Relevance: GS-2: Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Key Phrases: SDMCs, empowering society through community engagement in education, flexibility and autonomous dimensions of NEP 2020, community engagement as an intrinsic effort; social justice and social transformation are at the backdrop and education is a vehicle to attain them; cluster schools; experiential learning; holistic and multidisciplinary education; school cluster management committees; Samajik Chetna Kendra; Global Citizenship Education.
Why in News?
- National Education Policy 2020 has given importance to community engagement
- Community engagement in education ensures
- Accountability of teachers
- Relevant content being taught to students
- Relevant skills being imparted to students to make them job-ready
- Strengthening of educational institutions in terms of finances, experience and quality
Key highlights of the article
Evolution of educational ecosystem
- The first two Education policies of the country have aimed at
- Compulsory education for children and
- Achieving uniformity in education across social groups
- They have been successful in establishing regulatory structures, systems, and processes to achieve access, quality, and equity outcomes.
- With the growth of the education sector, there have also been several challenges.
- The focus on excellence has made education more knowledge-oriented with lesser importance to the application of knowledge to the society
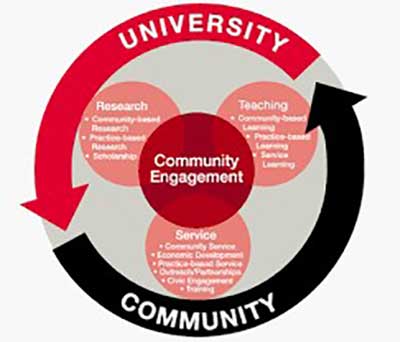
Need and benefits of Community Engagement
- Community engagement is an essential element which links education to the society.
- The interconnectedness can be established only through community
extending its ownership to the educational endeavours and educational
institutions offering its programmes and services, that in turn empowers
the society.
- In the current structure, the community takes ownership by participating through School Development and Monitoring Committees (SDMCs) and Educational institutions work with communities through programmes of NSS, NCC, Red Cross, and other voluntary efforts of institutions.
NEP 2020 and community engagement
- The flexibility and autonomous dimensions of the National
Education Policy 2020 makes community engagement an intrinsic element
of education rather than making it a discrete effort.
- Flexibility element provides for greater opportunities to build community engagement at institutional level and
- Autonomy gives the power to institutions.
- Institutions with flexibility and autonomy are free to design and develop programmes to bring interconnectedness with the society.
- All aspects of the 2020 Policy make us realise that social justice and social transformation are at the backdrop and education is a vehicle to attain them.
- NEP articulates the role of community in education both explicitly
and implicitly.
- Some of those which are explicit include
- Bringing Anganwadis in the education fold;
- Integrating skills at various levels;
- Making education holistic and multidisciplinary;
- Focusing on experiential learning;
- Creating an atmosphere of autonomy;
- Integrating local skills in the main course of education focusing on impactful research
- Some of those which are explicit include
Community Engagement in School Education
- NEP envisages a public education system with true philanthropic
private and community participation.
- The community is an integral part of School Education and there have been evidences that village schools function effectively only when the local community is active and participates in the functioning of the schools
- Regarding Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), NEP 2020 states
that Anganwadis shall be fully integrated complexes/clusters, and children’s
parents and teachers will be invited to participate in school complex
programmes.
- Role of Anganwadis have been focused on nutrition, their
integration with education enables supporting parents and building
communities in providing
- Early childhood education along with
- The necessary nutrition and health care.
- Role of Anganwadis have been focused on nutrition, their
integration with education enables supporting parents and building
communities in providing
- The concept of cluster schools brings in the role of community in
building schools and enhancing learning.
- A school complex groups neighbouring schools into a cluster.
- Apart from the benefits of pooling and sharing resources like teachers, learning, and physical resources; the biggest benefit would be the communities around the school complex.
- Broad-based school complexes and clusters enable innovations specific to the location and context.
- The school cluster management committees consisting of various stakeholders include the community along with local management experts who can take care of the governance and management of school clusters
- Non-governmental philanthropic organisations are encouraged to build
schools
- This has proved to be more proactive in achieving outcomes.
- Community participation has a critical role in school improvement across inputs, processes, and outcomes.
- The Policy recommends the participation of community, alumni, and volunteers in making learning more effective and in achieving Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN) outcomes
- Samajik Chetna Kendras
- To use the unutilised capacity of school infrastructure and to promote social, intellectual, and volunteer activities for the community, the policy suggests ‘Samajik Chetna Kendra’ which could promote social cohesion during non-teaching/schooling hours.
Community Engagement in Higher Education
- The policy contains important elements fostering social
responsibility and community engagement in Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
- In Higher Education, community engagement enables bridging the gap between theoretical concepts and its practice.
- Education has no meaning unless real-time problems of the society are identified and solutions are provided.
- This requires deeper interactions between higher education institutions and communities. Education and communities have a symbiotic relationship as education must contribute to society in finding solutions to the real time problems and in turn society has to support the institutions in facilitating curriculum development, teaching learning, and research
- The major recommendation of NEP is to make higher education
broad-based and holistic.
- To become multidisciplinary institutions of higher learning,
- Offering undergraduate and graduate programmes,
- Quality teaching, research, and community engagement.
- Multidisciplinary approach binds the courses to the needs of the
society with flexible and innovative curriculum.
- The Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) structure calls for varied combination of courses with integration of experiential learning.
- To make learning broad-based, courses are suggested in the areas concerning community service, environmental education, and value-based education, and projects in the areas of climate change, pollution, waste management, sanitation, conservation of biological diversity, management of biological resources and biodiversity, forest and wildlife conservation, and sustainable development and living.
- Value-based education includes development of humanistic, ethical, constitutional, and universal human values as also life-skills; lessons in seva/service; and participation in community service programmes.
- Students are to be provided with opportunities for internships with local industry, businesses, artists, crafts persons, etc., as well as research internships with faculty and researchers at their own or other HEIs, so that students actively engage with the practical side of their learning through sports, culture, environment clubs, and community service projects.
- NEP, in line with the Global Citizenship Education (GCED),
recommends empowering learners to
- Become aware of and understand global issues and
- Become active promoters of more peaceful, tolerant, inclusive, secure, and sustainable societies.
Directional Efforts
- In its pursuit of implementing the policy, the government and concerned bodies are in the process of developing guidelines for the implementation both at the national level and at respective States.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has also developed the National Curricular Framework and guidelines, 2020 specifically on fostering community engagement in higher educational institutions (HEIs).
- There are efforts to develop courses and curriculum to engage students with rural communities under the ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’.
- The Ministry has also entrusted Mahatma Gandhi National Council of Rural Education (MGNCRE) with the task of preparing and running Massive Online Open Courses (MOOCs) on SWAYAM platform on “Fostering Social Responsibility and Community Engagement”.
Implementing Community Engagement in Institutions
- The depth of community engagement depends on the priority that
institutions place on involving communities in Governance, Teaching
learning, Research, and Institutional Development.
- The policy has paved the way for the Institutions to become an integral part of the society, draw resources, and contribute knowledge to the communities.
- The policy gives great clarity on what Schools, Colleges and Universities have to do for better community engagement and why such an engagement is necessary. It is now to the institutions to move forward in the directions laid down by the Policy
- The challenge is how to go ahead with the implementation at individual
schools and colleges with its true spirit and proactiveness.
- Community engagement has to be institutionalised by incorporating the same in the vision, mission, objectives, and the institutional plans.
- Institutional mechanisms have to be developed to integrate community engagement with other areas of teaching-learning and research.
- However, institutions are feeling the need to be hand-held during the implementation.
Way Forward
- Institutions have to proactively respond and implement community engagement at their level.
- Institutions have three options in making community engagement a
reality.
- Firstly, anticipating directions from the government and implementing accordingly.
- Secondly, taking the spirit of the policies, implementing them with or without anticipating directions from the Government and other concerned bodies by setting teams, preparing plans, involving community stakeholders, and working towards implementation.
- Lastly, thinking beyond NEP, innovating newer ways of bringing
community closer to the institution.
- It is the Institutions which can build the interconnectedness within the society, in order to achieve this, the institutions have to instill amongst the stakeholders that they belong to the society and bring society closer to the institutions to respond to their needs.
Conclusion
- The new policy attempts to address the need for social connect through education. The role of government bodies, institutions, NGOs, and other organisations is crucial in realising these goals and creating an adequate ecosystem and opportunity for individuals to build a connect
- It also focuses on establishing a logical end to the process of learning which is not just accumulation of knowledge, instead building a robust environment that enables application of concept and understands the practical usage of the same in societal necessities.
- The ideology behind NEP is to bridge the divide between the
society and education. Education is intended to be part of the society and
society needs contribution of educational institutions to have a synergetic
relationship.
- This relationship could be strengthened only when institutions recognise their role and work towards making community engagement a reality.
Source: Yojana February
Image source: Loyola University
Mains Question:
Q. Mention the benefits of Community Engagement in education as per national education policy 2020? Also highlight the challenges and suggest a way forward in achieving community engagement.