India's journey into space exploration, led by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), is a remarkable tale of innovation and ambition. From launching satellites to exploring interplanetary frontiers, ISRO has continuously pushed boundaries, cementing India’s position as a global leader in space technology. The upcoming Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) is a game-changer, poised to redefine how India approaches space missions.
ISRO’s Vision for Space Exploration
India’s space program has grown from its initial focus on communication satellites to encompass ambitious missions aimed at deep space exploration. ISRO's vision includes:
- Human Spaceflight Missions: The Gaganyaan mission aims to send Indian astronauts into space, marking a historic milestone.
- Lunar and Mars Exploration: Successful missions like Chandrayaan-1 and Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) have set the stage for more complex lunar and interplanetary projects.
- Interplanetary Missions: Future missions to Venus, Mars, and beyond highlight ISRO’s growing expertise in interplanetary exploration.
- Space Station Development: Plans for an Indian Space Station reflect the nation’s aspiration to achieve self-reliance in space-based research and technology.
These initiatives demand advanced launch systems like the NGLV to support heavier payloads and cost-efficient operations.
What is the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)?
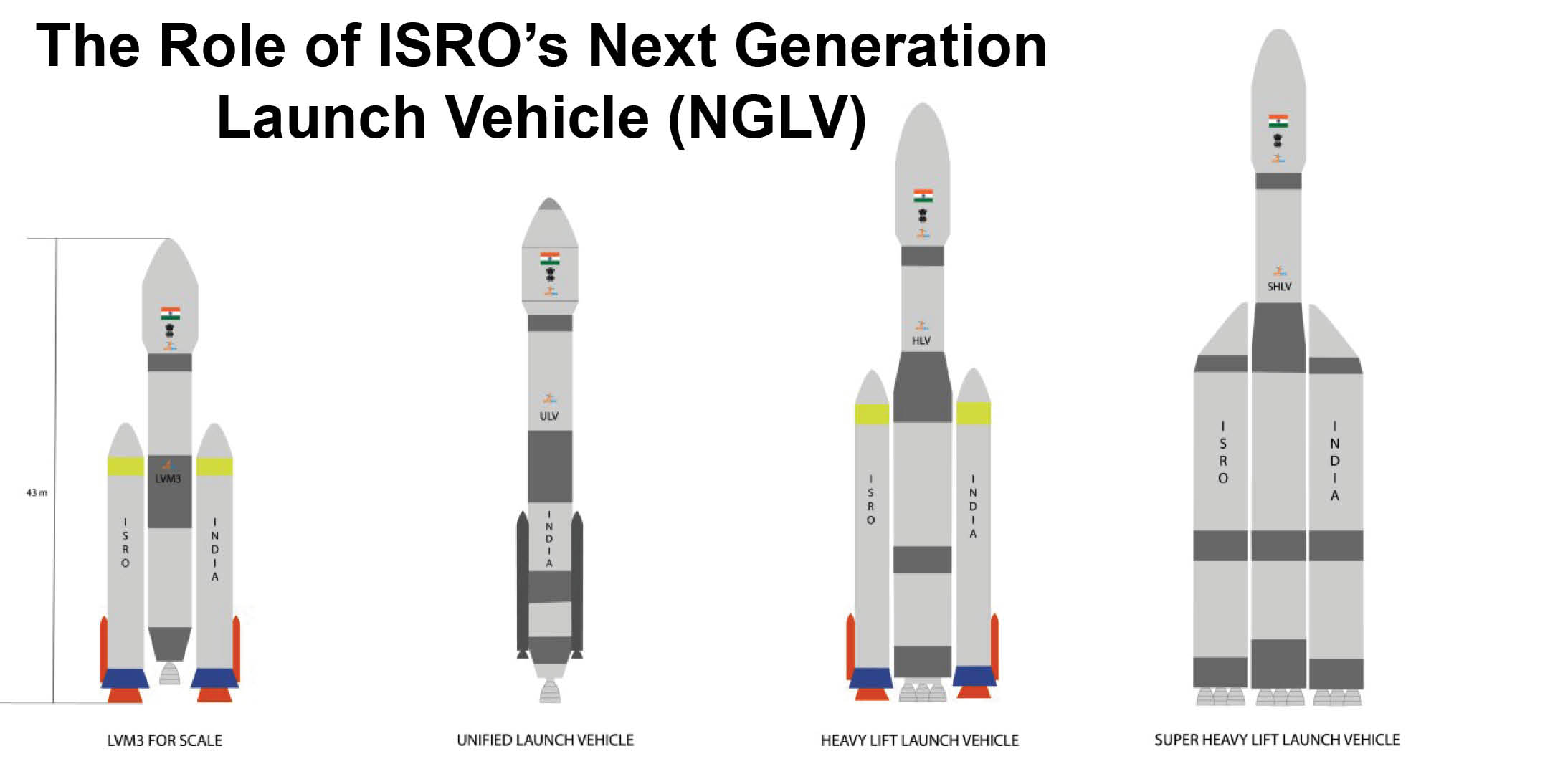
The Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) is ISRO's response to the evolving needs of space exploration and satellite deployment. Designed as a reusable, heavy-lift rocket, the NGLV will serve as a cornerstone for future missions.
Key Features of NGLV
1. Reusable Design: The NGLV will feature a reusable design, significantly reducing costs per mission.
2. Semi-Cryogenic Propulsion: Using refined kerosene as fuel and liquid oxygen (LOX) as an oxidizer, the propulsion system enhances efficiency and performance.
3. Heavy Payload Capacity: The rocket is capable of carrying up to 10 tonnes to Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO), making it suitable for diverse missions.
4. Modular Structure: Its modular architecture enables bulk manufacturing and quicker turnaround between launches.
Applications of NGLV
The versatility of the NGLV opens doors to:
- Satellite Deployment: Supporting global satellite launches for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Deep Space Exploration: Essential for missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
- Human Spaceflight: A key enabler for India’s manned missions, including Gaganyaan.
- Space Cargo Transport: Facilitating cargo supply to space stations and other orbital platforms.
ISRO’s Evolution in Launch Vehicle Technology
Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV)
ISRO’s first launch vehicle, the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV), carried small payloads into Low Earth Orbit (LEO). While basic in its capabilities, it was a significant milestone for India.
Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV)
The ASLV improved upon the SLV, capable of carrying payloads up to 150 kg. Its design laid the foundation for future advancements in launch vehicle technology.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), first launched in 1994, became ISRO’s workhorse. Key achievements include:
- Launching Chandrayaan-1 (India’s first lunar probe) in 2008.
- Deploying the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) in 2013, making India the first country to reach Mars on its maiden attempt.
- Setting a global record by launching 104 satellites in a single mission.
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
The GSLV is a more powerful rocket, designed for missions involving geostationary satellites. The Mk III variant, equipped with an indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS), can carry heavier payloads, ensuring India’s self-sufficiency in satellite launches.

Why India Needs the NGLV?
· The increasing demand for satellite launches, interplanetary exploration, and commercial space opportunities underscores the need for a versatile, heavy-lift launch vehicle. While the PSLV and GSLV Mk III have served well, their payload capacities are limited compared to the growing needs of modern space missions.
· The NGLV will not only enhance India’s capability to launch heavier satellites but also reduce operational costs through its reusable design. Additionally, its capacity to support human and cargo missions will play a pivotal role in the Gaganyaan mission and the proposed Indian space station.
Private Sector Collaboration in Space Exploration
· India’s space ecosystem is witnessing a surge in private sector involvement. Startups like Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos are contributing innovative solutions for launch vehicles and space technology. ISRO’s focus on public-private partnerships will accelerate the development of reusable rockets like the NGLV.
· Government initiatives such as the creation of Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) provide a platform for private companies to participate in building a robust space economy.
International Collaboration and Market Potential
· The NGLV’s competitive pricing and reusable design will position India as a leader in the global satellite launch market. With the increasing demand for commercial satellite launches, ISRO’s expertise in cost-effective solutions can attract international clients, boosting India’s space economy.
· By partnering with space agencies worldwide, ISRO can also leverage international expertise in advancing reusable rocket technologies.
Future Missions Enabled by the NGLV
The capabilities of the NGLV are aligned with India’s long-term goals in space exploration, including:
- Lunar Bases: Supporting construction of habitats on the Moon.
- Interplanetary Exploration: Missions to Mars, Venus, and beyond.
- Space Station Operations: Transporting astronauts and cargo to India’s future space station.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Technical Challenges
- Developing efficient reusable propulsion systems.
- Ensuring reliability and safety for human spaceflight missions.
Financial Investments
Space exploration is capital-intensive. Increased funding from both government and private sectors will be crucial for achieving long-term goals.
Global Competition
With countries like the United States (SpaceX) and China advancing their reusable rocket technologies, India must innovate rapidly to stay competitive.
Conclusion
The Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV) represents a significant leap forward in India’s space exploration capabilities. With its reusable design, heavy-lift capacity, and cost efficiency, the NGLV is set to transform India’s role in global space exploration. As ISRO works towards ambitious goals like human spaceflight, interplanetary missions, and the establishment of a space station, the NGLV will be a cornerstone of these efforts. Coupled with increased private sector participation and global collaboration, India is well on its way to becoming a leading player in the next era of space exploration. By combining technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and efficient execution, the Next Generation Launch Vehicle will not only bolster India’s space economy but also inspire the next generation of space scientists and enthusiasts.
|
Probable questions for UPSC Mains exam: India’s space program has evolved significantly from the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) to the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV). Highlight the key milestones in this evolution and their implications for India’s global space standing. |