Context-
India, as the world's most populous nation, grapples with the imperative task of ensuring healthcare access to all its citizens. The nation's commitment to achieving Goal 3 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals - good health and well-being - by 2030 underscores the urgency of addressing healthcare disparities. Central to this endeavor is the concept of Universal Health Coverage (UHC), aiming to provide quality healthcare without financial strain.
Right to Health as a Fundamental Right:
- Constitutional provisions and judicial pronouncements in India recognize the fundamental right to health. Articles 38, 41, 42, and 47 emphasize the government's obligation to formulate policies for public health. The judiciary, notably in the Paschim Banga Khet Mazdoor Samity vs State of West Bengal (1996) case, has affirmed the Right to Health as intrinsic to the Right to Life.
- Public health, a cornerstone of comprehensive healthcare, extends beyond individual treatment to encompass preventive measures and community well-being. However, disparities persist, evidenced by India's minimal healthcare spending compared to its global counterparts. The launch of the Ayushman Bharat initiative marks a significant stride towards achieving UHC.
Development of India’s Healthcare System:
- India's healthcare journey since independence reflects strides in infrastructure development and disease eradication. Noteworthy achievements include the successful eradication of smallpox in 1977, epitomizing India's commitment to public health. Subsequent national health policies underscored equitable access and increased public health investment.
- The National Health Policy of 2017 laid the groundwork for Ayushman Bharat, envisaging universal access to quality healthcare without financial hardship. Launched in 2018, Ayushman Bharat comprises two components: Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Center (AB-HWC) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY). AB-HWC targets primary healthcare, aiming to transition from selective to comprehensive services. PM-JAY, the flagship component, provides insurance coverage for secondary and tertiary healthcare.
Ayushman Bharat Initiative:
- PM-HWC aims to enhance primary healthcare services by establishing Ayushman Arogya Mandir centers nationwide. Over 1,60,000 Ayushman Arogya Mandir centers have been established as of January 2024
- Ayushman Bharat's PM-JAY component offers insurance cover up to ₹5 lakh for beneficiary families. Criteria for eligibility vary between rural and urban areas, prioritizing marginalized demographics. Notably, PM-JAY supersedes the Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana, expanding coverage and beneficiary inclusion.
- Implementation of Ayushman Bharat entails collaboration between the National Health Authority (NHA), State Health Authorities (SHAs), and District Implementation Units (DIUs). The scheme operates under three models: Trust, Insurance, and Hybrid, offering flexibility in claims management. Despite operational efficiency, challenges persist in empanelment, bed availability, and beneficiary comprehension.
Accomplishments and Challenges:
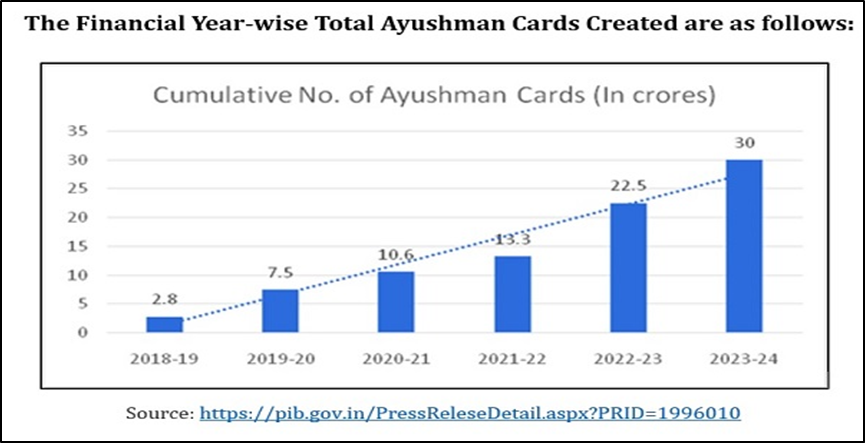
- While PM-JAY covers around 40% of the population of the country and the beneficiaries are chosen based on SECC (Socio-Economic Caste Census), as of January 2024, more than 30 crore Ayushman cards have been issued; Uttar Pradesh is the state with the highest number of Ayushman Bharat cards.
- Ayushman Bharat has recorded over 3.9 crore treatments since its inception, significantly enhancing public health infrastructure. Its integration of public and private hospitals underscores inclusivity and service accessibility.
|
Year |
Number of Treatments |
|
2018-19 |
46.5 lakh |
|
2019-20 |
1.9 crore |
|
2020-21 |
Approx 2 crore |
|
2021-22 |
3.0 crore + |
- As per the Annual Report 2021-22 by NHA, there are approximately 28,300 impaneled hospitals under this scheme out of which 46% are private and 54% are public hospitals.
|
Year |
Number of empanelled hospitals |
|
2018-19 |
18,236 |
|
2019-20 |
23,311 |
|
2020-21 |
Approx 27,000 |
|
2021-22 |
28,311 |
Source: National Health Authority Annual Report
- However, political dynamics impede scheme adoption, with certain states opting for independent health schemes. Challenges in hospital empanelment and bed availability hamper service delivery, necessitating strategic interventions.
- Low awareness and complex enrollment procedures undermine the scheme's effectiveness, particularly among marginalized communities. Financial burdens and operational inefficiencies further exacerbate implementation challenges. While Ayushman Bharat's success is evident, optimizing its potential requires collaborative efforts and innovative solutions.
Enhancing Ayushman Bharat's Efficacy and Reach
- To bolster Ayushman Bharat, a concerted effort is warranted to foster cooperative federalism and streamline intergovernmental cooperation. States must be incentivized to adopt the scheme, leveraging centralized funding mechanisms for equitable healthcare access. Engaging private hospitals and augmenting public health infrastructure is pivotal for service expansion and quality enhancement.
- Addressing comprehension barriers and simplifying enrollment procedures are imperative to ensure inclusivity and beneficiary empowerment. Embracing technological innovations and community outreach initiatives can facilitate awareness dissemination and facilitate enrollment processes. Ayushman Bharat's evolution hinges on adaptive policymaking and stakeholder engagement to navigate evolving healthcare landscapes.
Conclusion:
Ayushman Bharat epitomizes India's commitment to equitable healthcare access and universal health coverage. Amidst evolving healthcare paradigms and demographic shifts, Ayushman Bharat stands as a beacon of progress and inclusivity. Despite challenges, its impact on public health infrastructure and socioeconomic well-being is undeniable.
As India charts its path toward sustainable development and global prominence, Ayushman Bharat emerges as a pivotal instrument for societal transformation. By harnessing collaborative frameworks and innovative strategies, India can realize its vision of a healthier, more resilient nation. Ayushman Bharat's journey underscores the transformative potential of proactive healthcare policymaking and collective action towards inclusive prosperity.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam- 1. How does the Ayushman Bharat initiative contribute to India's pursuit of Universal Health Coverage (UHC)? Discuss the key components of Ayushman Bharat and its significance in addressing healthcare disparities across the nation. ( 10 Marks, 150 words) 2. Analyze the accomplishments and challenges of the Ayushman Bharat initiative in improving India's healthcare landscape. Evaluate the role of collaborative governance, public-private partnerships, and innovative strategies in optimizing the scheme's effectiveness. ( 15 Marks, 250 words) |
Source- VIF









