The deportation of Indian migrants from the United States has gained renewed attention, especially with the recent expulsion of 205 Indian nationals via a U.S. military aircraft. This event highlights the Trump administration’s stringent immigration enforcement policies, marking a broader shift in U.S. migration control. Many of the deported migrants hail from Gujarat and Punjab, states with a history of high emigration rates. The large-scale removal of undocumented migrants has significant consequences, affecting India-U.S. diplomatic relations, socio-economic stability, and international human rights frameworks.
Understanding the factors driving illegal migration, the legal mechanisms governing it, and the consequences of deportation is crucial in shaping policies that balance border security with humanitarian concerns.
Migration: Definition and Types
Migration refers to the movement of people from one place to another due to economic, political, social, or environmental reasons. It can be classified into two main types:
- Legal migrants are those who relocate through authorized channels, obtaining visas, work permits, or permanent residency.
- Illegal migrants enter a country without permission or overstay their visas. According to India’s Citizenship Act, 1955, an illegal migrant is a foreigner who either enters India without valid documents or remains beyond the permitted duration.
Statistical Overview of Indian Migration to the U.S.
As of November 2024, U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) reported that 20,407 Indian nationals were either detained or facing removal orders. Among them, 17,940 had final removal orders but were not in detention, while 2,467 were held under Enforcement and Removal Operations (ERO). Indians ranked as the fourth-largest nationality group in ICE custody and the highest among Asians.
In the past year, approximately 1,100 Indian nationals were deported via special charter flights. Between November 2023 and October 2024, 519 Indians were sent back to India. The most recent deportation flight, operated by a U.S. military C-17 aircraft, departed from San Antonio, Texas. The cost of deportation is substantial; for instance, a military deportation flight to Guatemala costs around $4,675 per migrant.
Push and Pull Factors of Migration
Migration occurs due to a combination of push and pull factors.
Push Factors (Forcing Migration Out of India)
- Economic distress due to high unemployment rates and lack of job opportunities.
- Political instability, corruption, and governance-related dissatisfaction.
- Social discrimination, with disadvantaged communities seeking better prospects abroad.
- Exploitative human smuggling networks, where unauthorized agents lure migrants with false promises.
Pull Factors (Attracting Migrants to the U.S.)
- Higher wages and better economic opportunities.
- Established Indian immigrant networks in states like California, Texas, and New Jersey.
- Prospects of social mobility, including access to quality education and healthcare.
- Family reunification, where relatives sponsor visas or assist in illegal migration.
Challenges Faced by Indian Migrants Leading to Illegal Immigration
Many Indians resort to illegal migration due to obstacles in securing legal entry. The high cost, long processing times, and restrictive visa policies push individuals toward unauthorized routes. Employment challenges in India, combined with societal pressure to achieve financial success, often lead individuals to take risky journeys. Some rely on unscrupulous agents who charge exorbitant fees but provide unsafe or deceptive means of entry into the U.S.
Impact on India-U.S. Bilateral Relations
Large-scale deportations of Indian nationals carry diplomatic and economic implications. While India has agreed to accept deported migrants after verification, managing repatriation logistics remains a challenge. The issue also raises concerns about human trafficking networks and illegal migration channels.
From an economic perspective, deportations disrupt families that depend on remittances, especially in states like Punjab and Gujarat. Many returnees face difficulties reintegrating into Indian society due to financial instability and stigma.
Legal and Human Rights Considerations
Deportation policies must comply with international legal frameworks to ensure the protection of migrants' rights.
- The principle of non-refoulement prohibits deporting individuals to countries where they might face persecution.
- Due process and legal recourse must be provided, ensuring migrants have access to fair trials and legal representation.
- Concerns over the use of military resources, as human rights organizations argue that military-led deportations raise ethical and legal issues under international law.
Initiatives to Counter Illegal Migration
India too, grapples with significant illegal migration challenges, particularly along its eastern and northern borders. In the northeast, especially Assam, a longstanding influx of Bangladeshi migrants has reshaped the region’s demographics. More recently, persecuted Rohingyas from Myanmar have sought refuge in India.
From the north, religious minorities from Pakistan and Afghanistan have migrated due to persecution. These movements pose security risks, particularly in Kashmir, where militants exploit porous borders to infiltrate through the Line of Control.
To address these challenges, the Indian government has implemented various measures to curb illegal migration.
- 'Surakshit Jayen, Prashikshit Jayen' campaign, launched by the Ministry of External Affairs, promotes safe and legal migration pathways.
- Migration and mobility partnership agreements with countries like France, ensuring legal migration while returning identified illegal migrants.
- Border management measures, including:
- Physical infrastructure such as border fencing and floodlighting.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) for enhanced border surveillance.
- Regular patrolling and anti-tunneling operations by security forces like the BSF and Assam Rifles to prevent illegal infiltration.
Global Initiatives
International efforts to regulate migration include:
- Global Compact for Safe, Orderly, and Regular Migration, under the International Organization for Migration (IOM), which promotes responsible migration policies.
- Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea, and Air, under the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC), aiming to prevent human smuggling.
- INTERPOL’s support in breaking criminal networks facilitating illegal migration.
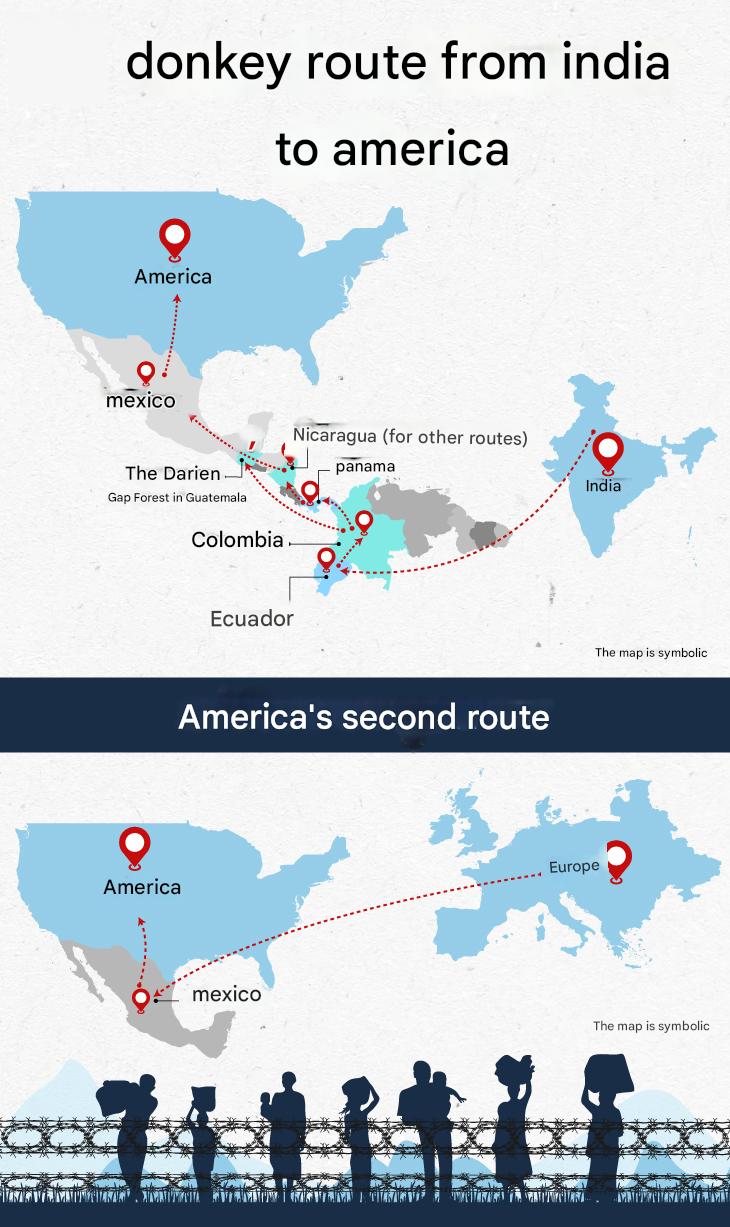
Dunki Routes: The Unauthorized Migration Pathways
"Dunki routes" refer to unauthorized migration pathways frequently used by Indian migrants. Initially associated with Punjab and Haryana, these routes have now expanded to Gujarat. Migrants typically enter the U.S. via Latin America, relying on human traffickers to navigate treacherous paths.
Stages of the Migration Journey
1. Entry into Latin America: Migrants first fly to Ecuador, Bolivia, or Guyana due to lenient visa policies. Others travel through Mexico after obtaining visas via Dubai.
2. Crossing the Darién Gap: This dense jungle between Colombia and Panama is one of the most dangerous migration routes. Migrants face extreme weather, wild animals, and criminal gangs engaged in robbery, kidnapping, and violence
3. Traversing Central America: Migrants bribe officials while traveling through Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, and Guatemala.
4. Crossing into the U.S.: The final hurdle involves entering the U.S. through the Rio Grande or scaling border fences, often facing the risk of arrest.
High Costs and Exploitation by Smugglers
The cost of unauthorized migration via dunki routes is extremely high. Smugglers charge anywhere between ₹30-40 lakh to ₹1 crore per migrant. Many migrants take on debt or sell property to finance their journey, making them vulnerable to further exploitation. Smuggling networks operate through encrypted communication channels and social media, luring desperate individuals with false promises.
Conclusion
The deportation of Indian nationals via U.S. military aircraft reflects the U.S. government’s intensified immigration enforcement measures. While the U.S. has the sovereign right to control its borders, the use of military resources raises ethical, diplomatic, and legal concerns. Addressing the root causes of illegal migration requires a multi-pronged approach that includes:
- Strengthening legal migration channels by expanding work visas and skill-based migration programs.
- Enhancing India-U.S. cooperation on migration management, including tackling human smuggling networks.
- Ensuring the protection of migrants' rights by providing humane treatment to deportees and preventing exploitation.
By fostering bilateral collaboration and implementing policies that balance security with humanitarian concerns, both India and the U.S. can develop a more effective and ethical approach to migration challenges.
| Main question: Illegal migration is often linked to human trafficking and organized crime. Discuss the challenges posed by unauthorized migration routes and the role of agencies like INTERPOL in combating this issue. |
Source: Indianexpress