Relevance: GS-3: Infrastructure: Energy ; Science and technology : developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
Key phrases: Fast-breeder reactor programme, Carbon neutrality, Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant, NPT and NSG, Atomic Energy Commission, Chernobyl and Fukushima
Why in News ?
- A decision by the EU to adopt nuclear energy as a mainstream green technology would give a boost to nuclear energy across the world.
- Recently, India has accelerated the development of its fast-breeder reactor programme that uses, as its starting block, thorium available in Kerala’s monazite sands.
- At the global stage, recently new advances are being made in nuclear power technology. Scientists are able to build what are called small, modular reactors, smaller than 300 MW in capacity, which are safe and cost effective.
- At COP 26, India has announced that it will reach carbon neutrality by 2070 which includes reducing emissions to 50% by 2030. Nuclear energy can play a significant role in achieving this target.
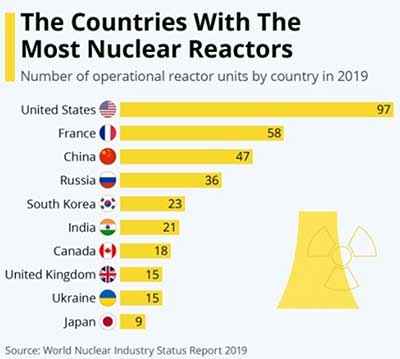
Nuclear Energy in World
- Approximately 10% of the world’s electricity is produced using nuclear energy.
- Worldwide, nuclear power plants are operational in around 30 countries.
- In France, approximately 75% of the electricity is produced by Nuclear energy.
- A total of around 450 nuclear reactors are operating worldwide for generating electricity.
Nuclear Energy in India
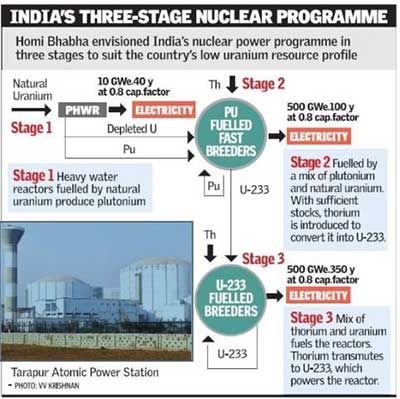
- India's nuclear programme can trace its origins to 1944 and its efforts in 3 stage technology were established by Homi Jehangir Bhabha when he founded the nuclear research centre, the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research.
- Today, India has 23 nuclear reactors in operation in 7 nuclear power plants, with a total installed capacity of 7,480 MW.
- Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant is the largest nuclear power station in India, situated in Tamil Nadu.

Issues of renewable Energy can be addressed with Nuclear power
- The trouble with renewable power is that it is intermittent, generated when the sun burns bright or when the wind blows strong.
- The power that is generated from solar and wind plants can be stored. It can be stored in giant batteries, or as pumped hydropower or even as green hydrogen or molten salt. But storage costs money, big time.
- Hybrid of renewable power plus nuclear power can keep the grid stable when unstable green power is coming from myriad, scattered sources.
- Nuclear power produces no carbon during generation. It is a reliable, stable form of power supply, ideally complemented with hydropower for peaking.
- India is short of oil, gas and even coal. Nuclear power helps diversify the sources of electricity and adds to energy security.
Challenges in development of nuclear energy in India
- Although Nuclear power offers an overall competitive electricity rate compared to other sources of energy, the initial cost is high.
- It requires a long time for nuclear power plants to turn profitable. This makes the investors less likely to invest.
- India lacks expertise in construction of nuclear plants and nuclear scientists and engineers.
- Proper disposal is necessitated so that the harmful effects of radiation can be reduced.
- India has not signed NPT and NSG which has contained India’s capacity to acquire the raw materials from abroad.
- It needs proper compensation and rehabilitation which adds up the time escalating the costs. There is grassroots resistance against nuclear plants due to potential health hazards.
India’s Three stage Nuclear Development
Way Forward
- If the entire life cycle of a nuclear plant is included in the calculation, nuclear energy certainly comes out ahead of fossil fuels like coal or natural gas.
- The Atomic Energy Commission said that India’s energy future depended on its rapid growth of nuclear power.
- The solution to various challenges is not to shun the technology altogether, but to use technology to counter the problems caused by technology. For example: lessons learnt from Chernobyl and Fukushima risks of proliferation, and of disposal of the spent fuel fixed, to a great extent.
- To our advantage, when it comes to nuclear power, India has established a good safety culture.Thus India has a lot going in its favour when it comes to replying on nuclear power generation.
Mains Question
Q. Keeping in mind India’s climate action commitments at COP 26, Glasgow, discuss the significance of nuclear energy as a cleaner fuel in achieving Panchamrit pledges given by India. Also highlight the factors that determine location of nuclear power plants in an area. (15 marks)