Introduction
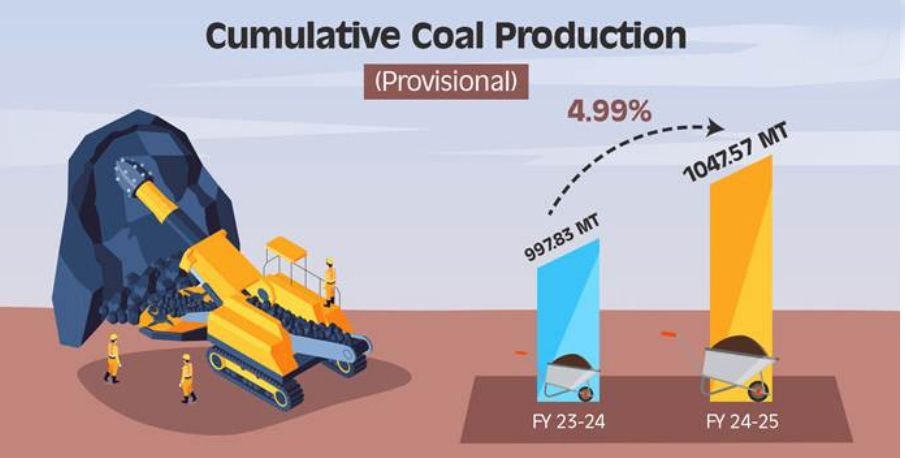
India's coal sector has achieved a historic milestone by surpassing one billion tonnes (BT) of coal production in the fiscal year 2024-25, reaching 1.04 BT on March 20, 2025—11 days ahead of the previous fiscal year's total of 997.83 million tonnes (MT). This achievement underscores the sector's pivotal role in the national energy framework, given that coal contributes 55% to India's energy mix and fuels over 74% of total power generation.
With the fifth-largest coal reserves globally and as the second-largest consumer, India has strategically enhanced domestic coal production to reduce import dependence and ensure energy security.
Growth in Coal Production and Dispatch
India's coal production has witnessed a significant increase, reaching 1.04 billion tonnes in FY 2024-25, marking a 4.99% growth from the previous fiscal year. This rise is attributed to:
- Public and Private Sector Contributions: Coal production from commercial, captive, and other private entities grew by 28.11%, reaching 197.50 MT (Provisional) compared to 154.16 MT in the previous year.
- Coal Dispatch: The total coal dispatch crossed 1 BT, with 1,024.99 MT (Provisional) distributed in FY 2024-25, reflecting a 5.34% growth from 973.01 MT in FY 2023-24.
- Private Sector Engagement: Dispatch from commercial and captive entities surged by 31.39%, reaching 196.83 MT compared to 149.81 MT in the prior fiscal year.
Coal dispatch, the process of transporting and distributing coal to power plants and industrial units, plays a critical role in maintaining an uninterrupted energy supply.
Reduction in Coal Imports and Energy Security
India has made notable progress in reducing coal imports, enhancing self-reliance in energy production.
- Coal imports declined by 8.4% from 200.19 MT in April-December 2023 to 183.42 MT in the same period of 2024, resulting in foreign exchange savings of $5.43 billion (₹42,315.7 crore).
- The Non-Regulated Sector (NRS) recorded a 12.01% decline in coal imports, while imports for blending by thermal power plants fell by 29.8%, despite a 3.53% increase in coal-based power generation.
- Initiatives such as Commercial Coal Mining and Mission Coking Coal boosted domestic output by 6.11%, further reducing dependency on foreign coal.
Although India continues to require imports of coking and high-grade thermal coal, government policies emphasize domestic coal mining expansion to enhance energy security.
Economic Significance of the Coal Sector
Coal remains a fundamental pillar of India's economy, with substantial contributions to revenue generation, employment, and industrial development.
1. Contribution to Railways and Freight Revenue
- Coal is the largest contributor to railway freight, accounting for nearly 49% of total freight earnings.
- In FY 2022-23, coal transport generated ₹82,275 crore, making up 33% of total railway earnings.
2. Government Revenue Generation
- The coal sector contributes over ₹70,000 crore annually to the central and state governments through royalties, GST, and other levies.
- Royalty collections from coal production alone amounted to ₹23,184.86 crore in FY 2022-23, supporting infrastructure and socio-economic development in coal-producing regions.
3. Employment and Workforce Development
- The coal industry directly employs over 239,000 workers in Coal India Limited (CIL), with thousands more engaged in contractual mining, transportation, and related industries.
- Substantial capital expenditure investments, averaging ₹18,255 crore annually over the past five years, have facilitated infrastructure expansion and employment generation.
Coal Gasification: A Path to Sustainable Coal Utilization
To promote cleaner coal technologies, India has prioritized coal gasification, a process that converts coal into syngas, which can be used for producing methanol, Synthetic Natural Gas (SNG), fertilizers, and ammonium nitrate.
Key Government Initiatives
1. Financial Incentives: The government approved ₹8,500 crore on January 24, 2024, to promote coal/lignite gasification projects.
2. Investment by Coal India Ltd (CIL): CIL has partnered with BHEL and GAIL for coal gasification ventures.
3. New Policy for Gasification-Based Auctions: The "Production of Syngas" category was introduced in 2022 under the NRS linkage auctions policy.
4. Revenue Share Rebates: A 50% rebate in revenue share has been offered for coal used in gasification projects, provided at least 10% of total production is utilized for gasification.
By 2047, coal gasification is expected to reduce environmental impact and align with India's long-term vision for sustainable energy development.
Coal Mine Safety and Technological Advancements
The Ministry of Coal has implemented several measures to enhance mine safety, workforce protection, and operational efficiency.
1. Safety Audits and Regulatory Framework
- Annual Safety Audits: Conducted under the "Safety Health Management System Audit" guidelines (December 2023).
- National Coal Mine Safety Report Portal: Launched on December 17, 2024, incorporating safety audit modules for online reporting.
2. Advanced Mining Technologies
- Blast-Free Mining Technologies: Adoption of Continuous Miner, Powered Support Longwall (PSLW), and Hybrid High Wall Mining to improve efficiency and reduce environmental hazards.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use of Environmental Telemonitoring Systems (ETMS) and Gas Chromatographs for underground mine air sampling.
- Strata Control Technologies: Implementation of mechanized roof bolting systems for structural stability.
3. Environmental and Worker Welfare Measures
- Health and Safety Provisions: Mines Rules, 1955, ensures health checks, first aid, canteens, and welfare facilities for workers.
- Environmental Monitoring: Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) are conducted before project approvals.
- Skill Development: Introduction of simulator-based training programs for Heavy Earth Moving Machinery (HEMM) operators and virtual reality (VR) training modules.
Conclusion
India's coal sector continues to be a cornerstone of the nation's energy security, economic growth, and industrial development. The recent milestone of one billion tonnes in production and dispatch, coupled with a notable reduction in imports, underscores India's commitment to energy self-reliance.
With ongoing investments in coal gasification, mine safety, and technological advancements, the coal industry is transitioning towards a more sustainable and efficient framework. Despite the expansion of renewable energy sources, coal will remain a critical energy resource, projected to constitute 55% of India's power generation in 2030 and 27% by 2047.
Through strategic policy initiatives and a dedicated workforce, India is well-positioned to ensure a sustainable coal sector that aligns with the national vision of Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
| Main question: Evaluate the economic contributions of the coal sector to India's economy, focusing on aspects such as employment, government revenue, and infrastructural development. How does the sector's growth align with the objectives of 'Viksit Bharat'? |