Date : 08/11/2023
Relevance – GS Paper3- Environment- Growth and Development
GS Paper 2- Governance - Government Policy and Intervention
Keywords –SDG12, 5R, G-20, Mission LIFE, Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Context –
In recent times, there has been a growing focus on the Circular Economy (CE) concept, which provides a solution to various environmental and economic issues. As awareness of resource limitations and the detrimental effects of waste and pollution has increased, the circular economy has emerged as a sustainable and robust replacement for the conventional linear economic growth model.
Do You Know?
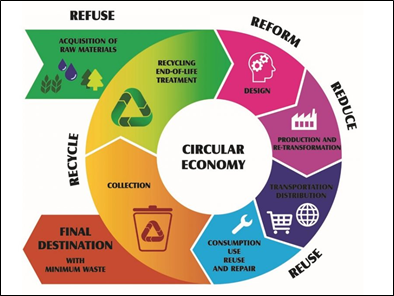
A Circular Economy is one where products are designed for durability, reuse, and recyclability and thus almost everything gets reused, remanufactured, and recycled into a raw material or used as a source of energy.
Need for Circular Economy:
- The global population is projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, driving increased demand for various products and services, including food, fashion, travel, and housing.
- Consequently, the annual extraction of materials has surged from 22 billion tonnes in 1970 to 70 billion tonnes in 2010, with expectations of doubling by 2060.
- In less than eight months this year, humanity's ecological resource consumption exceeded Earth's annual regenerative capacity, intensifying pressure on finite natural resources and leading to resource insecurity, biodiversity loss, pollution, rising emissions, and climate change.
- To align with the Sustainable Development Goal on Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG 12) and address these challenges, it is imperative to embrace more sustainable lifestyles and facilitate a just transition.
- This transition necessitates substantial investments in policy support, eco-friendly products, low-carbon alternatives, improved infrastructure, services, technologies, and capacity building across various sectors.
Circularity - A Blueprint for Sustainability
- Circularity represents a paradigm shift in consumption and production. It is a concept that underscores the importance of using materials for as long as possible at their highest possible value.
- This approach covers the entire lifecycle of products and materials, from designing products to be long-lasting and repairable to ensuring that materials can be recovered through recycling at the end of a product's life.
- The primary goal of circularity is to reduce the adverse environmental and socio-economic impacts resulting from unsustainable consumption and production.
- These impacts include resource insecurity, biodiversity loss, pollution, growing emissions, and climate change. Furthermore, circularity aims to avoid and minimize waste generation while creating opportunities for green jobs and circular business ventures.
Principles of circular economy
- The following ‘5R’ principles lie at the heart of achieving circularity.
- Reduce: The emphasis is on prioritizing the use of regenerative and restorative resources.
- Reuse: This encompasses to reuse of the useful parts/components of a product, wherever possible.
- Recycle: utilizing discarded material as a source of secondary resources, through extensive recycling.
- Re-manufacture: To create new products by utilizing waste streams.
- Repair/refurbish: The aim is to preserve and extend the life of a product.
Individual Lifestyle Choices Impacting Sustainability
Individual lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in facilitating the transition towards sustainable and low-carbon lifestyles. It's noteworthy that around two-thirds of greenhouse gas emissions are directly linked to households and lifestyles.
Four key areas are central to achieving sustainability and low-carbon living:
- Mobility: Transitioning towards eco-friendly modes of transportation and reducing the carbon footprint associated with travel.
- Housing and Energy Use: Embracing energy-efficient practices in housing and reducing energy consumption.
- Dietary Choices and Food: Shifting towards sustainable food sources and reducing food waste.
- New Business Models: Reimagining industries, such as the fashion sector, which has witnessed an alarming increase in consumption and waste. The fashion industry's consumption has more than doubled over the past 15 years, while the number of times a garment is worn before being discarded has decreased by 36%.
G20's Commitment to Circularity and Sustainable Consumption and Production
- The G20, during India's presidency, has emphasized the need for commitments to promote sustainable consumption and production.
- The High-Level Principles on Lifestyles for Sustainable Development, adopted by the G20, acknowledge the vital role played by the circular economy and resource efficiency in achieving sustainable development.
- The G20's focus on circularity and sustainable consumption and production is pivotal in addressing the global material footprint while meeting the basic needs of all individuals.
India's Proactive Approach to Circular Economic Growth
- The Government of India has shown a proactive approach to advancing the circular economy, resource efficiency, and sustainable consumption and production.
- India's transition to manufacturing-led growth offers a promising opportunity to integrate circular economy approaches into various manufacturing sectors.
- Reports indicate that this transition could generate a net economic benefit of approximately USD 624 billion annually in India by 2050, compared to a business-as-usual scenario.
- Transitioning to a circular economy can also have a global impact on employment, potentially creating six million jobs.
Initiatives to promote the Circular Economy:
- India has taken several initiatives to promote resource efficiency and circular economic growth, including the Draft National Resource Efficiency Policy (2019), the Steel Scrap Recycling Policy, the Vehicle Scrapping Policy, and sectoral action plans on circular economy.
- Additionally, India is a member of the Global Alliance on Circular Economy and Resource Efficiency (GACERE), a coalition of governments dedicated to advocating for a global, just circular economy transition and more sustainable resource management.
- India has also launched the Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition, which aims to enhance collaboration among businesses and facilitate experience sharing, capacity building, and actions for the circular economy transition.
- Mission LiFE: Mission LiFE, launched by India, is a global movement that operates based on three principles:
- Nudging Behaviors Towards Responsible Consumption (Demand): Encouraging individuals to adopt sustainable and responsible consumption patterns.
- Enabling Markets to Respond Swiftly to Changing Needs (Supply): Creating a market ecosystem that supports and provides sustainable alternatives.
- Influencing Government and Industrial Policy to Support Initiatives (Policy): Advocating for policy changes that support sustainable lifestyles.
- The Government of India has embedded the importance of sustainable lifestyles in its policies, emphasizing its role in combating climate change. One of the significant areas of focus is sustainable tourism, which can significantly accelerate the transition to low-carbon and circular business solutions.
- These rules set out target waste disposal standards for manufacturers, producers, importers, and bulk consumers, along with enabling transactions among stakeholders for Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) certificates.
Global Initiatives for Circular Economy and Sustainable Consumption and Production
Several global initiatives, frameworks, and tools support the transition to circularity and sustainable consumption and production:
- UNEP's Report on Lifestyles: UNEP provides the latest science-based evidence on lifestyles. Its report, '1.5-degree lifestyles: towards a fair consumption space for all,' offers policy recommendations on reducing lifestyle carbon footprints.
- The Life Cycle Initiative: This initiative offers tools and frameworks to support sustainable consumption and production.
- Global Opportunities for Sustainable Development Goals (GO4SDGs): This initiative aims to promote sustainable development by aligning efforts with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- International Resource Panel (IRP): IRP provides scientific assessments to guide resource management and policy options for achieving sustainable consumption and production.
- 10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production: This framework focuses on the promotion of sustainable consumption and production patterns.
- Sustainable Consumption and Production Hotspots Analysis Tool (SCP-HAT): This tool supports the identification of areas where sustainable consumption and production efforts can have the most significant impact.
Roadblocks to Achieving Circular Economy:
- Unclear Vision for CE: Lack of a clear vision towards the end goal of India’s circular economy mission and gaps in actual policy implementation.
- Reluctance of Industries: Industries are reluctant to adopt the circular economy model due to supply chain limitations, lack of incentives, complex recycling processes, and lack of information.
- Lack of Awareness and Understanding: Many people in India are unaware of the concept of a circular economy and its benefits, making it difficult to gain support.
- Infrastructure Challenges: India lacks suitable recycling facilities, hindering the recycling and reuse of materials.
- Cultural Challenges: There is cultural resistance to reusing and recycling products in India, making it challenging to shift towards a circular economy.
The Road Ahead - A Global Transition to Circular and Green Economic Growth
- A global transformation of consumption and production patterns is imperative to address the environmental, economic, and social crises we face.
- This transformation must occur swiftly and comprehensively to align with the magnitude of the challenges facing humanity. Environmental, economic, and social challenges must be addressed collectively, with a sense of urgency that matches the scale of these challenges.
- At the same time, it is essential to recognize the specific needs of each country and respect their developmental circumstances. India's proactive measures in embracing the circular economy, resource efficiency, and sustainable consumption and production are indicative of its commitment to these principles.
Conclusion
The shift towards circular and sustainable consumption and production is no longer an option but a necessity. The global population is growing, and with it, the demand for resources and services. It is imperative that we transition to circular economic growth, adopt sustainable lifestyles, and promote responsible consumption and production to mitigate environmental degradation, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and preserve our planet for future generations. Through international cooperation, commitment, and transformative action, we can pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future.
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
- What are the key principles of the circular economy, and how do they address the environmental and socio-economic challenges associated with unsustainable consumption and production? (10 Marks, 150 Words)
- How is India actively promoting circular economic growth and sustainable consumption and production? What initiatives and policies has the Indian government introduced to facilitate this transition? (15 Marks, 250 Words)
Source – Indian Express