Donald Trump was recently reelected as the U.S. President, beginning his second term with significant implications for India-U.S. relations. The personal rapport between Prime Minister Modi and President Trump, demonstrated through events like the "Howdy, Modi!" and "Namaste Trump" rallies, reflects alignment in leadership style and policy. Both leaders prioritize strong governance, economic nationalism, and protectionism, alongside a pragmatic, transactional foreign policy approach. These shared priorities provide a foundation for deeper cooperation in defense, technology, and counterterrorism. As Trump’s second term unfolds, these common objectives are expected to continue shaping the trajectory of India-U.S. relations, influencing both nations’ foreign and economic policies.
Significance of India-U.S. Relations
India and the U.S. share a strategic partnership that has evolved over decades. As the world’s largest democracies, they have common values and mutual interests, particularly in global stability, counterterrorism, and economic growth. India’s growing economic influence and the U.S.’s global leadership make them crucial partners in addressing global challenges such as climate change, security threats, and trade imbalances.
Strategic Dimensions of India-U.S. Relations
1. Shared Strategic Interests
India and the U.S. are motivated by common strategic goals:
· Defense and Security Cooperation: Trump’s “America First” policy aims to reduce U.S. military involvement abroad, presenting India with an opportunity to take a more prominent role in regional security. This includes joint military exercises, arms deals, and access to advanced U.S. military technology.
· Indo-Pacific Stability and Counterterrorism: Both countries face common security threats and are committed to maintaining stability in the Indo-Pacific region. Cooperation on counterterrorism, maritime security, and intelligence sharing is likely to increase.
· China Containment: Both nations share concerns about China’s growing influence. This alignment offers opportunities for deeper cooperation to counter China’s military and economic dominance in the region.
2. Geopolitical Balancing
Trump’s unpredictable foreign policy requires India to balance its strategic partnership with the U.S. while managing relations with other global powers like China and Russia. This balancing act will be key to maintaining India's strategic interests.
Economic Dimensions of Trump 2.0 Policies
Trade Relations: Opportunities and Challenges
Trump’s “America First” stance focuses on reducing trade imbalances and promoting U.S. industries. Key aspects of the trade relationship between India and the U.S. include:
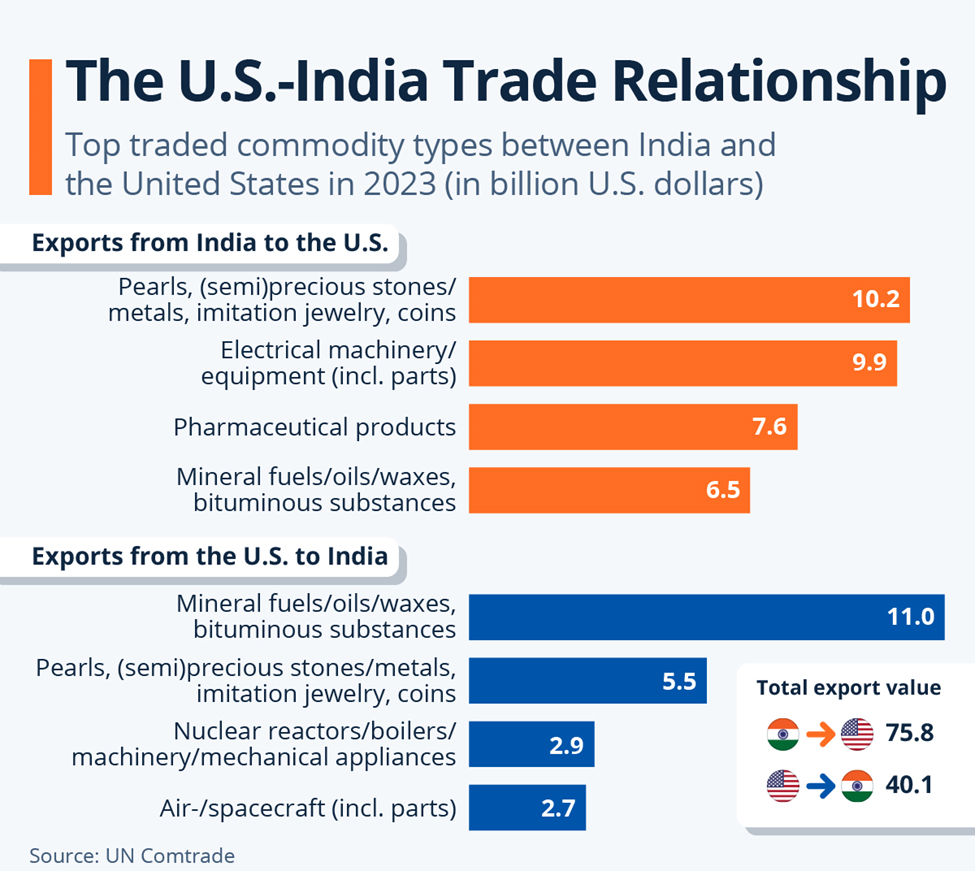
· Tariffs and Trade Barriers: Trump’s protectionist policies in his first term included tariffs on Indian goods like steel, aluminum, and textiles. This could continue or even escalate under Trump 2.0, challenging Indian exporters. The U.S. may push India for greater market access in agriculture, intellectual property, and services.
· Free Trade Agreement (FTA): Despite stalled discussions in Trump’s first term, there is hope for renewed FTA negotiations. While an FTA could boost bilateral trade, India will need to balance U.S. demands for market access and intellectual property protections with its domestic priorities.
· Manufacturing and Supply Chain Diversification: Trump’s push to reshore manufacturing to the U.S. presents an opportunity for India. As U.S. companies seek alternatives to China, India’s labor force, low production costs, and improving infrastructure make it an attractive destination for American firms. The rise of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India reflects this trend.
Impact of the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
India’s PLI scheme, aimed at boosting domestic manufacturing, positions India to attract U.S. investments. These reforms offer incentives for U.S. firms to expand operations in India, fostering job creation and economic growth.
Immigration and Workforce Challenges
Trump’s strict immigration policies could impact India’s IT sector and the broader workforce in the U.S. under Trump 2.0:
· H-1B Visa Restrictions: The H-1B visa program, crucial for Indian professionals, may face stricter regulations, making it harder for skilled Indian workers to obtain U.S. work permits. This could affect India’s IT sector, which relies heavily on the flow of professionals to the U.S.
· Deportations and Legal Migration: Trump’s hardline stance on illegal immigration may not directly impact legal Indian migrants but could create uncertainty for the Indian diaspora, especially regarding deportations and migration policies.
Energy and Climate Policy Implications
· Energy Import Benefits: As a major oil importer, India could benefit from Trump’s policies that lower global oil prices due to U.S. fossil fuel production. This could reduce India’s import bill and improve energy security.
· Challenges for Climate Change Initiatives: Trump’s skepticism about climate change and his withdrawal from the Paris Agreement are concerning for India, which is vulnerable to climate impacts. India is pursuing sustainable development goals, and Trump’s stance could slow global efforts to address climate change, affecting India’s climate adaptation strategies.
Global and Regional Implications
Impact on Global Trade and Supply Chains
· Opportunities for India: With the ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions, American firms may seek to diversify supply chains away from China. India, with its large consumer market and favorable policies like the PLI scheme, is positioned as an attractive alternative for U.S. companies looking to expand in Asia.
· Challenges for India: However, global trade tensions could disrupt India’s trade relationships, requiring careful navigation of its partnerships with the U.S., China, and other global players. The risk of trade skirmishes could complicate India’s economic growth and stability.
Geopolitical Considerations
Trump’s foreign policy, characterized by unpredictability, will require India to carefully manage its relationships with both the U.S. and other powers, including Russia and China. India’s challenge will be to balance its engagement with the U.S. while maintaining strategic ties with these nations.
Conclusion:
Trump’s second term presents both opportunities and challenges for India. His protectionist trade policies, stricter immigration laws, and skepticism about climate change could pose hurdles for India’s economic and geopolitical aspirations. However, opportunities for collaboration in defense, technology, and regional stability could strengthen the India-U.S. partnership.
India’s ability to navigate these challenges will depend on its strategic diplomacy, economic reforms, and adaptability. By leveraging its growing economy, strategic importance, and initiatives like the PLI scheme, India can deepen its partnership with the U.S. while balancing its relations with other global powers. As the world’s largest democracies, India and the U.S. have the potential to build a robust and resilient partnership, but this will require careful navigation of the evolving global and regional dynamics under Trump 2.0.
|
Probable questions for UPSC Mains exam: What are the key developments in defence and security cooperation between India and the US, and what impact could this have on the Asia-Pacific region? |