Context:
India's Scheduled Tribe (ST) population, which comprises 10.42 million individuals (8.6% of the total population), represents over 705 distinct communities spread across the country. Most of these groups reside in remote and rural areas, making their socio-economic development a unique challenge. To address these concerns, the government has launched various welfare schemes aimed at improving living standards, promoting education, ensuring better healthcare, and preserving the cultural heritage of these communities.
Celebrating and Honoring Tribal Heritage:
· In recognition of the contributions of tribal communities to India’s socio-cultural fabric, the government introduced Janjatiya Diwas, celebrated annually on November 15 to honor the birth anniversary of Bhagwan Birsa Munda. Revered as a freedom fighter and a tribal hero, Birsa Munda led resistance movements against British colonial exploitation and oppression.
· To commemorate tribal heritage and legacy, Janjatiya Gaurav Divas was established in 2021. This initiative not only acknowledges the sacrifices of tribal freedom fighters but also integrates development initiatives focused on uplifting tribal communities. Notably, in 2024, on Birsa Munda’s 150th birth anniversary, the government unveiled development projects worth over ₹6,640 crores aimed at improving infrastructure, education, healthcare, and livelihood opportunities in tribal areas.
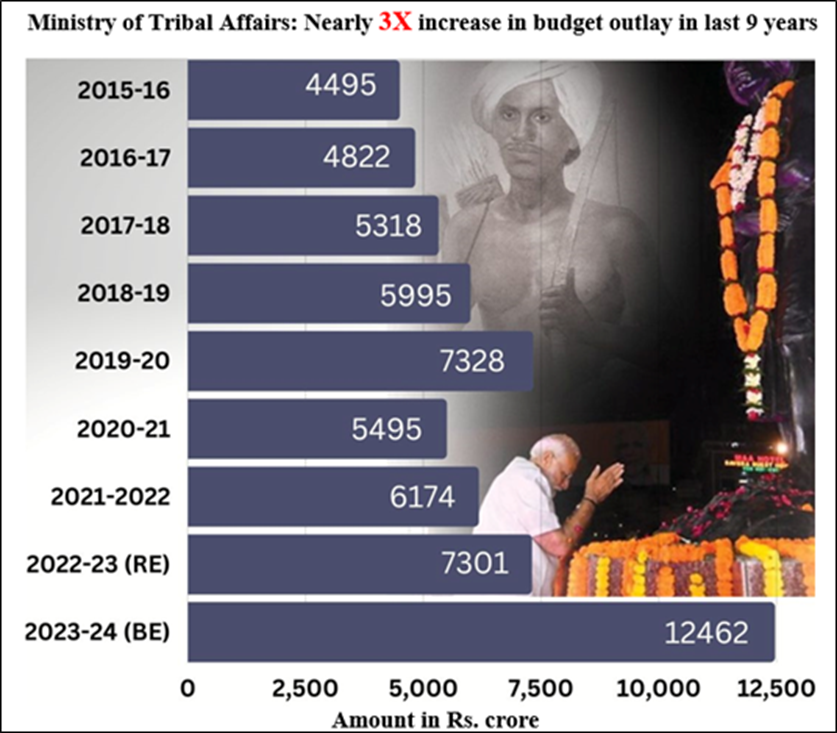
Union Budget 2024-25: Strengthening Tribal Welfare:
The Union Budget for 2024-25 allocated ₹13,000 crore to the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, showcasing the government’s commitment to tribal welfare. Under the Development Action Plan for Scheduled Tribes (DAPST), previously known as the Tribal Sub-Plan (TSP), 42 ministries and departments earmark funds for tribal development. The allocation under DAPST has significantly grown over the years, from ₹21,528 crore in 2013-14 to ₹1,24,908 crore in 2024-25.
Major Initiatives and Programs for Tribal Welfare
1. Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (2024): Launched on October 2, 2024, this initiative addresses critical gaps in social infrastructure, education, healthcare, and livelihood development across 63,843 tribal villages. With an outlay of ₹79,156 crore, the program seeks to uplift tribal villages by providing essential amenities.
2. Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN): Launched on November 15, 2023, this scheme focuses on the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), addressing their specific needs such as housing, education, healthcare, clean water, road connectivity, and livelihood support. PM-JANMAN is an umbrella initiative designed to ensure equitable development for the most marginalized tribal communities.
3. Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAAGY): Revamped in 2021-22 from the earlier Special Central Assistance to Tribal Sub-Scheme (SCA to TSS), this program focuses on developing infrastructure in villages with a predominant tribal population. So far, 36,428 villages, including those in aspirational districts, have been identified for comprehensive development.
4. Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS): EMRS, launched in 2018-19, aims to provide quality education to tribal children. These schools integrate academic learning with cultural and skill development, empowering students for the future. By 2024, 728 EMRS had been approved, with 40 schools inaugurated and 25 more under construction at an estimated cost of ₹2,800 crore.
5. Pradhan Mantri Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana (PMVKY): Launched in 2014, PMVKY addresses the unique challenges faced by tribal communities, such as access to healthcare, education, and livelihood opportunities, while preserving their cultural heritage.
Education Initiatives for Tribal Empowerment:
Education plays a critical role in empowering tribal communities. The government has introduced several scholarship schemes to reduce dropout rates and provide better educational opportunities:
- Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarships: Financial assistance for students in Classes IX to postgraduate levels to ensure a smooth educational transition.
- National Overseas Scholarship: Enables meritorious ST students to pursue higher education abroad.
- National Fellowship for ST Students: Provides financial aid for tribal students pursuing advanced studies through a fully digital process integrated with DigiLocker for efficient grievance redressal.
Promoting Tribal Entrepreneurship
Tribal communities possess rich traditional knowledge and resources. To harness these, the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM) promotes tribal entrepreneurship by supporting local businesses based on natural and minor forest products (MFPs).
Additionally, the National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation (NSTFDC) offers concessional loans to empower tribal communities economically. Key schemes include:
- Term Loan Scheme: Loans for projects up to ₹50 lakh.
- Adivasi Mahila Sashaktikaran Yojana: Provides loans for income-generating activities specifically for tribal women.
- Micro Credit Scheme for Self-Help Groups (SHGs): Loans of up to ₹5 lakh per SHG.
- Adivasi Shiksha Rin Yojana (Education Loan): Financial support for professional education up to ₹10 lakh.
Health and Nutrition Programs for Tribal Communities
Healthcare remains a significant challenge in tribal areas. To address this, the government has launched several targeted programs:
- Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission: Launched in 2023, this initiative aims to eradicate Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) through universal screening and affordable treatment.
- Mission Indradhanush: Ensures full immunization for children and pregnant women, particularly in tribal areas.
- Nikshay Mitra Initiative: Focuses on supporting tuberculosis patients in tribal regions with nutritional and diagnostic aid.
Research and Cultural Preservation
Preserving the cultural heritage of tribal communities is essential for maintaining India’s diverse cultural fabric. The government supports several initiatives in this regard:
- Support to Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs): These institutes document tribal traditions, languages, and medicinal practices while organizing cultural festivals and exchange programs.
- Development of PVTGs Scheme: Focused on 75 identified Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, this program bridges gaps in education, housing, and healthcare, ensuring their inclusion in mainstream society.
Integrated Development through TRI-ECE
The Tribal Research Information, Education, Communication, and Events (TRI-ECE) scheme promotes mass awareness about tribal issues through exhibitions, competitions, and cultural events at the state and national levels. In 2023-24, ₹25 crore was allocated for activities under this initiative.
Conclusion
India’s efforts to empower tribal communities are rooted in the principles of inclusivity and sustainable development. By focusing on education, healthcare, livelihood generation, and cultural preservation, the government aims to bridge socio-economic gaps and ensure holistic progress. These initiatives align with the vision of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas”, fostering unity and equality for all sections of society. Tribal communities, with their unique heritage and potential, are poised to play an integral role in India’s development journey.
|
Probable questions for UPSC Mains exam: · Critically examine the importance of tribal communities in India’s socio-cultural framework. Discuss the government’s initiatives aimed at their empowerment, with a focus on education, healthcare, and livelihood. · Empowering tribal youth through education and skill development is key to socio-economic inclusion.” Analyze the role of the Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) in shaping the future of tribal children in India. |








