Context:
The youth of India are playing a crucial role in the country's digital transformation. This change is not just about improving efficiency; it aims to empower individuals to enhance their lives. Digitalization has opened up new opportunities for many, especially for rural youth, who are increasingly adopting technology in their daily routines.
· According to the Comprehensive Annual Modular Survey conducted from July 2022 to June 2023, rural youth are integrating digital tools into various aspects of life, helping to close the gap between different sectors.
Mobile Usage in Rural India:
Rural India is witnessing a remarkable transformation as young people increasingly adopt technology and connect to the digital world. Key statistics highlight this trend:
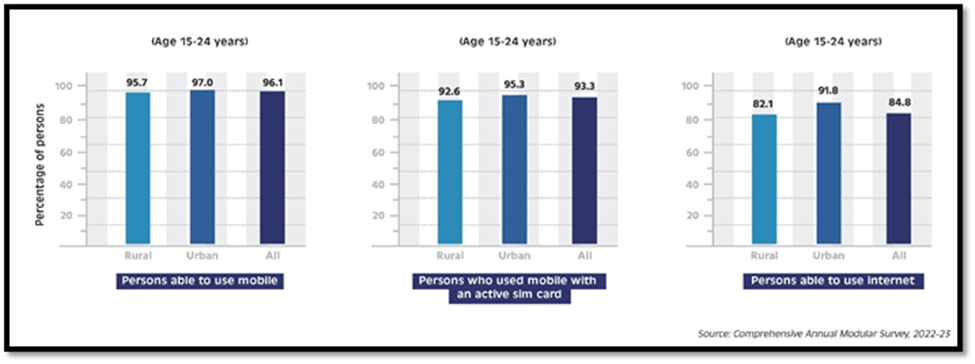
- Mobile Phone Usage: Approximately 95.7% of individuals aged 15-24 in rural areas can use mobile phones, compared to 97% in urban areas.
- 4G Coverage: 99.5% of the rural population has access to 4G connectivity, while urban areas report a coverage of 99.8%.
- Internet Accessibility: Among rural youth aged 15-24, 82.1% can access the internet, indicating a shift towards a more connected generation. Urban areas have a higher accessibility rate of 91.8% for the same age group.
- Recent Internet Usage: The survey found that 80.4% of rural youth aged 15-24 used the internet in the three months leading up to the survey, the highest percentage recorded in rural India. In contrast, urban youth in the 15-29 age group reported a usage rate of 91.0%.
Purpose of Using Technology:
The digital journey of rural India is advancing as young people gradually acquire various technological skills. Key findings include:
- Basic Communication Skills: Among the 15-24 age group, 74.9% can send basic messages, marking a crucial step toward embracing digital communication.
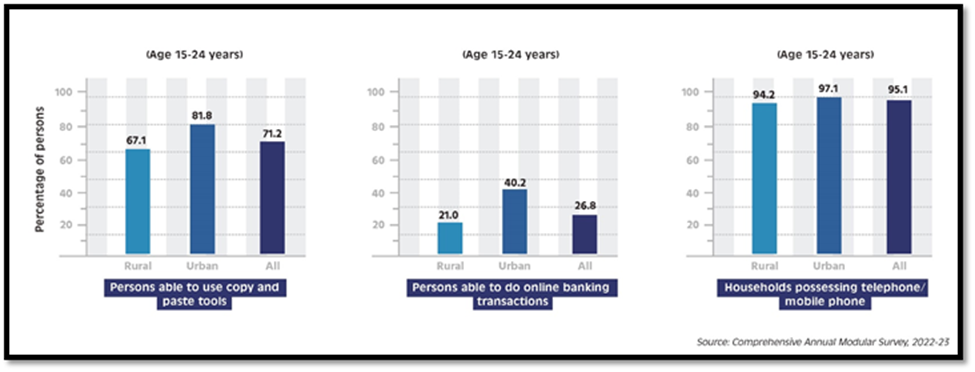
- Data Management Skills: 67.1% of those aged 15-24 and 65.6% of the 15-29 age group can perform data management tasks such as copying, pasting, and moving data.
- Information Searches: 60.4% of youth aged 15-24 and 59.3% of the 15-29 age group are actively searching for information online.
However, challenges remain in certain areas:
- Email Proficiency: Only 43.6% of rural youth aged 15-24 can send emails.
- Online Banking: 31% of youth in the 15-24 age group and 33.3% of those aged 15-29 can conduct online banking transactions.
Despite these gaps, the gradual adoption of digital skills among rural youth signals progress toward a more connected and empowered rural India, where technology increasingly opens doors to opportunity and growth.
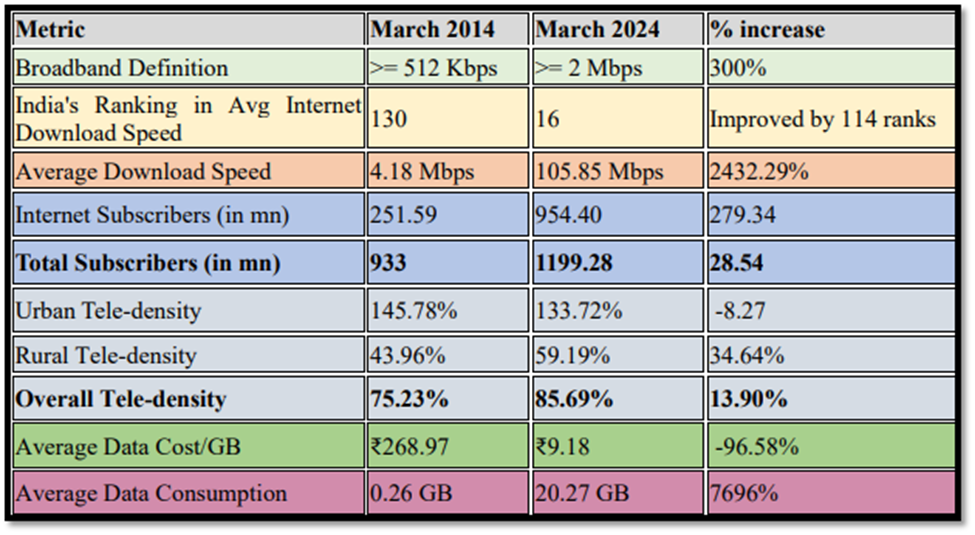
Digital India Initiative:
Launched on 1st July 2015 by the Indian Government, the Digital India Initiative aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
· This program builds upon earlier e-governance efforts that began in the mid-1990s, addressing the need for a cohesive and interactive framework to enhance technology access and promote digital literacy across the country.
Key aspects of the initiative:
· Transformative Focus: The central aim is to make technology a catalyst for change across various sectors.
· Umbrella Programme: Digital India encompasses a wide range of departments and initiatives, bringing together multiple ideas and strategies under a single vision.
· Comprehensive Vision: It connects numerous individual elements, allowing each to function independently while also contributing to a larger, unified goal.
· Coordination and Implementation: The programme is coordinated by the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY) and is implemented across the entire government.
· Synchronized Execution: Existing schemes will be restructured and refocused for effective implementation, ensuring that they work together harmoniously.
· Cost-Effective Improvements: Many components of the initiative focus on process improvements that require minimal expenditure, maximizing efficiency and impact.
Government Initiatives for Universal Connectivity and Digital India:
To promote digitalization and connectivity, the Indian government has launched several initiatives:
- Digital India Initiative: This initiative supports various technology-led startups and innovation schemes, including:
- Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE 2.0)
- Gen-Next Support for Innovative Startups (GENESIS)
- Domain-specific Centres of Excellence (CoEs)
- Next Generation Incubation Scheme (NGIS)
- BharatNet Project: Aimed at connecting rural areas with Optical Fibre Cable, expanding broadband access.
- Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF): Initiatives to bring 4G services to remote villages.
- India BPO Promotion Scheme (IBPS) and North East BPO Promotion Scheme (NEBPS): Encourage IT/ITeS growth in underserved regions, creating employment opportunities.
- PM-WANI Initiative: Aims to provide public Wi-Fi hotspots across the country.
Conclusion:
Rural digital expansion in India is empowering youth to adopt technology, transforming their daily lives and bridging the urban-rural divide. With affordable high-speed internet and government initiatives, rural young people are increasingly using digital tools for communication, education, and finance. This shift highlights technology's role in fostering development and opportunities. As digital literacy and infrastructure improve, rural youth are set to play a vital role in creating a more connected and inclusive future for the country.