On November 27, 2024, Israel and Lebanon entered into a ceasefire agreement, following a proposal backed by the United States. This decision came after 13 months of escalating conflict, especially in September 2024. US President Joe Biden confirmed that the ceasefire was designed to be permanent, aimed at ending hostilities, particularly with Hezbollah, and restoring security along the Israel-Lebanon border.
This ceasefire builds on the framework of UN Security Council Resolution 1701 passed in 2006 after the Israel-Hezbollah war. Understanding the key elements of this ceasefire, its historical context, and its implications is crucial for anyone studying international relations and security issues in the Middle East.
Historical Context: The 2006 Israel-Hezbollah Conflict and UNSC Resolution 1701
The relationship between Israel and Hezbollah has been marked by tension and conflict for decades. The 2006 war broke out after Hezbollah launched an attack on Israeli soldiers, killing three and kidnapping two others. The war lasted over a month, resulting in over 1,000 Lebanese civilian deaths and 170 Israelis. The conflict devastated Lebanon, leading to widespread displacement and destruction.
In response, the UN Security Council adopted Resolution 1701 on August 11, 2006, aiming to end hostilities between Israel and Hezbollah. The resolution included:
- Disarmament of all armed groups in Lebanon, except for the Lebanese state’s forces.
- No foreign forces in Lebanon without the government’s consent.
- Establishment of a buffer zone between Israel and Lebanon, monitored by the UN and Lebanese military.
- Deployment of UNIFIL (United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon) to ensure the ceasefire's implementation.
While the resolution halted active hostilities, its full implementation was incomplete, particularly regarding Hezbollah’s disarmament. The 2024 ceasefire proposal seeks to revisit and strengthen these provisions.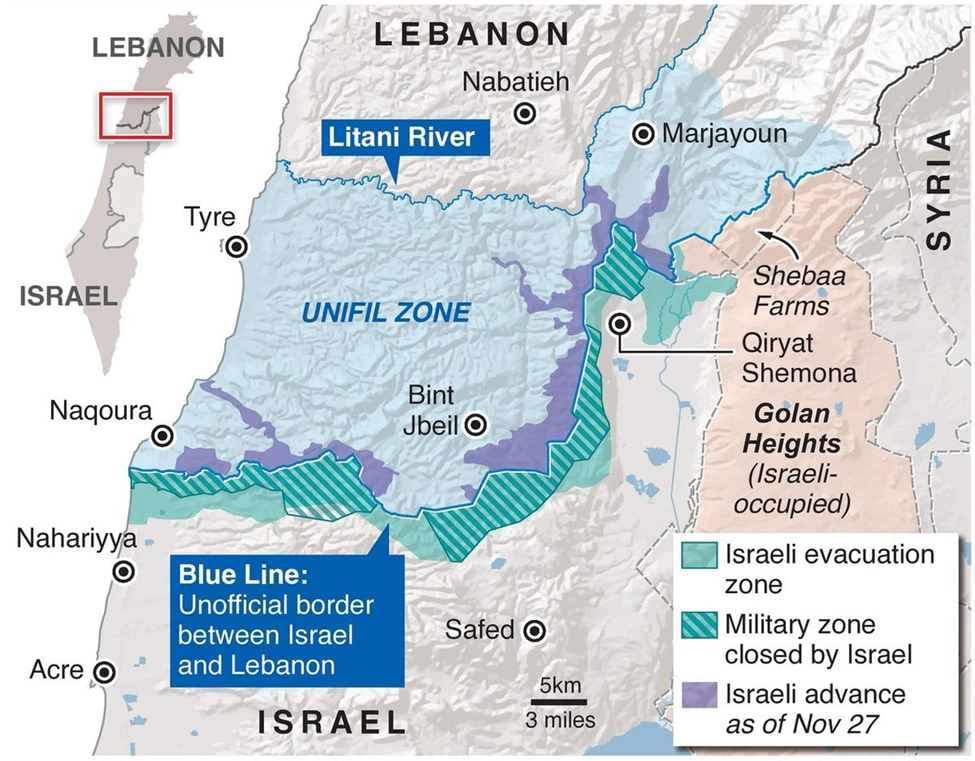
Details of the 2024 Ceasefire Proposal:
The 2024 ceasefire agreement between Israel and Hezbollah builds on UNSC Resolution 1701 but introduces modifications. Key aspects of the proposal include:
- Cessation of Hostilities: The ceasefire is initially set for 60 days, with Hezbollah fighters expected to retreat 40 kilometers from the Israel-Lebanon border. Israeli forces, who have occupied parts of southern Lebanon since October 2023, are also expected to withdraw.
- Role of Lebanon and Hezbollah: Lebanon will supervise Hezbollah’s movements south of the Litani River to prevent regrouping. The Lebanese military, UN peacekeepers, and a multinational committee will monitor the situation.
- Israeli Conditions: Israel retains the right to resume military operations if Hezbollah violates the ceasefire terms.
- The Role of the US and France: The proposal includes the participation of the United States and France in a tripartite mechanism to oversee the ceasefire’s implementation. This mechanism will consist of representatives from Lebanon, Israel, the UNIFIL, and the two Western powers.
This agreement represents a shift from the 2006 ceasefire by including more international oversight. However, the disarmament of Hezbollah remains contentious, as the current proposal does not call for complete disarmament in southern Lebanon.
Why Did Israel Agree to the Ceasefire?
Israel’s decision to agree to the ceasefire can be attributed to several military and political factors. Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu outlined three main reasons:
- Focus on Iran: Israel views Hezbollah as an Iranian proxy. By halting the conflict in Lebanon, Israel can focus its military efforts on countering Iranian influence in Syria, Iraq, and Yemen.
- Replenishing Military Resources: The ceasefire gives the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) a chance to regroup and replenish their resources after a prolonged and costly military engagement.
- Separation of Fronts: By reaching a ceasefire with Hezbollah, Israel can focus on Hamas in Gaza, reducing the risk of fighting on multiple fronts.
Additionally, internal factors within Israel’s government influenced the decision. Former Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, who had been advocating for a ceasefire in both Gaza and Lebanon, represented a faction within the IDF that believed continuing military engagement in Lebanon would be unsustainable. Gallant’s concerns, along with his call for clearer military objectives, likely influenced Netanyahu’s decision.
Implications for the Israel-Lebanon Border:
The ceasefire has significant implications for the security situation along the Israel-Lebanon border. The Blue Line, demarcated by the United Nations, separates Israel and Lebanon and is a focal point for tensions between Hezbollah and Israel. Despite the ceasefire, the situation remains fragile.
Key considerations include:
- Military Balance: While Hezbollah has been weakened, it still possesses the ability to strike Israel, meaning the potential for future conflict remains high.
- Lebanese Army’s Role: The Lebanese Army is now the only recognized armed force in southern Lebanon between the Litani River and the Blue Line. Its ability to control the region and prevent Hezbollah from regrouping is crucial to maintaining peace.
- Hezbollah’s Sociopolitical Influence: Hezbollah holds significant political and social influence in Lebanon. The group has seats in the Lebanese Parliament and a strong presence in the government. After the ceasefire, Hezbollah is likely to regain political support and rebuild its infrastructure.
Implications for the Broader Middle East:
The broader Middle Eastern context plays a crucial role in understanding the implications of the Israel-Lebanon ceasefire. Key factors include:
- Iran’s Influence: Iran, which sponsors Hezbollah, has been a major player in the region, using the group as a proxy force to counter Israeli influence. The ceasefire is a diplomatic victory for Iran, as it reduces the immediate military threat to its proxy. This may enable Iran to focus on other strategic objectives, including its relations with the West.
- Israel’s Focus on Gaza and Iran: The ceasefire allows Israel to focus on its ongoing conflict with Hamas in Gaza and Iranian military activities in Syria and Iraq. Israel’s strategic priorities will continue to center on countering Iranian influence.
India’s Role and Position:
India has played a significant diplomatic role in the context of the Israel-Lebanon ceasefire. The Indian government welcomed the ceasefire, expressing hope that it would lead to peace and stability in the broader region.
India reiterated its longstanding position on the importance of dialogue and diplomacy in resolving conflicts. India has called for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza while condemning civilian casualties and emphasizing the adherence to international humanitarian law.
Conclusion:
The ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah is a significant development in the region. While immediate military objectives have been achieved, the long-term stability of the Israel-Lebanon border remains uncertain. The framework established by UNSC Resolution 1701 and the 2024 ceasefire proposal provides a case study of how international diplomacy, military strategy, and regional politics intersect in efforts to prevent conflict escalation and ensure long-term stability. India's diplomatic efforts, alongside the US and France, have contributed to creating space for this temporary peace, signaling the importance of dialogue and multilateral engagement in addressing regional security challenges.
| Main question: The Israel-Hezbollah conflict has been a long-standing issue. Critically analyze the role of international diplomacy, especially that of India, in conflict resolution. |







