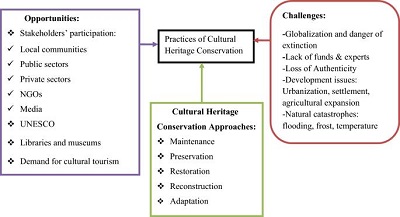
Context
Public engagement with heritage sites is vital not only for preserving cultural identities but also for enhancing community well-being. In rapidly evolving urban landscapes, the digital preservation of built heritage plays a crucial role in raising public awareness, fostering participation, and ensuring effective conservation efforts. This article explores both global best practices and specific challenges and initiatives in India related to using digital technologies for urban heritage conservation. It highlights key strategies, case studies, and recommendations for enhancing these efforts to safeguard cultural heritage amidst urbanization pressures.
Global Digital Conservation Practices
- Leadership in Digital Preservation:
- Italy has been at the forefront of integrating augmented reality (AR) simulations to bring historic sites to life, such as the successful application in Cagliari where AR was used to recreate historical environments and engage visitors in immersive experiences.
- China's extensive use of 3D Geographic Information Systems (GIS) has revolutionized heritage conservation by providing detailed visibility analysis and planning tools for sites like Chiang Mai, allowing for precise management of urban development pressures while preserving historical integrity.
- Spain combines advanced technologies like unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry and terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) for comprehensive data collection and structural analysis. Projects like Cortijo del Fraile in Almería exemplify this approach, where UAVs and TLS were used to create detailed 3D models for accurate preservation planning and structural analysis.
- Italy has been at the forefront of integrating augmented reality (AR) simulations to bring historic sites to life, such as the successful application in Cagliari where AR was used to recreate historical environments and engage visitors in immersive experiences.
- Japan's Society 5.0 Initiative:
- Japan aims to create digital twins for all societal heritage elements, integrating cyberspace and physical space to optimize conservation and management strategies effectively. This initiative emphasizes the use of advanced technologies to simulate and manage heritage sites in a virtual environment, ensuring sustainable preservation practices.
- Japan aims to create digital twins for all societal heritage elements, integrating cyberspace and physical space to optimize conservation and management strategies effectively. This initiative emphasizes the use of advanced technologies to simulate and manage heritage sites in a virtual environment, ensuring sustainable preservation practices.
- Remote Sensing Initiatives in the Middle East:
- Initiatives like the Aerial Photographic Archive for Archaeology in the Middle East (APAAME) and Endangered Archaeology in the Middle East and North Africa (EAMENA) use remote sensing technologies to catalog and safeguard culturally significant but physically inaccessible sites. These initiatives leverage satellite imagery and drone technology to map archaeological sites, providing valuable data for preservation efforts in regions facing rapid urbanization and environmental challenges.
- Initiatives like the Aerial Photographic Archive for Archaeology in the Middle East (APAAME) and Endangered Archaeology in the Middle East and North Africa (EAMENA) use remote sensing technologies to catalog and safeguard culturally significant but physically inaccessible sites. These initiatives leverage satellite imagery and drone technology to map archaeological sites, providing valuable data for preservation efforts in regions facing rapid urbanization and environmental challenges.
Urban Heritage Conservation in India
- Challenges and Existing Efforts:
- India boasts a rich cultural heritage managed by diverse entities such as the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), state governments, and religious trusts, totaling thousands of sites across the country. However, challenges such as a shortage of skilled professionals in heritage conservation, insufficient funding for comprehensive documentation, and varying levels of awareness and engagement from local communities hinder effective preservation efforts.
- India boasts a rich cultural heritage managed by diverse entities such as the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), state governments, and religious trusts, totaling thousands of sites across the country. However, challenges such as a shortage of skilled professionals in heritage conservation, insufficient funding for comprehensive documentation, and varying levels of awareness and engagement from local communities hinder effective preservation efforts.
- Case Studies and Projects:
- Notable projects include IIT Kharagpur's community-based GIS mapping initiative in West Bengal, which aimed to digitally inventory and restore a cluster of Hindu and Jain temples with funding support from governmental bodies. This project highlighted the importance of community involvement and digital documentation in preserving architectural heritage.
- States like Gujarat and Rajasthan are pioneering the use of virtual reality (VR) and Heritage Building Information Modeling (HBIM) to integrate both tangible and intangible heritage elements, enhancing visitor experiences and aiding in more accurate conservation efforts. These technologies allow for immersive experiences and detailed structural analysis, ensuring sustainable management and preservation of historical sites.
- Notable projects include IIT Kharagpur's community-based GIS mapping initiative in West Bengal, which aimed to digitally inventory and restore a cluster of Hindu and Jain temples with funding support from governmental bodies. This project highlighted the importance of community involvement and digital documentation in preserving architectural heritage.
- Impact of Government Initiatives:
- The Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY), launched to revitalize heritage sites across 12 cities in India, aimed to improve infrastructure, sanitation, and tourism facilities. However, its impact was limited due to challenges such as bureaucratic hurdles, inadequate inter-departmental coordination, and insufficient focus on digital documentation and community engagement. These factors have underscored the need for integrated approaches that prioritize both physical restoration and digital preservation strategies.
- The Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY), launched to revitalize heritage sites across 12 cities in India, aimed to improve infrastructure, sanitation, and tourism facilities. However, its impact was limited due to challenges such as bureaucratic hurdles, inadequate inter-departmental coordination, and insufficient focus on digital documentation and community engagement. These factors have underscored the need for integrated approaches that prioritize both physical restoration and digital preservation strategies.
The Way Forward for India
- Strategic Recommendations:
- India should prioritize the integration of digital documentation and verification processes into conservation master plans to ensure comprehensive preservation and management of urban heritage. This includes leveraging advanced technologies like AR, VR, and GIS for accurate mapping and preservation planning.
- Clearly defining roles and responsibilities for stakeholders and end-users is essential for ensuring accountability and effective implementation of conservation initiatives. This involves fostering partnerships between government agencies, academic institutions, and local communities to promote sustainable heritage management practices.
- India should prioritize the integration of digital documentation and verification processes into conservation master plans to ensure comprehensive preservation and management of urban heritage. This includes leveraging advanced technologies like AR, VR, and GIS for accurate mapping and preservation planning.
- Enhancing Public Participation:
- Promoting greater community involvement through participatory approaches and educational campaigns can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards cultural heritage. This includes engaging local communities in heritage conservation workshops, digital storytelling initiatives, and heritage tourism programs that highlight the cultural and economic benefits of preserving historical sites.
- Encouraging the incorporation of traditional crafts and local knowledge into conservation practices can enhance authenticity and sustainability. This involves supporting artisan communities and traditional craftsmen through training programs and financial incentives for heritage conservation projects.
- Promoting greater community involvement through participatory approaches and educational campaigns can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards cultural heritage. This includes engaging local communities in heritage conservation workshops, digital storytelling initiatives, and heritage tourism programs that highlight the cultural and economic benefits of preserving historical sites.
- Improving Policy and Implementation:
- Developing robust and enforceable guidelines for heritage conservation that encompass digital technologies and community engagement as integral components is crucial. This includes establishing national standards for digital documentation, preservation planning, and heritage impact assessments to guide conservation efforts across different regions and heritage sites.
- Allocating sufficient resources for capacity building in digital technologies and heritage management will strengthen conservation efforts nationwide. This involves investing in training programs, research initiatives, and technological infrastructure to support ongoing preservation efforts and innovation in heritage conservation practices.
- Developing robust and enforceable guidelines for heritage conservation that encompass digital technologies and community engagement as integral components is crucial. This includes establishing national standards for digital documentation, preservation planning, and heritage impact assessments to guide conservation efforts across different regions and heritage sites.
Conclusion
India's urban heritage conservation efforts are at a critical juncture, balancing the need for sustainable development with the preservation of cultural diversity. Integrating digital technologies with community engagement is essential for safeguarding the country's rich architectural heritage amidst rapid urbanization and development pressures. By addressing institutional challenges, enhancing public participation, and improving policy frameworks, India can effectively preserve its cultural legacy for future generations while promoting inclusive and responsible urban development.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
|
Source – ORF