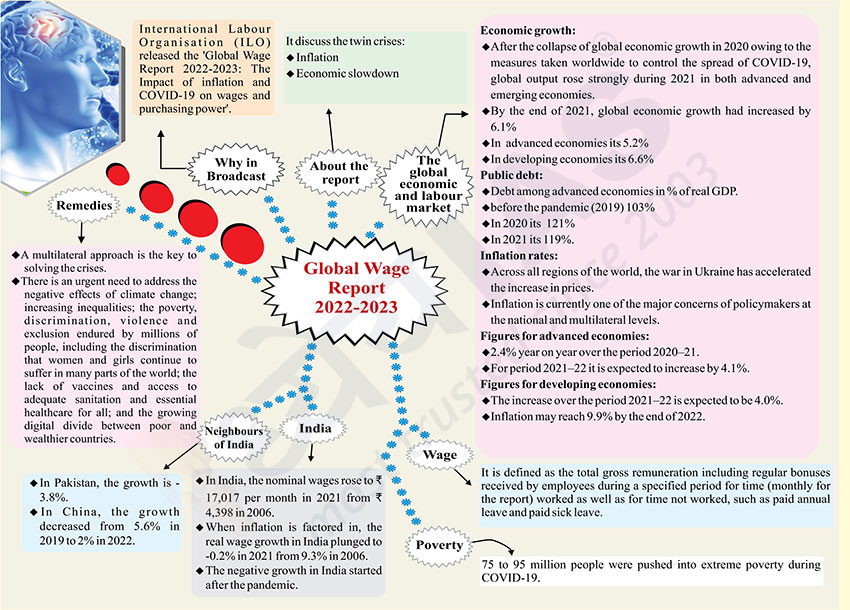
Why in Broadcast?
- International Labour Organisation (ILO) released the 'Global Wage Report 2022-2023: The Impact of inflation and COVID-19 on wages and purchasing power'.
About the report
It discuss the twin crises:
- Inflation
- Economic slowdown
The global economic and labour market
Economic growth:
- After the collapse of global economic growth in 2020 owing to the measures taken worldwide to control the spread of COVID-19, global output rose strongly during 2021 in both advanced and emerging economies.
- By the end of 2021, global economic growth had increased by 6.1%
- In advanced economies its 5.2%
- In developing economies its 6.6%
Public debt:
- Debt among advanced economies in % of real GDP.
- before the pandemic (2019) 103%
- In 2020 its 121%
- In 2021 its 119%.
Inflation rates:
- Across all regions of the world, the war in Ukraine has accelerated the increase in prices.
- Inflation is currently one of the major concerns of policymakers at the national and multilateral levels.
Figures for advanced economies:
- 2.4% year on year over the period 2020–21.
- For period 2021–22 it is expected to increase by 4.1%.
Figures for developing economies:
- The increase over the period 2021–22 is expected to be 4.0%.
- Inflation may reach 9.9% by the end of 2022.
Wage
- It is defined as the total gross remuneration including regular bonuses received by employees during a specified period for time (monthly for the report) worked as well as for time not worked, such as paid annual leave and paid sick leave.
Poverty
- 75 to 95 million people were pushed into extreme poverty during COVID-19.
India
- In India, the nominal wages rose to ₹17,017 per month in 2021 from ₹4,398 in 2006.
- When inflation is factored in, the real wage growth in India plunged to-0.2% in 2021 from 9.3% in 2006.
- The negative growth in India started after the pandemic.
Neighbours of India
- In Pakistan, the growth is -3.8%.
- In China, the growth decreased from 5.6% in 2019 to 2% in 2022.
Remedies
- A multilateral approach is the key to solving the crises.
- There is an urgent need to address the negative effects of climate change; increasing inequalities; the poverty, discrimination, violence and exclusion endured by millions of people, including the discrimination that women and girls continue to suffer in many parts of the world; the lack of vaccines and access to adequate sanitation and essential healthcare for all; and the growing digital divide between poor and wealthier countries.