Context-
The impact of climate change on food production requires an urgent transformation of global food systems. This is crucial for improving climate resilience, ensuring sustainability, and securing food for future generations, particularly in developing countries where nutritional deficiencies are common and agriculture is predominantly rain-fed. Effective strategies and practices are essential.
Transforming Food Systems Under Climate Change
- Adoption of Sustainable Agricultural Practices : A key strategy for developing climate-resilient food systems is the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices. This approach involves techniques such as crop rotation, polycultures, and cover crops, which improve soil health and decrease susceptibility to pests and diseases. Agroecology incorporates ecological principles into farming practices, fostering biodiversity and ecosystem services. Conservation agriculture emphasizes maintaining a continuous soil cover, reducing soil disturbance, and diversifying plant species. According to a study, conservation agriculture enhances soil structure, improves water retention, and boosts resilience to climate extremes. Organic farming, which avoids synthetic inputs and focuses on natural processes, also supports soil fertility and ecosystem health, making it a sustainable choice for climate resilience.
- Diversifying Crops and Livestock : Another crucial strategy to enhance resilience is diversifying crops and livestock. Climate change can alter pest and disease patterns, making monocultures especially susceptible. Diversified farming systems, which include a variety of crops and livestock breeds, help mitigate these risks. Evidence suggests that crop diversification lowers the risk of total crop failure and can boost overall farm productivity. Incorporating climate-resilient crop varieties and livestock breeds is crucial. These varieties and breeds are better adapted to withstand extreme weather conditions like heat, drought, and floods. A study from Sub-Saharan Africa highlights that diversified farming systems help maintain productivity under varying climate conditions, ensuring a stable food supply.
- Efficient Water Management : Efficient water management is crucial for climate resilience. Adopting efficient irrigation methods like drip irrigation, which delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizes waste. Additionally, rainwater harvesting is an effective practice, capturing and storing rainwater for use during dry periods.
- Utilizing Climate-Smart Technologies : Utilizing climate-smart technologies is crucial for modernizing agricultural practices and enhancing resilience. Precision agriculture, remote sensing, and data analytics enable farmers to make informed decisions, optimize resource use, and boost productivity. Mobile applications and digital tools provide real-time weather forecasts, pest alerts, and best practice recommendations, aiding farmers in adapting to changing conditions. Precision agriculture employs GPS and sensors to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns, allowing farmers to apply inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently, reducing waste and improving yields. Remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery, facilitate the monitoring of large areas, early identification of stress signals, and mitigation of potential losses.
Enhancing Social and Economic Resilience
- Building Community Resilience : Climate resilience in food systems also involves enhancing social and economic resilience among farming communities and vulnerable populations. This includes providing access to climate information and early warning systems, improving market access and value chains, and implementing social safety nets and insurance schemes for farmers. Empowering local communities and fostering inclusive economic development are crucial elements of building climate resilience.
- Recognizing and Formalizing Community Knowledge : Regenerating or afforesting lands requires the support of local communities, who can manage and oversee adaptive management practices. Recognizing and formalizing community knowledge systems and efforts in forest stewardship is essential. Farmer-managed natural regeneration (FMNR) systems, where local communities protect and manage naturally regenerating trees, have demonstrated significant economic and ecosystem benefits across many states.
Innovation in Food Systems
In addition to traditional adaptation strategies, innovation plays a vital role in transforming food systems for climate resilience. Research and development in areas such as climate-resilient crop varieties, biofortification, sustainable aquaculture, and alternative protein sources are critical for addressing food security challenges in a changing climate. Advances in digital agriculture, blockchain technology, and data analytics also offer new opportunities for improving resilience and transparency in food supply chains.
Effective Policy and Governance Frameworks
- Effective policy and governance frameworks are essential for driving the transformation of food systems towards climate resilience. Integrating climate change considerations into agricultural policies, promoting sustainable land use planning, incentivizing climate-smart practices through subsidies and incentives, and fostering international cooperation and knowledge exchange can be adopted. Collaboration between governments, civil society, the private sector, and research institutions is key to implementing holistic and inclusive strategies.
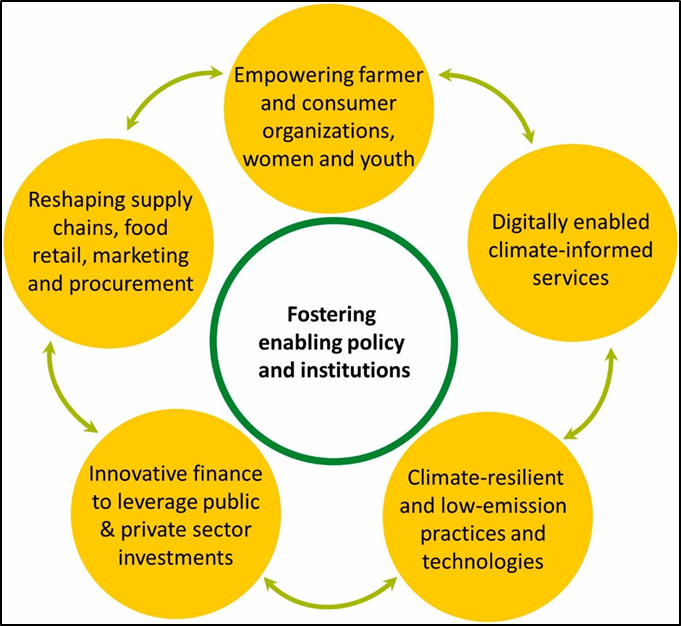
Challenges and Opportunities
- Despite the progress made in addressing climate resilience in food systems, several challenges remain. This includes limited access to finance and technology for smallholder farmers, the lack of awareness and capacity among stakeholders, competing land-use priorities, and policy gaps at the national and global levels. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and investment in sustainable agriculture and food systems.
Conclusion
Although making our food systems climate resilient is complex, it is an imperative task in the face of climate change. It requires a combination of adaptive agricultural practices, technological innovation, social and economic empowerment, biodiversity conservation, and effective governance. By addressing these challenges and seizing opportunities, we can build resilient food systems that ensure food security, protect natural resources, and promote sustainable development for future generations.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam-
|
Source- ORF







