Context:
As 2024 unfolds, global security experts are confronting a wave of new threats. The 33rd Summer Olympic Games in France, held in July-August 2024, were anticipated as a potential target for digital and cyber criminals, prompting heightened security measures worldwide.
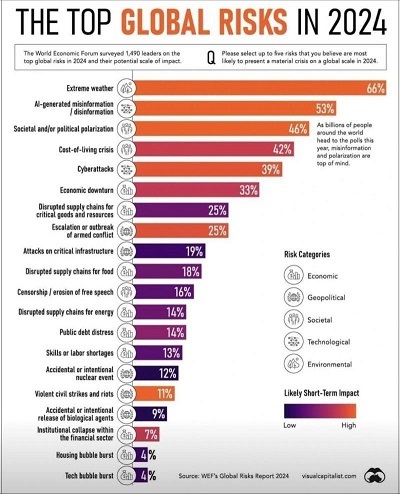
Emerging Threats of 2024
- Initial Concerns and Global Vigilance : The year began with concerns about a diverse array of security threats, largely driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its various manifestations. The potential for digital attacks, including those perpetrated by known terror groups, was high. Although the Paris Games concluded without major incidents, this does not diminish the need for ongoing vigilance. The absence of attacks thus far is a relief but not a reason to lower defences as new digital threats continue to evolve.
- Disinformation and AI : Disinformation has become increasingly prevalent, exacerbated by the advent of AI technologies. In January 2024, the run-up to the Taiwan elections was marred by fake posts and videos, attributed to China but reflecting a broader problem. AI's capability to generate deep fakes—manipulated videos, audio, and images—has made spreading disinformation easier and more convincing, often revealing the truth only after significant damage has occurred.
- The Impact on National Security : The combination of cyber attacks and AI-enabled disinformation is wreaking havoc, particularly in conflict zones like Ukraine. Both sides in the Ukraine conflict have used disinformation and cyber tactics against each other, causing severe disruptions in critical infrastructure such as telecommunications and power grids.
Case Study
The CrowdStrike Outage
A recent incident—a software glitch in a Microsoft Windows update—offered a glimpse into the potential scale of disruption from a major cyberattack. This glitch, which initially affected parts of the United States and rapidly spread worldwide, including to India, caused significant disruptions to flight operations, air traffic, and stock exchanges. Although not a cyberattack, it highlighted the massive impact such an event could have, with over eight million Windows devices failing globally.
Historical Cyberattacks
Several notable cyberattacks underscore the potential for large-scale disruption:
- WannaCry Ransomware (2017): Infected over 230,000 computers in 150 countries, causing billions of dollars in damage.
- Shamoon Computer Virus (2017): Targeted oil companies like SA ARAMCO and RasGas, initially deemed the 'biggest hack in history.'
- Petya Malware (2017): Affected banks, electricity grids, and institutions across Europe, the UK, the U.S., and Australia.
- Stuxnet Worm (2010): Targeted Iran's nuclear program, physically degrading over 200,000 computers and demonstrating the potential of state-sponsored cyber warfare.
Growing Cyber Threats
- Increasing Vulnerabilities: Cyber threats are escalating, with a significant rise in cyber fraud and hacking incidents. Common threats include phishing, identity theft, and false credit card transactions. Fraudsters posing as delivery agents and compromising business emails further exacerbate the risk.
- Challenges for Industry and Government: While governments are working to address digital threats, private sector defences lag behind. Many companies lack adequate protection and preparedness, highlighting the need for dedicated chief information security officers to oversee and enhance their cybersecurity measures.
- Economic Impact: Attacks targeting financial institutions or e-commerce platforms can result in substantial economic losses and undermine investor confidence. For instance, Cyfirma reported that Indian companies suffered over $4 billion in losses due to cyber threats in 2020.
- Data Breaches: Cyber-attacks can lead to the exposure of personal and sensitive information, posing risks to individual privacy and potentially leading to identity theft or fraud. The 2021 data breach at Air India, which affected 4.5 million customers globally, serves as a stark example of these risks.
- Public Services Disruption: Cyber-attacks on government systems can disrupt essential public services, leading to inconvenience and potential disorder. The 2020 cyberattack on the Ministry of Health, which affected crucial services during the COVID-19 pandemic, exemplifies the potential chaos caused by such disruptions.
- Cyber Attacks on Critical Infrastructure: Cyber-attacks have the potential to severely disrupt vital infrastructure, including power grids, communication networks, and defense systems, thereby compromising national security. A notable example is the 2019 breach at the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant, which highlighted the significant security threats posed by cyber incidents.
Addressing Digital Threats
- Awareness and Preparedness: Raising awareness about digital threats is crucial. Unauthorised use of Generative AI for digital bullying and manipulation requires significant effort and resources to combat. Proper awareness and coordinated action are essential to address digital surveillance, disinformation, and manipulation.
- Promote Cyber Hygiene: Encourage both individuals and organizations to maintain good cyber hygiene by regularly updating software, managing passwords securely, and practicing safe online behaviors.
- Foster International Cooperation: Strengthen partnerships with international organizations, law enforcement, and other nations to share threat intelligence, best practices, and coordinate efforts in investigating and prosecuting cross-border cybercrimes. For example, India and Japan have committed to enhancing collaboration to bolster cybersecurity skills at both bilateral and multilateral levels.
- Encourage Cyber Insurance: Promote the adoption of cyber insurance policies to mitigate financial losses from cyber incidents. These policies often cover remediation costs, including legal assistance, investigations, crisis management, and customer reimbursements.
- Policy and Governance: Establishing a robust policy framework and ensuring its effective implementation is essential. Clearly defining roles and responsibilities will facilitate smoother operations and better coordination among departments and stakeholders.
Conclusion
The year 2024 may well be marked by a broad spectrum of security threats. The evolving nature of digital and cyber threats, driven by advancements in AI and the proliferation of disinformation, necessitates sustained vigilance and coordinated global action. Ensuring robust defences and preparedness is critical for safeguarding national security and combating the emerging challenges of the digital age.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains 1. Discuss the impact of Artificial Intelligence and disinformation on global cybersecurity, citing recent examples. What measures should be implemented to enhance resilience against such evolving threats? (10 Marks, 150 Words) 2. Analyse the significance of international cooperation in combating cyber threats. Use examples like the collaboration between India and Japan to illustrate how bilateral and multilateral efforts can strengthen global cybersecurity. Additionally, suggest strategies for improving national and international responses to cyber-attacks. (15 Marks, 250 Words) |
Source: The Hindu







