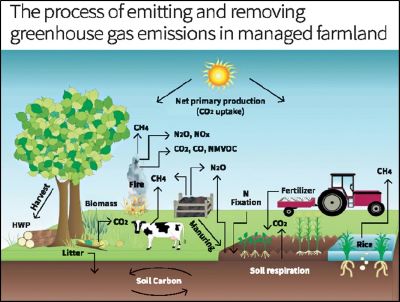
Context-
The goal of carbon farming is to mitigate climate change by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
What is Carbon Farming?
Carbon farming is a practice that combines farming techniques with regenerative agricultural practices to restore ecosystem health, improve agricultural productivity and soil health, and mitigate climate change by enhancing carbon storage in agricultural landscapes and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It involves various techniques that can be easily implemented across different agro-climatic zones, offering numerous benefits such as soil degradation amelioration, water scarcity mitigation, and climate variability challenges.
Techniques Within Carbon Farming and their Benefits
● Rotational Grazing: Rotational grazing is a simple implementation of carbon farming that involves rotating livestock through different pastures to allow for vegetation recovery, soil regeneration, and carbon sequestration. By managing grazing patterns, farmers can improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from livestock.
● Agroforestry: Agroforestry practices, such as silvopasture and alley cropping, integrate trees and shrubs with crops or pastureland. These practices not only diversify farm income but also sequester carbon in vegetation, enhance soil fertility, and provide additional ecosystem services like shade and windbreaks.
● Conservation Agriculture: Conservation agriculture techniques, including zero tillage, crop rotation, cover cropping, and crop residue management, minimize soil disturbance and enhance organic content. These practices improve soil structure, increase water retention, and reduce erosion, thus contributing to carbon sequestration and climate resilience.
● Integrated Nutrient Management: Integrated nutrient management practices promote soil fertility and reduce emissions by using organic fertilizers and compost instead of synthetic fertilizers. By improving nutrient cycling and soil health, these practices enhance crop productivity and contribute to carbon sequestration in soils.
● Agro-ecology: Agro-ecological approaches, such as crop diversification and intercropping, enhance ecosystem resilience and reduce the reliance on external inputs like pesticides and synthetic fertilizers. By mimicking natural ecosystems, these practices improve soil biodiversity, increase carbon sequestration, and enhance farm sustainability.
● Livestock Management: Livestock management strategies, including rotational grazing, optimizing feed quality, and managing animal waste, can reduce methane emissions and increase carbon storage in pasturelands. By improving grazing efficiency and nutrient cycling, these practices contribute to carbon sequestration and climate mitigation.
Challenges in Implementing Carbon Farming
● Geographical and Environmental Factors: The effectiveness of carbon farming varies depending on factors such as geographical location, soil type, crop selection, water availability, and biodiversity. Regions with long growing seasons, sufficient rainfall, and fertile soil are best suited for carbon farming practices, while hot and dry areas with limited water availability face challenges in vegetation growth and carbon sequestration.
● Financial Constraints: The adoption of carbon farming practices may require financial assistance for farmers to overcome the costs of implementation. In developing countries like India, small-scale farmers often lack the resources to invest in sustainable land management practices and may require support through subsidies, grants, or credit facilities.
● Policy Support: The success of carbon farming depends on supportive policies that incentivize and facilitate the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices. However, inadequate policy support, inconsistent regulations, and bureaucratic hurdles can hinder the widespread implementation of carbon farming initiatives.
● Technological Barriers: The adoption of advanced technologies and practices, such as precision agriculture, remote sensing, and carbon monitoring, can enhance the effectiveness of carbon farming. However, limited access to technology, inadequate infrastructure, and low digital literacy among farmers pose barriers to adoption and implementation.
● Community Engagement: Effective community engagement and stakeholder participation are essential for the successful implementation of carbon farming initiatives. However, limited awareness, resistance to change, and cultural barriers may hinder the adoption of new agricultural practices and technologies.
Global Initiatives in Carbon Farming
● Carbon Trading Markets: In recent years, carbon trading in the agriculture sector has gained importance globally, with voluntary carbon markets emerging in countries like the U.S., Australia, New Zealand, and Canada. Initiatives such as the Chicago Climate Exchange and the Carbon Farming Initiative in Australia incentivize carbon mitigation activities in agriculture through financial mechanisms and market-based incentives.
● International Partnerships and Projects: International partnerships and projects, supported by organizations like the World Bank, aim to promote carbon farming and climate-smart agriculture in developing countries. Initiatives such as the Agricultural Carbon Project in Kenya highlight the potential of carbon farming to address climate mitigation, adaptation, and food security challenges in economically developing regions.
● COP21's '4 per 1000' Initiative: The '4 per 1000' initiative, launched during the COP21 climate talks in Paris, emphasizes the role of soil carbon sequestration in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. By promoting practices that increase soil organic carbon by 0.4% annually, the initiative aims to enhance soil health, improve agricultural productivity, and contribute to climate change mitigation efforts globally.
● Research and Innovation: Research institutions, universities, and agricultural organizations worldwide are conducting research and innovation projects to develop and promote carbon farming practices. These initiatives focus on improving soil carbon sequestration, enhancing ecosystem resilience, and increasing agricultural sustainability through interdisciplinary approaches and collaboration.
Opportunities for Carbon Farming in India
● Climate Resilience and Adaptation: As climate change intensifies, climate-resilient and emission-reducing agricultural practices can benefit from adaptation strategies. Carbon farming offers opportunities to enhance soil health, improve water management, and increase farm resilience to climate variability and extreme weather events.
● Economic Benefits: Grassroots initiatives and agrarian research in India demonstrate the viability of organic farming and agro-ecological practices for carbon sequestration. These practices have the potential to generate significant economic benefits, including additional income for farmers through carbon credit systems and payment for ecosystem services.
● Regional Suitability: Regions with extensive agricultural land, such as the Indo-Gangetic plains and the Deccan Plateau, are well suited to adopt carbon farming practices due to favorable agro-climatic conditions. However, mountainous terrain and coastal areas may face challenges related to soil erosion, water scarcity, and salinization, limiting the adoption of traditional farming practices.
● Policy Support and Incentives: Government policies and programs that promote sustainable agriculture and carbon farming can create an enabling environment for adoption and implementation. Incentives such as subsidies, grants, and technical support can help overcome financial barriers and encourage farmers to adopt carbon farming practices.
● Carbon Credit Systems: The development of carbon credit systems and market-based mechanisms can incentivize farmers to sequester carbon in soils and vegetation. By monetizing the environmental benefits of carbon farming, these systems provide additional income streams for farmers and contribute to climate change mitigation efforts at the national and global levels.
Conclusion
Carbon farming offers a promising approach to address the dual challenges of climate change and sustainable agriculture. By integrating farming techniques with regenerative practices, carbon farming can enhance soil health, increase agricultural productivity, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, realizing the full potential of carbon farming requires addressing various challenges related to geographical, financial, policy, technological, and social factors. Global initiatives, research efforts, and policy support can help promote carbon farming and unlock its benefits for farmers, communities, and the environment.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam- 1. "Discuss the concept of carbon farming and its significance in addressing climate change and promoting sustainable agriculture. Explain with examples two key techniques within carbon farming and their benefits." (10 Marks, 150 words) 2. "Evaluate the challenges in implementing carbon farming, particularly in developing countries like India. Discuss the role of policy support, technological innovations, and community engagement in overcoming these challenges and promoting the adoption of carbon farming practices." (15 Marks, 250 words) |
Source- The Hindu