Context-
India, having surpassed China as the world's most populous country, is uniquely positioned to address labor shortages in many advanced nations. With a population exceeding 1.4 billion, nearly 65 percent of whom are of working age (15–64 years), and more than 27 percent between the ages of 15 and 24, India’s youthful demographic profile presents significant potential to positively impact the global labor market.
India's Economic Growth and Job Market Dynamics
- India's job market is undergoing significant changes as it emerges as the world's fastest-growing large economy post-COVID-19, with a GDP growth rate of 7.8 percent. This rapid economic expansion, driven by robust private consumption and public investment, could help India achieve its target of a US$ 5 trillion economy by 2026-27.
- Employment elasticity estimates from a recent ORF report reveal significant differences across sectors, regions, and genders. The service sector shows the highest long-run employment elasticity, particularly in rural areas (0.53) and among females (0.31).
Global Demographic Shifts and Labor Shortages
- In contrast, many high-income countries are experiencing rapid demographic shifts characterized by aging populations and declining birth rates. By 2050, the working-age populations in these countries will have shrunk by more than 92 million, while their elderly populations (65 and older) will grow by over 100 million.
- This demographic shift creates a critical imbalance: working-age individuals are essential for contributing to pension and healthcare systems that support the older generation, thus maintaining financial and social stability.
The Need for New Workers in Advanced Nations
- To preserve the current ratio of working-age individuals to the elderly, advanced nations will need over 400 million new workers in the next 30 years, a need that domestic workforce mobilization alone cannot meet.
- This highlights how India can strategically align its labor supply with the demands of advanced economies, ensuring mutual economic growth and integration.
- For instance, Germany’s working-age population is projected to decline by 10 million by 2050, while the elderly population will rise significantly. Similar trends are observed in Japan, Italy, and other developed nations as shown in Figure below.
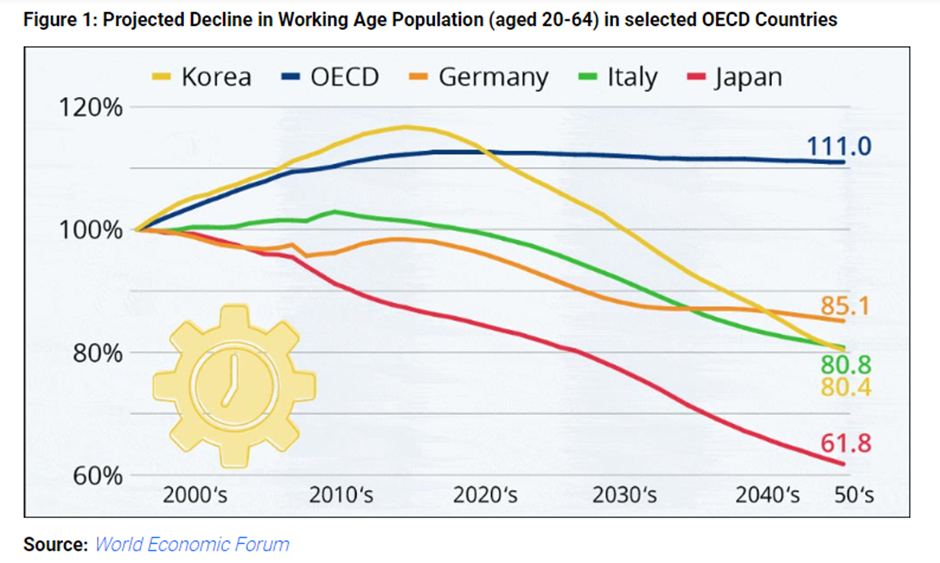
Enhancing Global Equity and Productivity Through Labor Mobility
- Labor mobility can connect potential migrants with employers in need, enhancing global equity and productivity. Workers moving to richer countries can expect to increase their incomes by 6 to 15 times, significantly alleviating poverty.
- India's demographic advantage provides a substantial potential workforce. Projections estimate that low-income countries, including India, will have two billion new working-age individuals by 2050. This surplus labor force presents an opportunity to bridge the gap between labor demand and supply in advanced nations.
The Role of Remittances
- The positive impacts of labor mobility extend beyond individual migrants. Remittances sent back home by migrant workers can play a crucial role in the economies of their home countries.
- In 2022, India received over US$ 111 billion in remittances, making it the first country to surpass the US$ 100 billion mark. These funds contribute to poverty reduction, improved healthcare, education, and overall economic development. However, the pandemic severely impacted migrant workers, particularly those in low-skilled jobs, leading to significant job losses and debt.
Challenges to Labor Mobility
- Despite the clear benefits, current systems supporting labor mobility are insufficient to handle the necessary scale and are often hindered by negative public perceptions.
- Anti-immigrant sentiments and restrictive immigration policies in many high-income countries create barriers for potential migrants. These cultural issues often lead to policies that limit the number of immigrants and fail to provide adequate support systems for them.
- Moreover, the legal and bureaucratic hurdles associated with migration can be daunting.
- Many countries have complex immigration processes that can deter potential migrants.
- Additionally, there is often a lack of comprehensive integration programs to help migrants adapt to their new environments and become productive members of society.
Strategic Solutions to Enhance Labor Mobility
To overcome these challenges, a strategic and well-coordinated approach is required.
- Enhancing bilateral and multilateral agreements to facilitate labor mobility, simplifying immigration processes, providing clear information about migration opportunities, and offering support services for migrants can make the process more accessible and efficient.
- Addressing negative public perceptions through public awareness campaigns and highlighting the positive contributions of migrants can help create a more favorable environment for labor mobility.
- Transition from being a “Vishwa Guru” (global teacher) to a “Vishwa Bandhu” (global partner), focusing on collaboration and mutual benefit. This shift is essential for effectively addressing global labor market demands.
- Invest in skilling initiatives to equip its workforce with the necessary skills to meet international market needs.
- Identify High-Demand Sectors: Identify high-demand sectors in advanced nations that face acute labor shortages, such as healthcare, information technology, education, and manufacturing.
- Analyze Economic Implications: Analyze the economic implications of integrating Indian labor into these sectors using labor market frameworks, including assessing the productivity of Indian workers and the overall global financial impact.
- Enhance Labor Mobility: Enhance labor mobility by identifying enabling conditions for global labor migration from India. This includes reducing labor mobility transaction costs and ensuring the smooth reintegration of returning workers into the Indian labor market.
Conclusion
Effectively aligning India’s abundant workforce with global demand requires a multifaceted approach involving targeted skilling initiatives, enhanced labor mobility frameworks, and robust support systems for migrant workers. Through such strategic efforts, India can alleviate global workforce gaps and establish itself as a pivotal partner in the international labor market.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam-
|
Source- ORF







