economic Effects of Inequality
However, this optimistic view of inequality as a growth driver needs to be revised. Inequality can lead to several negative economic outcomes, particularly when it results in the concentration of monopoly power.
- Monopoly Power and Its Consequences : Billionaires often accumulate their wealth through monopolistic practices. Dominant business groups can set prices, deviating from market-determined levels. This leads to higher mark-ups above production costs, reducing real wages for the broader population.
● Greedflation and the Cost-of-Living Crisis : The developed economies are currently experiencing these monopoly effects in the form of cost-of-living crises. The phenomenon of “greedflation,” where companies raise prices to increase profit margins amidst demand-and-supply shocks, has been a significant contributor to high inflation rates in the West. Basic economic principles indicate that monopolies produce lower output levels than competitive markets, leading to welfare losses. Thus, monopolies result in lower real wages, reduced output, and diminished investment levels.
Inequality's Effect on Economic Growth
- The Multiplier Effect : Consider the scenario where a company decides to establish a new factory. Before the capital stock is created, workers are paid wages to build it. These wages are spent on goods, increasing the incomes of goods-sellers, who in turn spend on other goods, creating a multiplier effect. This process ensures that the total increase in incomes exceeds the initial investment.
- Impact of Market Power : However, in a market dominated by monopolies, mark-ups and prices are higher, resulting in lower real wages. Consequently, workers can purchase fewer goods. Despite this, companies maintain their profit levels due to higher margins from selling fewer goods. The overall increase in income from a given investment is reduced under monopoly conditions because of decreased consumption power. Therefore, investment has a weaker impact on growth in a monopolistic economy while profits remain unaffected.
- Consumption Patterns of the Rich vs. Poor : While the rich consume more in absolute terms, they spend a smaller proportion of their incomes compared to the poor. The effectiveness of the multiplier process depends significantly on the proportion of income spent on consumption. In an unequal economy, higher incomes are concentrated in the hands of those with a lower propensity to consume, leading to weaker economic expansion.
Redistribution and Economic Growth
- Arguments Against Redistribution : Some argue that redistribution could harm economic growth by reducing incentives for wealth accumulation, which in turn might affect job creation. The concern is that high taxes could deter entrepreneurs from investing, thereby stifling economic activity and job growth.
- Distinguishing Wealth and Profits : However, it is essential to distinguish between wealth and profits. Investment decisions are influenced by expectations of future profits, not by past wealth accumulation. Polish economist Michal Kalecki argued that taxes on wealth would not impact investment because they do not alter future profit expectations. For instance, taxing the wealth of a billionaire like Gautam Adani would not affect investment in infrastructure, as the expected profits from such projects depend on demand rather than the value of Adani's existing wealth.
- Redistribution as a Growth Driver : While some business owners might hesitate to invest if converting profits into wealth becomes difficult, an economy with high profit expectations will still attract investment despite wealth taxes. Redistribution can enhance economic growth by strengthening the multiplier effect. If wealth is redistributed, increasing income levels, the multiplier process becomes more robust. Businesses are more likely to invest in an economy where purchasing power is strong. Additionally, curtailing monopolies can lower prices and increase real wages, boosting demand.
|
Causes of Increasing Inequality in India
|
Policy Proposals
- Progressive Taxation: Economist Thomas Piketty has proposed taxing billionaire wealth to fund a basic income. While this might drive some wealthy individuals out of the economy, it could also foster a new class of entrepreneurs.
- Implement land reforms to ensure fair and equitable distribution of land resources
- Promote inclusive governance by encouraging citizen participation, transparency, and reducing corruption.
- Encourage corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives focusing on inclusive development.
- Prioritize labor-intensive manufacturing to boost job creation, even for domestic consumption.
- Green Manufacturing: Explore sustainable development through green manufacturing opportunities.
- Tackle structural issues related to caste, gender, and religion to ensure equitable growth benefits.
- Ensure universal access to quality public services, including healthcare, education, social security, and employment guarantee schemes, to significantly reduce inequality.
- Balancing Redistribution: Redistribution is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Excessively high tax rates can become a net drain on the economy. Therefore, redistribution policies need to be balanced and implemented alongside other measures to ensure a healthy economic environment.
Conclusion
The debate over inequality and its impact on economic growth is multifaceted. While some inequality can incentivize entrepreneurship, excessive inequality particularly when it results in monopolistic practices can have deleterious effects on economic growth and democratic processes. Redistribution, if done correctly, can enhance economic growth by strengthening the multiplier effect and increasing purchasing power. Thus, carefully crafted policies aimed at reducing inequality can lead to a healthier and more robust economy.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam-
|
Source- The Hindu







