Context:
India’s economic growth trajectory and the strategies required to transform the nation into a $30-trillion economy by 2047. It emphasises the need to focus on sustainable growth driven by liberal economic policies and private sector engagement, despite criticisms of income inequality.
Economic Growth and Future Prospects
Current Economic Achievements
India’s impressive 7% GDP growth rate and its position as the fastest-growing large economy fuel predictions of the 21st century being India’s. While these achievements are noteworthy, the country must navigate beyond the initial successes and avoid the pitfalls faced by other nations at similar junctures in their development.
The Challenge of Sustained Growth
To reach the $30-trillion economy target, India needs to sustain rapid economic growth through liberal economic policies that leverage the private sector. Critics may highlight income inequality, but the focus should remain on the overall improvement in living standards, which economic growth can facilitate.
The Role of India's Working-Age Population
Economic Growth and Poverty Alleviation
India’s economic reforms since 1991 have significantly reduced poverty, with the poverty rate dropping from about 50% to 20%. Economic growth has lifted 35 crore people out of poverty, underscoring the link between economic development and poverty reduction.
Challenges in Labour Market Participation
Despite progress, India’s female labour force participation rate (FLFPR) remains low at 37%, compared to 60%-70% in other rapidly growing economies. To fully capitalise on the working-age population of 950 million, India must address employment equity and increase the employment rate among its populace.

Strategies for Growth
Export-Oriented Industrialization
To emulate the success of South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Vietnam, India should focus on low-skilled, employment-intensive manufacturing with an emphasis on exports. Historical data shows that openness to global markets and focusing on comparative advantages are crucial for growth.
Avoiding the Middle-Income Trap
India must avoid the middle-income trap by advancing beyond low-end manufacturing and increasing competitiveness in high-tech sectors. The IT boom provided an alternative growth path, but there is a need to build a robust foundation in low-tech manufacturing for future industrial advancements.
|
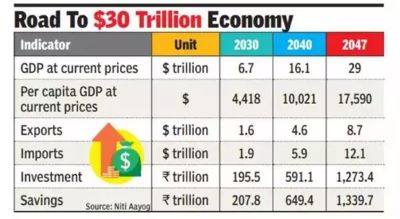
Vision India@2047 ● The primary concern of the Vision 2047 initiative is to prevent India from falling into the middle-income trap. According to the World Bank, the middle-income trap occurs when a country, despite reaching middle-income status, fails to transition to high-income status due to rising costs and declining competitiveness. The Vision 2047 document is being developed by NITI Aayog. It outlines action points and outcome goals for two distinct periods- the year 2030 and the subsequent 17-year period leading up to 2047. ● The Vision India@2047 initiative began in December 2021, involving 10 groups of secretaries from various sectors such as rural and agriculture, infrastructure, social vision, welfare, technology, governance, security, and foreign affairs. ● This comprehensive document will outline the necessary structural changes and reforms to achieve the goal of becoming a $30-trillion developed economy by 2047, with a per-capita income of $18,000-20,000. It will address government process re-engineering to eliminate redundancies among ministries and departments. ● The Vision India@2047 document will also detail India's global engagement strategies in trade, investment, technology, and research and development. It is expected to highlight which Indian companies are poised to become global leaders and the strategies required to build an ecosystem to support this. ● Furthermore, the document will focus on developing human capital, leveraging India’s market size, and addressing regional disparities. It will outline a roadmap for where India aims to be in 2030 and its targets for 2047. |
Navigating the Middle-Income Trap
The Perils of Protectionism
Relying on high import tariffs to protect domestic industries can lead to inefficiencies and inflate costs, harming both manufacturers and consumers. India should resist the temptation of protectionism to avoid a cycle of inefficiency and maintain its competitive edge.
The Importance of Market-Led Growth
India’s strategy should involve a market-led economy that encourages private enterprise. Reducing bureaucratic hurdles and improving the ease of doing business are essential for fostering a conducive environment for growth.
Building Industrial Clusters
Government Initiatives and Infrastructure
To address cost disabilities and low labour productivity, the government should focus on developing industrial clusters with comprehensive infrastructure. These clusters should offer plug-and-play facilities and ancillary services to attract employers and workers.
The Role of Cluster-Led Development
A cluster-led model can alleviate regulatory burdens and create favourable conditions for manufacturing. By improving infrastructure and regulatory environments in designated areas, India can attract investment and boost industrial growth.
Way Forward to Achieve Vision 2047
● Harnessing the Demographic Dividend: To fully leverage India's large working-age population, efforts must focus on upskilling millions of youth to prepare them for future job markets and make them industry-ready.
● Increasing Investment in Education: Government expenditure on education in India has remained below 3.5% of GDP, while the global average is approximately 4.5% of GDP. Increasing investment in education is crucial for long-term growth.
● Promoting Inclusive Growth: Boosting female participation in the labour force and ensuring wage parity are essential for achieving inclusive economic growth in India.
● Unlocking Manufacturing Potential: India aims to expand its manufacturing sector's contribution to the economy from the current 15% to 25%. Effective implementation of initiatives such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme is vital for this objective.
Conclusion
India must harness the strengths of the private sector and pursue reforms to enhance industrial growth in sectors like electronics and apparel. Monitoring indicators such as inter-state migration, urbanisation, and FLFPR will help assess progress towards becoming a $30-trillion economy. India faces significant opportunities and challenges on its path to economic prosperity. By addressing these challenges with forward-thinking policies and ambitious goals, India can achieve its economic objectives and fulfil its potential as a global economic leader.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains 1. Discuss the key strategies required for India to achieve its goal of becoming a $30-trillion economy by 2047. IAnalyse the role of sustainable economic policies, the development of industrial clusters, and the need to overcome the middle-income trap. (10 Marks, 150 Words) 2. Evaluate the potential challenges and opportunities associated with Vision India@2047. How can India leverage its demographic dividend and improve female labour force participation to support its economic growth objectives? Provide recommendations to address regional disparities and enhance educational investment. (15 Marks, 250 Words) |
Source: The Hindu