Date : 26/08/2023
Relevance: GS Paper 2 - international relations - Global politics and policies affecting India's interest
Keywords: Arctic region, Northern Sea Route (NSR), Cargo traffic, Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC), Climate change impact
Context-
- The Arctic region, with its remote landscapes and icy expanses, has become an arena of growing interest for nations across the globe. In recent times, India's involvement in cargo traffic through Murmansk, the beginning point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), has been gaining momentum.
- This article delves into the various dimensions of India's engagement with the Arctic, the significance of the Arctic region for India's interests, and the intricate interplay between the NSR and India's maritime strategies.
Arctic Significance for India
- The Arctic, situated above the Arctic Circle and encompassing the Arctic Ocean with the North Pole at its epicenter, holds immense significance for India.
- Climate change-induced alterations in the Arctic climate can have cascading effects on India's economic security, water security, and overall sustainability.
- The melting ice caps and shifting weather patterns could disrupt established trade routes, impacting global trade flows and potentially affecting India's maritime trade.
- Additionally, the Arctic region presents a treasure trove of untapped resources. It is estimated that the region holds over 40% of the world's current reserves of oil and gas, along with potential reserves of coal, zinc, and silver.
- Despite this wealth of resources, India's approach to Arctic economic development is aligned with the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, reflecting a commitment to responsible resource utilization.
India's Historical Arctic Engagement
- India's engagement with the Arctic dates back to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920, a significant milestone that laid the foundation for India's scientific pursuits in the region.
- Over the years, India has undertaken diverse scientific studies and research activities spanning atmospheric, biological, marine, hydrological, and glaciological domains.
- The establishment of the research station "Himadri" at Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard, in 2008 marked India's tangible presence in the Arctic research landscape.
- In subsequent years, India's commitment to Arctic research grew stronger with the launch of a multi-sensor moored observatory in 2014 and a northernmost atmospheric laboratory in 2016.
- This scientific exploration culminated in India's status as an observer state of the Arctic Council in 2013, a position shared with five other nations, including China.
Unveiling the Northern Sea Route (NSR)
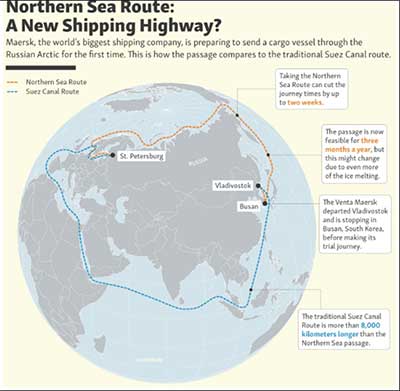
- The Northern Sea Route (NSR) stands as a pivotal focal point in India's Arctic engagement. This route, spanning 5,600 km, emerges as the shortest shipping passage connecting Europe with the Asia-Pacific region.
- It traverses four Arctic Ocean seas, commencing at the boundary between the Barents and Kara seas and culminating in the Bering Strait.
- The NSR's allure stems from its potential to drastically reduce shipping distances, offering as much as a 50% reduction in comparison to the traditional Suez or Panama routes. The 2021 Suez Canal blockage heightened interest in the NSR, underscoring the need for alternative, reliable maritime pathways.
Russia's Role in Navigating the NSR
- Navigating the NSR poses a unique challenge due to the Arctic Ocean's seasonal icebound conditions. Russia has pioneered efforts to ensure the navigability of the NSR, boasting the world's sole fleet of nuclear-powered icebreakers.
- The historic launch of the nuclear icebreaker "Lenin" in 1959 marked a transformative moment in NSR development.
- Presently, FSUE Atomflot, a subsidiary of Rosatom, manages the fleet of nuclear-powered icebreakers. The fleet, comprising seven such icebreakers and an additional nuclear-powered container ship, guarantees safe passage along the NSR. Further expansion is planned, with three more nuclear icebreakers anticipated to join the fleet between 2024 and 2027.
Driving Factors for India's NSR Participation
- India's involvement in the NSR is driven by several compelling factors. The burgeoning cargo traffic along the NSR, boasting a growth rate of around 73% during 2018-2022, is a primary motivator.
- This increase aligns with India's heightened imports of crude oil and coal from Russia, solidifying the NSR's significance as a secure and efficient transport route for vital energy resources.
- India's geographical location further amplifies the NSR's importance. The country's substantial reliance on maritime trade underscores the need for optimal trade routes, and the NSR's potential to expedite maritime journeys holds immense appeal.
Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor: A Strategic Confluence
- The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) emerges as a key piece in India's Arctic puzzle. The project, conceived through a memorandum of intent signed in 2019, could serve as a bridge to the NSR. Stretching over 10,500 km, the CVMC would dramatically reduce transport time, connecting the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea, and the Malacca Strait. This corridor promises to slash travel time by almost a third compared to the existing St. Petersburg-Mumbai route.
- CVMC's potential impact on India's trade landscape is substantial. Essential cargoes like coking coal, crude oil, liquefied natural gas (LNG), and fertilizers could be seamlessly imported from Russia to India through this corridor, benefiting diverse industries.
Geostrategic Dynamics and Future Prospects
- As India deepens its engagement with the NSR, broader geostrategic implications come into play. The collective influence of China and Russia over the NSR's development is a topic of discussion among experts, raising questions about potential shifts in regional power dynamics.
- Looking ahead, Russia's NSR development plan until 2035 outlines ambitious cargo traffic targets. Despite economic sanctions imposed by the West, Russia remains steadfast in pursuing NSR growth. This commitment is evident in Russia's engagement with India, including dialogues with the Indian business community to facilitate year-round NSR operations.
Conclusion
India's burgeoning involvement in Murmansk's cargo traffic is a testament to its strategic interest in the Arctic region and the Northern Sea Route. The Arctic's vulnerability to climate change, coupled with its vast untapped resources, presents both challenges and opportunities for India. As the NSR emerges as a transformative maritime pathway, India's participation aligns with its quest for secure and efficient trade routes. The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor adds another layer of strategic depth, potentially reshaping trade dynamics between India and Russia. In a world marked by shifting geopolitical dynamics, India's foray into the Arctic holds the promise of shaping its future maritime endeavors.
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam-
- How does India's geographical location enhance the significance of the Northern Sea Route (NSR) in its maritime trade strategies? (10 Marks,150 Words)
- What are the driving factors behind India's increasing involvement in cargo traffic through Murmansk and the NSR, and how does the Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) complement this engagement? (15 Marks, 250 Words)
Source - The Indian Express