India's foreign direct investment (FDI) journey has reached a significant milestone, with total FDI inflows crossing the $1 trillion mark since April 2000. This achievement underscores India’s growing stature as an investment destination, further reflected by a 26% increase in FDI during the first half of the fiscal year 2024-25, amounting to $42.1 billion. This surge in FDI highlights the country’s expanding economic appeal, fueled by a robust policy framework, increasing international competitiveness, and a dynamic business environment. Over the last decade, India has attracted $709.84 billion in FDI, contributing to 68.69% of the total inflows over the past 24 years.
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
· FDI refers to investments made by a company or individual from one country into business interests in another country, usually through acquiring a significant stake (typically 10% or more) in an existing business or setting up new operations. Unlike foreign portfolio investment (FPI), which focuses on short-term investments in stocks or bonds, FDI involves a long-term interest and influence over the business operations in the host country.
· FDI brings various benefits to the host country, including capital infusion, job creation, technology transfer, and the development of infrastructure. However, it can also have certain drawbacks, such as the potential domination of local markets by large foreign firms, which can stifle local entrepreneurship and competition.
Factors Driving India’s FDI Growth
India’s remarkable achievement in FDI can be attributed to several factors that have enhanced its attractiveness as an investment destination.
1. Competitiveness and Innovation: India has seen significant improvements in its global competitiveness. The country’s ranking in the World Competitive Index 2024 rose three positions to 40th, up from 43rd in 2021. Furthermore, India’s rise in the Global Innovation Index 2023, where it ranked 40th out of 132 economies, is a testament to its growing innovation ecosystem. This progress reflects the government's focus on fostering a competitive and innovative business environment, which is essential for attracting global investments.
2. Global Investment Standing: India's increasing prominence in global investments is also evident from its performance in greenfield projects and international project finance deals. According to the World Investment Report 2023, India was the third-largest recipient of greenfield investments, with 1,008 greenfield project announcements. Additionally, the country saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals, securing the second-largest number of such deals globally.
3. Improved Business Environment: India’s business environment has improved significantly, which has boosted investor confidence. The country jumped 79 ranks in the World Bank’s Doing Business Report, moving from 142nd in 2014 to 63rd in 2019. This improvement is attributed to efforts aimed at simplifying regulations, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and making it easier to start and operate businesses in India. Such reforms have made India more attractive for both domestic and international investors.
Key Policy Reforms and Initiatives
· India’s government has implemented a series of policy reforms to encourage FDI. The country’s investor-friendly policies, including liberalized sectoral norms, have been crucial in boosting FDI inflows. Most sectors are now open for 100% FDI under the automatic route, with certain exceptions in sensitive areas. The amendment of the Income Tax Act in 2024 to abolish angel tax and reduce tax rates for foreign companies has further streamlined FDI procedures and made the country more attractive to investors.
· The "Make in India" initiative, launched in 2014, has played a pivotal role in attracting FDI by promoting India as a manufacturing hub. This initiative focuses on transforming India into a global manufacturing leader, enhancing its infrastructure, and creating a more conducive environment for foreign businesses to set up operations in the country.
FDI in India: Key Sectors and Investment Routes
India’s FDI inflows are spread across various sectors, with the services sector (including banking, finance, and insurance) receiving the largest share. Other key sectors attracting FDI include computer software and hardware, telecommunications, trading, and the automobile industry.
India’s FDI policy allows for investments through two primary routes:
- Automatic Route: Under this route, foreign investors do not require prior approval from the government or the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Most sectors fall under this route.
- Government Route: In certain sectors, where FDI is sensitive or strategic, approval from the government is required before investments can be made.
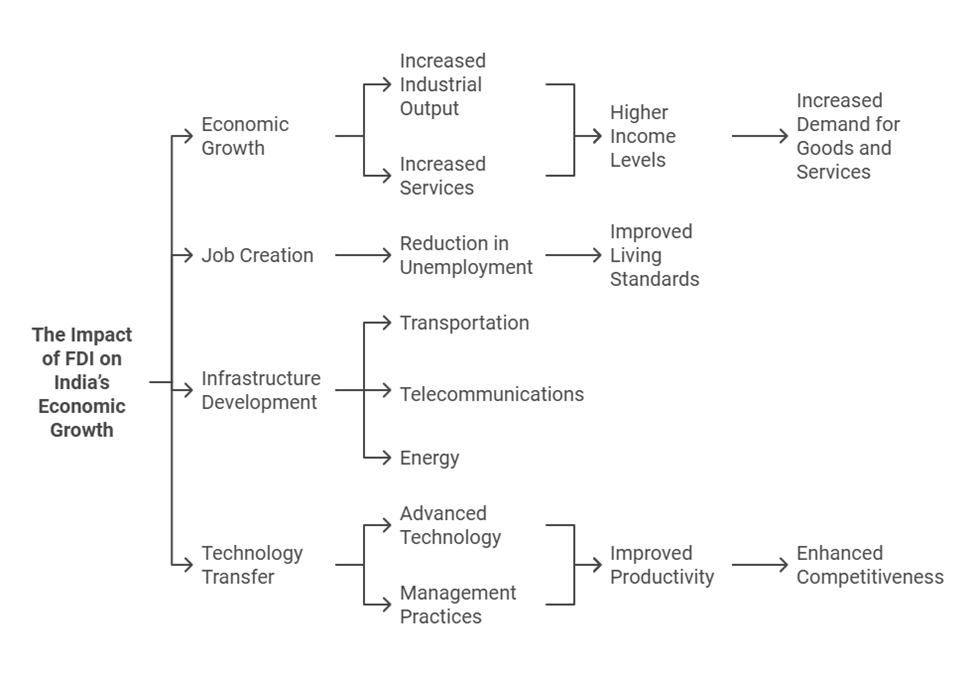
The Impact of FDI on India’s Economic Growth
FDI has been a key driver of India’s economic growth, contributing significantly to the country’s development. Some of the major impacts of FDI in India include:
1. Economic Growth: FDI infuses capital into the Indian economy, which helps boost industrial output and services. The resulting economic growth leads to higher income levels, which in turn drive demand for goods and services.
2. Job Creation: Foreign investments have resulted in the creation of millions of jobs, especially in sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and services. These jobs help reduce unemployment and improve living standards across the country.
3. Infrastructure Development: FDI has played a crucial role in the development of India’s infrastructure, including transportation, telecommunications, and energy sectors. This infrastructure development enhances the efficiency of the economy, facilitating further investments and economic activity.
4. Technology and Knowledge Transfer: FDI also facilitates the transfer of advanced technology and management practices from foreign companies to local businesses. This helps improve productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness in the Indian market.
FDI Challenges and Criticisms
While FDI has brought substantial benefits to India, it is not without its criticisms. Some of the key challenges and concerns surrounding FDI include:
· Market Domination by Foreign Firms: Large foreign corporations may dominate local markets, pushing out smaller domestic businesses. This can lead to reduced competition and hinder the growth of local entrepreneurs.
· Profit Repatriation: One of the concerns with FDI is that the profits generated by foreign investments are often repatriated to the investor’s home country, limiting the long-term economic benefits for India.
· Exploitation of Resources: Some critics argue that foreign investors may exploit India’s natural resources and labor force for their benefit, without providing significant benefits to local communities or the environment.
· Environmental Concerns: Certain FDI projects, particularly in industries such as mining and manufacturing, may lead to environmental degradation. Critics argue that these projects often prioritize economic gains over sustainability.
· Regional Disparities: FDI tends to flow disproportionately into more developed states with better infrastructure and business environments, leading to regional imbalances in economic development. States like Maharashtra and Gujarat attract the largest share of FDI, while other regions remain underdeveloped.
Conclusion:
India’s FDI journey is a testament to its increasing global prominence as an investment hub. The country’s favorable business environment, competitive labor costs, and proactive government policies have positioned it as a top destination for foreign investments. With a cumulative FDI of $1 trillion since 2000 and a steady increase in inflows, India is set to continue its growth trajectory. However, addressing concerns such as market domination, environmental impact, and regional disparities will be crucial for ensuring that the benefits of FDI are widely distributed and contribute to sustainable, inclusive development.
Main question:
The growth in FDI inflows reflects India’s increasing role in the global economy. Discuss how FDI contributes to India’s international competitiveness and position in global investment trends, citing specific examples from recent developments.