Context
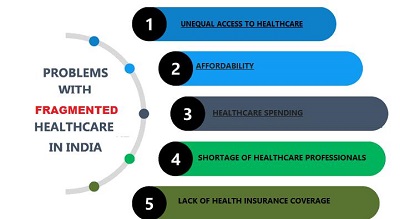
Navigating the complex landscape of Indian health care, the balance between cost considerations and service delivery has become increasingly crucial. With growing health disparities and unequal access to medical services, the need for equitable and sustainable health-care policies is more pressing than ever. Discussions surrounding the standardization of rates for medical services are not merely bureaucratic tasks but are fundamental in shaping the delivery, perception, and accessibility of health care across India. By examining international approaches to similar challenges, shaped by various cultural, economic, and systemic factors, India can refine its strategies to manage health-care costs more effectively.
Private Hospitals: Innovation and Access
Private hospitals in India are not only centers of specialized care but also hubs of innovation. Institutions accredited by the Joint Commission International (JCI) and the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals (NABH) are prime examples, having adopted cutting-edge technologies that significantly enhance patient outcomes, especially in complex procedures. These hospitals invest heavily in top-tier infrastructure and advanced technologies, allowing them to integrate telemedicine and remote care seamlessly, thereby broadening access to healthcare services and building patient trust.
These technological advancements enable private hospitals to offer specialized and high-quality care, making them leaders in medical innovation. By embracing such technologies, these institutions set a high standard for patient care, demonstrating the potential of private sector involvement in elevating health-care quality. However, this also raises questions about affordability and accessibility for the broader population, underscoring the need for balanced health-care policies that do not compromise on quality while striving for inclusivity.
Price Caps, Quality, and Innovation
As the Supreme Court of India deliberates on the standardization of medical procedure rates across both government and private sectors, the appeal of affordability becomes a significant consideration. However, the imposition of one-size-fits-all price caps could potentially undermine health-care quality. A study published in the Health Care Management Review indicates that hospitals facing financial pressure from price caps report a 15% increase in patient dissatisfaction. Such caps could also slow the development of new treatments and technologies, particularly in areas requiring substantial investment, such as cancer research and robotic surgery. A possible solution could be value-based pricing, where payments reflect health outcomes rather than service volume.
Value-based pricing emphasizes the importance of quality over quantity, incentivizing hospitals to improve patient outcomes. This approach could foster innovation while ensuring that healthcare remains affordable. However, the broader economic implications of such pricing policies extend beyond the health-care sector. Properly implemented rate standardization can alleviate health-care disparities, but caution is necessary to avoid destabilizing the economic health of providers. Economists suggest dynamic pricing models that adjust based on medical complexity and the financial status of patients, offering a more balanced solution. For instance, Thailand’s tiered pricing system, which considers patient-income levels and medical necessity, successfully balances cost and care and could serve as a model for India’s diverse economic landscape.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Effectively managing health-care costs in India requires significant legislative reform. Tailoring approaches to accommodate local demographic and economic conditions can support the goals of rate standardization and high-quality care. States like Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu have highlighted gaps in current rate fixation provisions, advocating for robust legal frameworks to navigate these issues successfully. Legislative changes need to address these gaps to create a more equitable and efficient health-care system.
The legal landscape must also evolve to support the integration of technology in health care. As technology revolutionizes medical diagnostics and care coordination, new regulations will be necessary to ensure these advancements are implemented effectively and equitably. For example, telemedicine initiatives in Karnataka have reduced hospital visits by 40%, demonstrating how technology can make medical care more accessible and cost-effective, especially in remote areas. Ensuring that legislative frameworks are flexible and forward-thinking will be crucial in harnessing the full potential of technological advancements in health care.
The Role of Technology in Health Care
Technology is playing a transformative role in the health-care sector, making diagnostics faster and more accurate with the help of artificial intelligence, and improving care coordination through electronic health records. Telemedicine initiatives have shown significant potential in making medical care more accessible and cost-effective. For instance, Karnataka's telemedicine projects have reduced hospital visits by 40%, highlighting how technology can ease the burden on healthcare facilities while delivering timely care directly to patients’ homes.
Additionally, innovations such as mobile health apps and wearable devices are essential in managing chronic conditions outside hospitals, significantly reducing costs and enhancing patient outcomes. As India pushes these technologies forward, ensuring their reach to all population segments becomes key. Investing in infrastructure for broader Internet access and improving digital literacy will empower more people to benefit from these advancements, positioning India as a global leader in health-care innovation. The challenge lies in bridging the digital divide to ensure that technological benefits are not confined to urban areas but are also accessible to rural and underserved populations.
The Importance of Data in Shaping Policies
In today’s era of big data, health-care policy decisions should increasingly rely on data-driven insights. Data analytics can provide valuable information on patient outcomes, treatment efficacy, and cost-efficiency, helping to inform more nuanced rate-setting frameworks. Predictive analytics, for example, could foresee the long-term impacts of rate fixation on health-care innovations, allowing policymakers to adjust regulations to encourage both innovation and accessibility.
Balancing access, innovation, and affordability in health care is delicate but imperative. Implementing pilot projects in select districts could help gauge the impact of rate caps on health-care quality and innovation. Additionally, allocating government subsidies to support research and development in private hospitals and establishing public-private partnerships to integrate cutting-edge technologies in public hospitals can ensure widespread access to advanced healthcare solutions.
Conclusion
As India aspires to be a global leader in health care, fostering an environment conducive to innovation while ensuring equitable access to quality care is crucial. It is essential to prioritize the well-being of every individual, aligning with the vision articulated by Dr. Vinod K. Paul, Member, NITI Aayog: "Affordable healthcare is not just a necessity but a priority for our nation, and we are committed to innovating and leveraging technology to bring down healthcare costs for every citizen." The delicate balancing act of managing health-care costs while maintaining quality and fostering innovation is complex but necessary for building a sustainable and inclusive health-care system in India.
|
Probable Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
|
Source - The Hindu