Relevance: GS-3: Indian Economy, Growth & Development, Inclusive Growth,
Key phrases: RBI, Go Digital, Go Secure, Global Financial Literacy Excellence, financially literate, National Strategy for Financial Education Report 2020-2025, Project Financial Literacy, Financial Literacy Week
Why in News?
-
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has selected “Go Digital, Go Secure" as this year’s theme for Financial Literacy Week.
Context:
-
According to the report conducted by the Global Financial Literacy Excellence Center, only 24% of the Indian adult population is financially literate. In comparison to other major emerging economies, the financial literacy rate of India is the lowest. This is due to inter-state disparities, lack of formal training and awareness. While other emerging economies have better financial literacy rates, there’s still scope for more improvement.

-
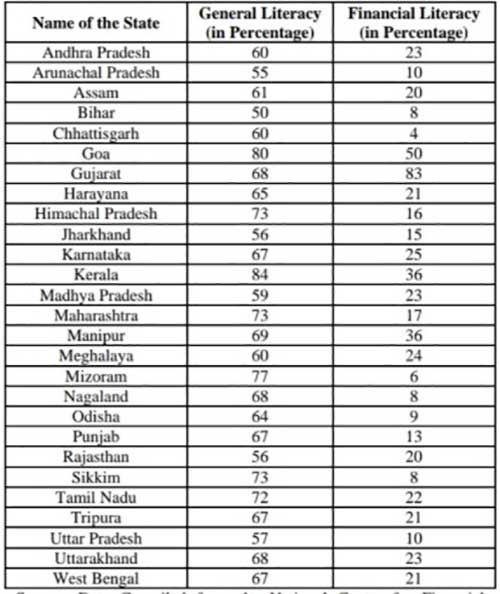
State and Union: Territories wise levels of Financial Literacy in India is a major concern. Metropolitan areas like Maharashtra, Delhi, and West Bengal have financial literacy rates of 17%, 32%, and 21%, respectively. States like Bihar, Rajasthan, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh where poverty is rampant have low literacy rates. The data identifies inter-state disparities. While Goa has the highest literacy rate of 50%, Chhattisgarh is lacking financial education and has the lowest literacy rate of 4%.
Financial literacy is the ability to understand and effectively use various financial skills, including personal financial management, budgeting, and investing. Financial literacy is the foundation of your relationship with money, and it is a lifelong journey of learning.
Why Financial Literacy in India is Important?
- Encourage active savings behaviour. Individuals and young people aren’t able to manage their income. There’s a imbalance between consumption and savings. Savings and investment are alien concepts for the majority of the population. With a strong financial education, people effectively manage their saving and investment.
- Develop credit discipline and encourage availing credit from formal financial institutions as per requirement. In the RBI Working Paper Series titled “Persistence of Informal Credit in Rural India,” 42.9% of the population borrow money from informal sources like commission agents and money-lenders. These non-institutional sources extend loans on high rates of interest. The firms are unable to manage their finances, hence, landing into the debt trap. With a strong financial education, small firms and owners will be able to make informed decisions and take advantage of resources available to them.
- Manage risk at various life stages through relevant and suitable insurance cover. In the urban cities and metropolitan areas like Mumbai and Delhi, Individuals are unable to allocate their spending’s. According to the data published by The Hindu, while Investment in Fixed assets has been increasing exponentially, there has been a major lack of financial planning in terms of life and health insurance. Most of the people accumulate piles of cash at their home, rather than using it on investments. Such decisions are a testimony to the lack of financial planning. Thus, the value of the accumulated money never increases. With financial education, people will manage their finances effectively.
- Inculcate financial literacy concepts among the various sections of the population through financial education to make it an important life skill.
- Encourage participation in financial markets to meet financial goals and objectives.
- Improve usage of digital financial services in a safe and secure manner.
- India is growing and expanding its base, a good financial education would become an asset for people to get higher earning benefits in return.
Recent Initiatives Towards Financial Literacy
- National Strategy for Financial Education Report 2020-2025: The Reserve Bank of India has released a document titled “National Strategy for Financial Education Report 2020-2025.” The prime strategy includes a “5 C’s” approach for increasing financial education in the country. The approach focuses on Content, Capacity, Community,Communication and Collaboration. The report focuses on creating financially aware and empowered Indians. The Technical Group of Financial Inclusion and Financial Literacy (TGFIFL) and Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) work in coordination to ensure the implementation of the same. These policies are in the right direction to make India: a financially literate country.
- The Reserve Bank of India has undertaken a project titled “Project Financial Literacy”, the objective of which is to disseminate information regarding the central bank and general banking concepts to various target groups, including school and college students, women, rural and urban poor, defense personnel and senior citizens.
- In 2012, FSDC (Financial Stability and Development Council) had formulated a National Strategy on Financial Education (NSFE) to spread awareness among masses about basic questions such as – why one should invest?, why one should borrow from bank? Under this, FSDC had proposed to make financial literacy an official responsibility of the industry stakeholders such as financial institutions, banks and regulators including RBI, SEBI, IrDA and PFRDA.
Way forward:
-
In a population of 1.3 billion, emphasis on financial education will make a long-lasting impact. There’s no doubt that Indian schools need to make financial education compulsory for all.
-
Over the years, the government has initiated policies to improve unsatisfactory literacy rates. However, all the programs initiated have a fundamental problem – a lack of implementation.
-
Government spending on financial education would give them higher returns. Financial literacy is the doorway to effective human capital formation.
-
Financial skills will help to raise the standard of living and contribute to overall growth. Our labour force combined with good financial education would help us in eradicating poverty to some extent. In short, a financially smart India would be a major force in the world.
Financial Literacy Week
-
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been conducting Financial Literacy Week (FLW) every year since 2016 to propagate financial education messages on a particular theme across the country.
-
The theme selected for current year FLW is “Go Digital, Go Secure” which will be observed between February 14-18, 2022. This theme is one of the strategic objectives of the National Strategy for Financial Education 2020-2025. Focus will be on creating awareness about (a) Convenience of digital transactions; (b) Security of digital transactions; and (c) Protection of customers.
-
Banks have been advised to disseminate the information and create awareness among their customers and general public. Further, RBI will undertake mass media campaign during the month of February 2022 to disseminate essential financial awareness messages to the general public.
Source: Live Mint
Mains Question:
Q. Explain the importance of financial literacy to develop a vibrant and stable financial system in India. Suggest measures to improve financial literacy in India.







